Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary purpose of a CT scan?
What is the primary purpose of a CT scan?
- To generate a three-dimensional image of an object from a single X-ray image
- To monitor only cancer and heart disease
- To provide detailed cross-sectional images of internal structures (correct)
- To perform biopsies and radiation therapy
What is the function of the detector array in a CT scanner?
What is the function of the detector array in a CT scanner?
- To acquire measurements and perform calculations to create a viewable image (correct)
- To rotate the X-ray tube around the patient
- To generate X-rays
- To move the patient table into the gantry
How many profiles are acquired within one rotation of the scanner?
How many profiles are acquired within one rotation of the scanner?
- 1,000 (correct)
- 2,000
- 100
- 500
What is the purpose of the patient couch (table) in a CT scanner?
What is the purpose of the patient couch (table) in a CT scanner?
What is the result of one complete rotation of the scanner?
What is the result of one complete rotation of the scanner?
What is digital geometry processing used for in a CT scanner?
What is digital geometry processing used for in a CT scanner?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Purpose of CT Scans
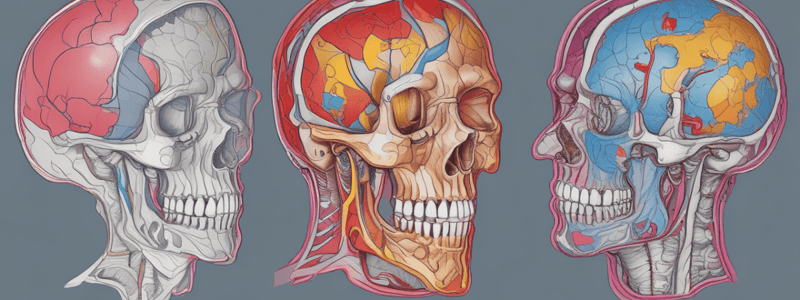
- CT scans provide detailed cross-sectional images of internal structures such as internal organs, blood vessels, bones, and soft tissue
- CT scans are used for diagnostic purposes, guidance for treatment or further tests, surgeries, biopsies, and radiation therapy
- CT scans are used to detect and monitor conditions such as cancer, heart disease, lung nodules, and liver masses
CT Scan Technique
- Digital geometry processing is used to generate a 3D image of the inside of the body from a large series of 2D X-ray images taken around a single axis of rotation
- The CT scanner has a circular opening with a flat "patient couch (table)" that can be adjusted upwards, downwards, frontwards, or backwards to position the patient for imaging
- The patient lies flat on the table, which moves into the gantry while the X-ray tube rotates around the patient
- The scanner gantry contains the rotating portion that holds the X-ray tube generator and the detector array
- As X-rays pass through the patient, they are detected and a computer system acquires and performs the necessary calculations to create a viewable image
- One cross-sectional slice of the body is obtained for each complete rotation
- Multiple shots are taken as the scanner rotates, resulting in around 1,000 "profiles" per rotation
- A 2D image (slice) is formed when a full set of profiles from each rotation are analyzed by a computer and compiled
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.