Podcast
Questions and Answers
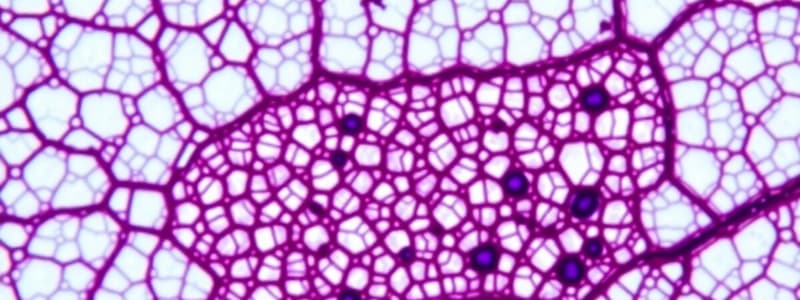
A 60-year-old woman presents with several small, pearly nodules on the back of her neck. A biopsy of one lesion reveals a basal cell carcinoma and adjacent areas of normal skin (shown in the image). The area indicated by the asterisk is typically composed of which of the following tissue types?
A 60-year-old woman presents with several small, pearly nodules on the back of her neck. A biopsy of one lesion reveals a basal cell carcinoma and adjacent areas of normal skin (shown in the image). The area indicated by the asterisk is typically composed of which of the following tissue types?
- Dense, irregular connective tissue (correct)
- Dense, regular connective tissue
- Skeletal muscle
- Glandular epithelium
- Smooth muscle
For the biopsy described in Question 1, which of the following types of connective tissue is found directly beneath the basophilic surface epithelium? This tissue is highly cellular and contains capillary loops that provide nutrients and oxygen to the overlying epithelium.
For the biopsy described in Question 1, which of the following types of connective tissue is found directly beneath the basophilic surface epithelium? This tissue is highly cellular and contains capillary loops that provide nutrients and oxygen to the overlying epithelium.
- Dense irregular connective tissue
- Adipose tissue
- Loose connective tissue (correct)
- Reticular connective tissue
- Elastic connective tissue
A 43-year-old woman presents with a mass in her right breast that she first detected 4 months ago. A firm 4-cm mass is palpated on breast examination. An excisional biopsy is obtained (shown in the image). The area indicated by arrows is primarily composed of which of the following types of connective tissue?
A 43-year-old woman presents with a mass in her right breast that she first detected 4 months ago. A firm 4-cm mass is palpated on breast examination. An excisional biopsy is obtained (shown in the image). The area indicated by arrows is primarily composed of which of the following types of connective tissue?
- Elastic
- Reticular
- Dense regular
- Dense irregular (correct)
- Loose
Which of the following cells are responsible for the synthesis and deposition of collagens and other extracellular matrix proteins in the area of the breast biopsy specified in Question 3?
Which of the following cells are responsible for the synthesis and deposition of collagens and other extracellular matrix proteins in the area of the breast biopsy specified in Question 3?
A biopsy of an axillary lymph node from the patient described in Question 3 is examined by light microscopy. In this silver-stained section (shown in the image), the irregular black lines indicated by the arrows represent which of the following stromal connective tissue components?
A biopsy of an axillary lymph node from the patient described in Question 3 is examined by light microscopy. In this silver-stained section (shown in the image), the irregular black lines indicated by the arrows represent which of the following stromal connective tissue components?
The delicate stromal fibers described in Question 5 are composed primarily of which of the following structural proteins?
The delicate stromal fibers described in Question 5 are composed primarily of which of the following structural proteins?
Which of the following bone marrow-derived cells is typically found within open spaces formed by the extracellular matrix fibers described in Question 5? These cells are believed to play an important role in anticancer immune surveillance.
Which of the following bone marrow-derived cells is typically found within open spaces formed by the extracellular matrix fibers described in Question 5? These cells are believed to play an important role in anticancer immune surveillance.
A 3-year-old girl is found to have extremely pliable skin. Her parents note that she bruises easily and that her joints can be hyperextended. Biochemical and genetic studies establish a diagnosis of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. This patient's genetic disease is caused by an abnormality or deficiency of which of the following proteins?
