Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which cranial nerve is most likely affected if a stroke patient develops a hoarse voice and difficulty swallowing?
Which cranial nerve is most likely affected if a stroke patient develops a hoarse voice and difficulty swallowing?
- Cranial Nerve IX (Glossopharyngeal)
- Cranial Nerve VII (Facial)
- Cranial Nerve X (Vagus) (correct)
- Cranial Nerve V (Trigeminal)
What cranial nerve dysfunction could lead to an inability to smile or pucker lips?
What cranial nerve dysfunction could lead to an inability to smile or pucker lips?
- Cranial Nerve III (Oculomotor)
- Cranial Nerve IX (Glossopharyngeal)
- Cranial Nerve VII (Facial) (correct)
- Cranial Nerve XII (Hypoglossal)
Which cranial nerve is likely responsible for a loss of sensation on one side of the face?
Which cranial nerve is likely responsible for a loss of sensation on one side of the face?
- Cranial Nerve X (Vagus)
- Cranial Nerve V (Trigeminal) (correct)
- Cranial Nerve VII (Facial)
- Cranial Nerve XI (Accessory)
Which cranial nerve contains a parasympathetic component that regulates glands and viscera in the head and neck?
Which cranial nerve contains a parasympathetic component that regulates glands and viscera in the head and neck?
A woman feels a loss of sensation while drinking coffee. Which cranial nerve dysfunction can explain this difficulty?
A woman feels a loss of sensation while drinking coffee. Which cranial nerve dysfunction can explain this difficulty?
Match the cranial nerves with their corresponding functions:
Match the cranial nerves with their corresponding functions:
Match the cranial nerves with their Roman numeral designations:
Match the cranial nerves with their Roman numeral designations:
Match the cranial nerves with their primary anatomical locations:
Match the cranial nerves with their primary anatomical locations:
Match the cranial nerves with the sensory or motor functions they are primarily associated with:
Match the cranial nerves with the sensory or motor functions they are primarily associated with:
Match each cranial nerve with its specific eye movement function:
Match each cranial nerve with its specific eye movement function:
Match the cranial nerves with the regions they predominantly provide sensation to:
Match the cranial nerves with the regions they predominantly provide sensation to:
Match the cranial nerves with the specific types of motor functions they control:
Match the cranial nerves with the specific types of motor functions they control:
Match the cranial nerves with their clinical significance:
Match the cranial nerves with their clinical significance:
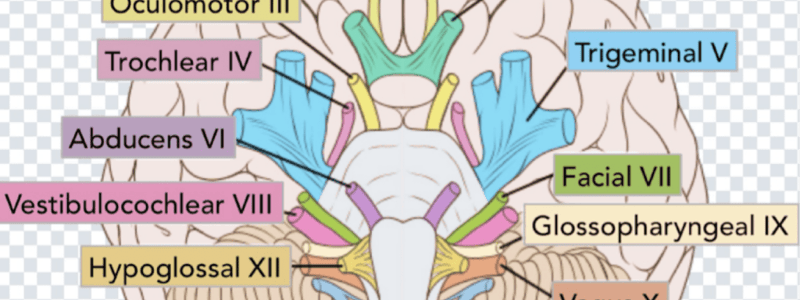
Label these cranial nerves with the picture
Label these cranial nerves with the picture
Label this picture with the cranial nerves
Label this picture with the cranial nerves
Label these cranial nerves with this picture
Label these cranial nerves with this picture
Which cranial nerve provides motor innervation to virtually all of the tongue muscles?
Which cranial nerve provides motor innervation to virtually all of the tongue muscles?
Which cranial nerve is responsible for motor innervation to the major muscles of mastication?
Which cranial nerve is responsible for motor innervation to the major muscles of mastication?
What cranial nerve transmits sensory information from the oropharynx that initiates the swallow reflex?
What cranial nerve transmits sensory information from the oropharynx that initiates the swallow reflex?
Which cranial nerve mediates facial expression?
Which cranial nerve mediates facial expression?
Which cranial nerve is responsible for general sensation to the entire palate and upper teeth?
Which cranial nerve is responsible for general sensation to the entire palate and upper teeth?
Flashcards
Hoarse voice and swallowing problems
Hoarse voice and swallowing problems
These symptoms suggest a dysfunction of the Vagus nerve (CN X).
Lip pucker,smile, understand speech problems
Lip pucker,smile, understand speech problems
These difficulties indicate potential damage to the Facial nerve (CN VII).
Face numbness, hot coffee sensation
Face numbness, hot coffee sensation
These symptoms point to a possible dysfunction of the Trigeminal nerve (CN V).
Cranial nerve for head/neck & body glands
Cranial nerve for head/neck & body glands
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cranial nerve controlling facial muscles
Cranial nerve controlling facial muscles
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are cranial nerves?
What are cranial nerves?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How are cranial nerves identified?
How are cranial nerves identified?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does CN V control?
What does CN V control?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does CN VII control?
What does CN VII control?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does CN X control?
What does CN X control?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are some possible clinical applications?
What are some possible clinical applications?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How is cranial nerve function assessed?
How is cranial nerve function assessed?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What kind of tests are used for cranial nerve evaluation?
What kind of tests are used for cranial nerve evaluation?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What nerve controls tongue muscles?
What nerve controls tongue muscles?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What nerve moves chewing muscles?
What nerve moves chewing muscles?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Which nerve senses food in the throat?
Which nerve senses food in the throat?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What nerve controls facial expressions?
What nerve controls facial expressions?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What nerve senses the palate?
What nerve senses the palate?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Cranial Nerve Dysfunction - Case Studies
-
Hoarse Voice and Swallowing Difficulty: A stroke patient experiencing a hoarse voice and difficulty swallowing likely has damage to Cranial Nerve X (Vagus Nerve). This nerve plays a crucial role in controlling various functions within the head and neck, including voice production and swallowing.
-
Lip Pucker, Smiling, and Speech Comprehension Issues: Inability to pucker lips, smile, and difficulties with speech comprehension point to potential damage in Cranial Nerve VII (Facial Nerve). This nerve controls facial muscles and aspects of taste.
-
Facial Sensory Loss and Mouth Sensation: A woman who experiences a loss of sensation on her face and possibly burning sensations from hot beverages is likely to be having issues with Cranial Nerve V (Trigeminal). This nerve is responsible for sensation in the face and mouth, as well as moving chewing muscles.
-
Parasympathetic Control of Glands and Viscera: The Vagus nerve (CN X) contains a parasympathetic component which controls glands and viscera in both the head/neck and body.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.