Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of the Olfactory cranial nerve?
What is the primary function of the Olfactory cranial nerve?
- Sight
- Taste
- Smell (correct)
- Hearing
Which cranial nerve is responsible for the opening of the eyelid and pupillary constriction?
Which cranial nerve is responsible for the opening of the eyelid and pupillary constriction?
- Facial (VII)
- Trochlear (IV)
- Optic (II)
- Oculomotor (III) (correct)
The cranial nerve responsible for taste and the elevation of the pharynx during swallowing is the:
The cranial nerve responsible for taste and the elevation of the pharynx during swallowing is the:
- Accessory (XI)
- Vagus (X)
- Glossopharyngeal (IX) (correct)
- Facial (VII)
Which cranial nerve is primarily associated with lateral eye movement?
Which cranial nerve is primarily associated with lateral eye movement?
What type of receptor is primarily activated by pressure, stretch, or vibrations?
What type of receptor is primarily activated by pressure, stretch, or vibrations?
Flashcards
Olfactory Nerve (I)
Olfactory Nerve (I)
The first cranial nerve, responsible for our sense of smell.
Optic Nerve (II)
Optic Nerve (II)
The second cranial nerve, responsible for our sense of sight.
Oculomotor Nerve (III)
Oculomotor Nerve (III)
The third cranial nerve, responsible for controlling eye movements, pupil constriction, and opening the eyelid.
Chemoreceptors
Chemoreceptors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mechanoreceptors
Mechanoreceptors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
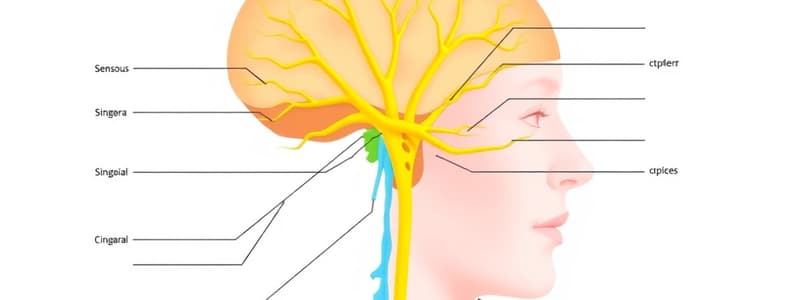
Cranial Nerves
- Olfactory (I): Smell
- Optic (II): Sight
- Oculomotor (III): Opening of eyelid, pupil constriction, focusing
- Trochlear (IV): Eye movement
- Trigeminal (V): Touch, sensations from face
- Abducens (VI): Lateral eye movement
- Facial (VII): Facial expressions, tears, saliva, taste
- Vestibulocochlear (VIII): Hearing
- Glossopharyngeal (IX): Taste, touch, pressure, temperature sensations
- Vagus (X): Taste, gastrointestinal discomfort, swallowing, speech
- Accessory (XI): Shoulder shrug, larynx movement during swallowing
- Hypoglossal (XII): Tongue movement, speech, swallowing
Receptor Classification
- Chemoreceptors: Respond to chemicals (e.g., odors, tastes, glucose, carbon dioxide)
- Mechanoreceptors: Respond to changes in position (e.g., pressure, stretch, vibrations)
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.