A 3-year-old girl is found to have extremely pliable skin. Her parents note that she bruises easily and that her joints can be hyperextended. Biochemical and genetic studies establish a diagnosis of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. This patient's genetic disease is caused by an abnormality or deficiency of which of the following proteins?
A 68-year-old man presents with a 2-week history of abdominal discomfort. A CT scan reveals a dilated and calcified segment of the abdominal aorta proximal to the bifurcation. Prior to surgery, the patient suffers a massive heart attack and expires. The abdominal aorta is examined at autopsy (shown in the image). Loss of which of the following cellular/biochemical components of the aortic media contributed the most to the development of this patient's abdominal aneurysm?
A 68-year-old man presents with a 2-week history of abdominal discomfort. A CT scan reveals a dilated and calcified segment of the abdominal aorta proximal to the bifurcation. Prior to surgery, the patient suffers a massive heart attack and expires. The abdominal aorta is examined at autopsy (shown in the image). Loss of which of the following cellular/biochemical components of the aortic media contributed the most to the development of this patient's abdominal aneurysm?
A 12-month-old boy is brought to the emergency room for examination of his right arm following a tumble at school. Radiologic examination of the limb reveals a recent fracture of the right ulna and evidence of several additional healing fractures. Further testing demonstrates that this child has osteogenesis imperfecta, an autosomal dominant genetic disease caused by mutations in the gene for which of the following structural proteins?
A 12-month-old boy is brought to the emergency room for examination of his right arm following a tumble at school. Radiologic examination of the limb reveals a recent fracture of the right ulna and evidence of several additional healing fractures. Further testing demonstrates that this child has osteogenesis imperfecta, an autosomal dominant genetic disease caused by mutations in the gene for which of the following structural proteins?
Type I collagen described in Question 10 belongs to which subfamily of collagens?
Type I collagen described in Question 10 belongs to which subfamily of collagens?
In patients with osteogenesis imperfecta, gene mutations that change which of the following amino acids can block the formation of collagen triple helices?
In patients with osteogenesis imperfecta, gene mutations that change which of the following amino acids can block the formation of collagen triple helices?
During fibrillogenesis of type I collagen, the triple helix of the procollagen molecule is formed at which of the following locations?
During fibrillogenesis of type I collagen, the triple helix of the procollagen molecule is formed at which of the following locations?
A 28-year-old marine complains of gingivitis, skin hemorrhages, multiple infections, and poor wound healing. Laboratory studies suggest vitamin C deficiency (scurvy). Lack of vitamin C in this patient primarily affects which of the following essential steps in collagen fibrillogenesis?
A 28-year-old marine complains of gingivitis, skin hemorrhages, multiple infections, and poor wound healing. Laboratory studies suggest vitamin C deficiency (scurvy). Lack of vitamin C in this patient primarily affects which of the following essential steps in collagen fibrillogenesis?
A 2-year-old girl with itchy skin and respiratory distress is brought to the emergency room by her parents 30 minutes after eating peanut butter cookies. On physical examination, the patient shows flushing and swelling of her lips and eyelids. Hives are present over her face and arms. Vital signs are blood pressure 90/40 mm Hg and pulse 100 per minute. Which of the following inflammatory cells is primarily responsible for the development of increased vascular permeability in this patient with a severe peanut allergy?
A 2-year-old girl with itchy skin and respiratory distress is brought to the emergency room by her parents 30 minutes after eating peanut butter cookies. On physical examination, the patient shows flushing and swelling of her lips and eyelids. Hives are present over her face and arms. Vital signs are blood pressure 90/40 mm Hg and pulse 100 per minute. Which of the following inflammatory cells is primarily responsible for the development of increased vascular permeability in this patient with a severe peanut allergy?
A 17-year-old boy presents with yellow and red-crusted lesions over his face of 5-day duration. He is a member of the high school wrestling team and has a recent history of intermittent low-grade fever. Skin cultures are positive for Streptococcus pyogenes. Spread of this bacterial infection within the patient's dermis may occur if the intrinsic viscosity of dermal connective tissue is altered by infection. Which of the following connective tissue components determines the viscosity of connective tissue and provides a protective barrier that limits the spread of deep-seeded bacterial infections in the skin?
A 17-year-old boy presents with yellow and red-crusted lesions over his face of 5-day duration. He is a member of the high school wrestling team and has a recent history of intermittent low-grade fever. Skin cultures are positive for Streptococcus pyogenes. Spread of this bacterial infection within the patient's dermis may occur if the intrinsic viscosity of dermal connective tissue is altered by infection. Which of the following connective tissue components determines the viscosity of connective tissue and provides a protective barrier that limits the spread of deep-seeded bacterial infections in the skin?
Which of the following connective tissue components binds the most water and regulates the crucial biological functions of the viscous and highly hydrated ground substance described in Question 16?
Which of the following connective tissue components binds the most water and regulates the crucial biological functions of the viscous and highly hydrated ground substance described in Question 16?
The parents of a 3-year-old boy are concerned that their son shows signs of physical and mental retardation. After a series of physical and laboratory examinations, the child is diagnosed with Hurler syndrome. This rare genetic disease is caused by disordered degradation and abnormal accumulation of which of the following connective tissue structural components?
The parents of a 3-year-old boy are concerned that their son shows signs of physical and mental retardation. After a series of physical and laboratory examinations, the child is diagnosed with Hurler syndrome. This rare genetic disease is caused by disordered degradation and abnormal accumulation of which of the following connective tissue structural components?
Which of the following components of connective tissue links cells to the extracellular matrix to help maintain tissue integrity and regulate cell behavior?
Which of the following components of connective tissue links cells to the extracellular matrix to help maintain tissue integrity and regulate cell behavior?
A 12-year-old girl has a 1.5-cm birthmark (benign congenital nevus) removed from her left upper thigh under local anesthesia. Which of the following families of cell adhesion molecules is the principal component of the “provisional matrix” that mediates cell-to-matrix interactions during wound healing in this patient?
A 12-year-old girl has a 1.5-cm birthmark (benign congenital nevus) removed from her left upper thigh under local anesthesia. Which of the following families of cell adhesion molecules is the principal component of the “provisional matrix” that mediates cell-to-matrix interactions during wound healing in this patient?
The right lower limb of a 6-year-old boy becomes swollen and enlarged following a visit to South Africa. He is diagnosed with lymphatic filariasis. The patient's soft tissue swelling (edema) is caused by an accumulation of which of the following connective tissue components?
The right lower limb of a 6-year-old boy becomes swollen and enlarged following a visit to South Africa. He is diagnosed with lymphatic filariasis. The patient's soft tissue swelling (edema) is caused by an accumulation of which of the following connective tissue components?
A 65-year-old woman jogger with a history of tendonitis affecting the pes anserinus at the knee suffers a massive stroke and expires. A section of her left sartorius tendon is examined at autopsy (shown in the image). This collagen-rich connective tissue is important in transmitting force from muscle to bone. Which of the following best describes this type of connective tissue?
A 65-year-old woman jogger with a history of tendonitis affecting the pes anserinus at the knee suffers a massive stroke and expires. A section of her left sartorius tendon is examined at autopsy (shown in the image). This collagen-rich connective tissue is important in transmitting force from muscle to bone. Which of the following best describes this type of connective tissue?
A 48-year-old man is admitted to the hospital with a fever of 38°C (103°F), night sweats, persistent cough, and prolonged diarrhea. Stool culture reveals the presence of acid-fast bacilli that are identified as Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare. Immune responses to the pathogen are known to involve IgA antibodies that are secreted into the lumen of the small intestine. This immunoglobulin is produced and secreted by which of the following bone marrow-derived cells?
A 48-year-old man is admitted to the hospital with a fever of 38°C (103°F), night sweats, persistent cough, and prolonged diarrhea. Stool culture reveals the presence of acid-fast bacilli that are identified as Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare. Immune responses to the pathogen are known to involve IgA antibodies that are secreted into the lumen of the small intestine. This immunoglobulin is produced and secreted by which of the following bone marrow-derived cells?
A biopsy of the small intestine is sectioned and stained with H&E (shown in the image). Identify the cell indicated by the arrow.
A biopsy of the small intestine is sectioned and stained with H&E (shown in the image). Identify the cell indicated by the arrow.
A 44-year-old woman presents with a 2-week history of fever and painful joints. Physical examination shows skin pigmentation, glossitis (inflammation of tongue), and generalized lymphadenopathy. The patient has lost 9 kg (20 lb) over the past 6 months. She reports that her stools are pale and foul smelling. Biopsy of the small intestine is shown in the image. Identify the cells indicated by the arrows.
A 44-year-old woman presents with a 2-week history of fever and painful joints. Physical examination shows skin pigmentation, glossitis (inflammation of tongue), and generalized lymphadenopathy. The patient has lost 9 kg (20 lb) over the past 6 months. She reports that her stools are pale and foul smelling. Biopsy of the small intestine is shown in the image. Identify the cells indicated by the arrows.
In the image shown for Question 25, which of the following types of connective tissue best describes the cellular layer that lies below the simple columnar, lining epithelium?
In the image shown for Question 25, which of the following types of connective tissue best describes the cellular layer that lies below the simple columnar, lining epithelium?
A section of the aorta is examined at autopsy using a special stain (shown in the image). Identify the tissue type in the region indicated by the double arrow.
A section of the aorta is examined at autopsy using a special stain (shown in the image). Identify the tissue type in the region indicated by the double arrow.
A 38-year-old woman delivers a stillborn neonate with craniofacial abnormalities at 24 weeks gestation. A section of fetal skull is examined by light microscopy (shown in the image). Which of the following types of connective tissue best describes this autopsy specimen?
A 38-year-old woman delivers a stillborn neonate with craniofacial abnormalities at 24 weeks gestation. A section of fetal skull is examined by light microscopy (shown in the image). Which of the following types of connective tissue best describes this autopsy specimen?
An obese, 18-year-old man (BMI = 32 kg/m²) presents with questions regarding his weight. The patient admits to an unusually strong appetite and uncontrolled food intake. His behavior may be related to decreased serum concentration of which of the following hormones?
An obese, 18-year-old man (BMI = 32 kg/m²) presents with questions regarding his weight. The patient admits to an unusually strong appetite and uncontrolled food intake. His behavior may be related to decreased serum concentration of which of the following hormones?
Thick Camper fascia from the abdomen of a 72-year-old man is examined at autopsy (shown in the image). Which of the following best describes histologic features of this tissue?
Thick Camper fascia from the abdomen of a 72-year-old man is examined at autopsy (shown in the image). Which of the following best describes histologic features of this tissue?
The adipocytes described in Question 30 are surrounded and supported by a network that is composed chiefly of which of the following fibers?
The adipocytes described in Question 30 are surrounded and supported by a network that is composed chiefly of which of the following fibers?
In addition to providing body insulation and maintaining energy homeostasis, adipose tissue is considered to be an important organ for which of the following biological functions?
In addition to providing body insulation and maintaining energy homeostasis, adipose tissue is considered to be an important organ for which of the following biological functions?
A 58-year-old obese man (BMI = 33 kg/m²) complains of headaches and blurry vision of 5-month duration. On physical examination, the blood pressure is 190/148 mm Hg. Malignant hypertension in this patient may be due, in part, to an increase in the serum concentration of which of the following adipocyte-produced hormones?
A 58-year-old obese man (BMI = 33 kg/m²) complains of headaches and blurry vision of 5-month duration. On physical examination, the blood pressure is 190/148 mm Hg. Malignant hypertension in this patient may be due, in part, to an increase in the serum concentration of which of the following adipocyte-produced hormones?
A 15-year-old girl suffers from anorexia nervosa. During your physical examination of the patient, you understand that, despite inadequate nutrition, white adipose tissue will generally remain undiminished in mass in which of the following anatomic locations?
A 15-year-old girl suffers from anorexia nervosa. During your physical examination of the patient, you understand that, despite inadequate nutrition, white adipose tissue will generally remain undiminished in mass in which of the following anatomic locations?
Flashcards
Loose Connective Tissue
Loose Connective Tissue
Connective tissue that is highly cellular with capillary loops providing nutrients and oxygen to overlying epithelium.
Area indicated by arrows in breast biopsy
Area indicated by arrows in breast biopsy
Tissue primarily composed of dense connective tissue.
Fibroblasts
Fibroblasts
Synthesizes and deposits collagens and extracellular matrix proteins.
Reticular fibers
Reticular fibers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Collagen type III
Collagen type III
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lymphocytes
Lymphocytes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
Signup and view all the flashcards
Osteogenesis imperfecta
Osteogenesis imperfecta
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ground substance
Ground substance
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glycosaminoglycans
Glycosaminoglycans
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Connective Tissue Questions
- A 60-year-old woman presents with small, pearly nodules as a basal cell carcinoma with normal skin area indicated by the asterisk is typically composed of dense, irregular connective tissue.
- Loose connective tissue is found directly beneath the basophilic surface epithelium; It is highly cellular and contains capillary loops that provide nutrients to the epithelium.
- A 43-year-old woman with a breast mass has an excisional biopsy; the area indicated by arrows consists primarily of dense, irregular connective tissue.
- Fibroblasts synthesize and deposit collagens and other extracellular matrix proteins in the breast biopsy area.
- In a silver-stained section of an axillary lymph node biopsy, irregular black lines indicate reticular fibers.
- The delicate stromal fibers described in Question 5 primarily consist of collagen type III.
- Macrophages, are bone marrow-derived cells are typically found within open spaces formed by the extracellular matrix fibers described; involved in anticancer immune surveillance.
- A 3-year-old girl with pliable skin and hyperextended joints has Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, caused by an abnormality or deficiency of collagen.
- A 68-year-old man with abdominal discomfort has a dilated and calcified abdominal aorta; loss of elastic fibers/lamellae in the aortic media contributed most to his abdominal aneurysm.
- A 12-month-old boy with multiple fractures has osteogenesis imperfecta, caused by mutations in the gene for collagen type I.
- Type I collagen as described belongs to the fibril-forming collagens subfamily.
- In patients with osteogenesis imperfecta, glycine mutations can block the formation of collagen triple helices.
- During fibrillogenesis of type I collagen, the triple helix of the procollagen molecule is formed at the rough endoplasmic reticulum.
- A 28-year-old marine with scurvy due to vitamin C deficiency lacks hydroxylation of proline and lysine residues affecting collagen fibrillogenesis.
- A 2-year-old girl with a peanut allergy has increased vascular permeability due to mast cells.
- A 17-year-old boy with a Streptococcus pyogenes infection has spread of skin infection is limited by ground substance in the dermis.
- Glycosaminoglycans bind the most water and regulate crucial biological functions of viscous and highly hydrated ground substance.
- A 3-year-old boy with Hurler syndrome has disordered degradation and abnormal accumulation of glycosaminoglycans.
- Glycoproteins link cells to the extracellular matrix to maintain tissue integrity and regulate cell behavior.
- A 12-year-old girl with a birthmark has cell-to-matrix interactions during wound healing is mediated by fibronectins.
- A 6-year-old boy with lymphatic filariasis has soft tissue swelling (edema) caused by an accumulation of tissue fluid.
- A 65-year-old woman jogger with tendonitis has a sartorius tendon; connective tissue is important in transmitting force from muscle to bone, best describes dense regular tissue.
- A 48-year-old man with Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare has immune responses involving IgA antibodies produced and secreted by the bone marrow-derived plasma cells.
- An H&E stained biopsy of the small intestine; the cell is identified as an eosinophil.
- A 44-year-old woman has pale and foul smelling stool. A biopsy of the small intestine; the cells are identified as eosinophils.
- The cellular layer that lies below the simple columnar, lining epithelium is reticular connective tissue.
- A special stain to show the tissue of the aorta is elastic connective tissue.
- A section of fetal skull is examined and is referred to as Nonmineralized bone.
- An Obese man has decreased serum concentration of Leptin.
- Camper fascia from the abdomen is Unilocular adipose tissue with cellular hypertrophy.
- The adipocytes in Camper fascia from the abdomen consists chiefly of reticular fibers.
- White adipose tissue provides body insulation and maintains energy homeostasis, it is also an important organ involved in Endocrine Secretion.
- A 58-year-old obese man with Malignant Hypertension is due to an increase in Angiotensinogen which is produced by adipocytes.
- A 15-year-old with anorexia and inadequate nutrition has white adipose tissue that will remain undiminished in the periorbital space.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.