Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary constituent of connective tissue?
What is the primary constituent of connective tissue?
- Extracellular matrix (ECM) (correct)
- Muscle fibers
- Epithelial cells
- Nerve cells
Which of the following is NOT considered a component of connective tissue?
Which of the following is NOT considered a component of connective tissue?
- Adipose tissue (correct)
- Cells
- Fibers
- Ground substance
What determines the specific characteristics of different types of connective tissue?
What determines the specific characteristics of different types of connective tissue?
- The combination of protein fibers and ground substance (correct)
- The amount of blood supply
- The size of the cells
- The presence of resident cells
Which type of connective tissue is characterized by adipocytes or fat cells?
Which type of connective tissue is characterized by adipocytes or fat cells?
What percentage of body weight does adipose tissue typically represent in men?
What percentage of body weight does adipose tissue typically represent in men?
Besides energy storage, what other primary function do adipocytes serve?
Besides energy storage, what other primary function do adipocytes serve?
Adipose tissue is now recognized as an important what?
Adipose tissue is now recognized as an important what?
Which function does adipose tissue NOT perform?
Which function does adipose tissue NOT perform?
Which of these is NOT a type of adipose tissue?
Which of these is NOT a type of adipose tissue?
What cellular characteristic distinguishes brown adipose tissue from white adipose tissue?
What cellular characteristic distinguishes brown adipose tissue from white adipose tissue?
White adipose tissue is subdivided into what?
White adipose tissue is subdivided into what?
What is the most common type of adipose tissue?
What is the most common type of adipose tissue?
Why do unilocular adipocytes often appear empty in standard light microscope preparations?
Why do unilocular adipocytes often appear empty in standard light microscope preparations?
What intermediate filament reinforces the lipid droplet-cytoplasm interface in adipocytes?
What intermediate filament reinforces the lipid droplet-cytoplasm interface in adipocytes?
What type of collagen is characteristically found in the external lamina surrounding adipocytes?
What type of collagen is characteristically found in the external lamina surrounding adipocytes?
What is the term for white adipocytes containing a single large lipid droplet?
What is the term for white adipocytes containing a single large lipid droplet?
The distribution of adipose tissue throughout the body is partly regulated by what?
The distribution of adipose tissue throughout the body is partly regulated by what?
What is mobilized and released into the blood when adipocytes are stimulated?
What is mobilized and released into the blood when adipocytes are stimulated?
Leptin, a hormone from adipocytes, has target cells where?
Leptin, a hormone from adipocytes, has target cells where?
Increased visceral adipose tissue is associated with a greater risk of what?
Increased visceral adipose tissue is associated with a greater risk of what?
Which areas of the body resist lipid mobilization from adipose tissue, even during starvation?
Which areas of the body resist lipid mobilization from adipose tissue, even during starvation?
From what type of cells do adipocytes differentiate?
From what type of cells do adipocytes differentiate?
Excessive formation of adipose tissue leading to obesity occurs when what happens?
Excessive formation of adipose tissue leading to obesity occurs when what happens?
Adult-onset obesity primarily involves what in regards to adipocytes?
Adult-onset obesity primarily involves what in regards to adipocytes?
Childhood obesity can involve what processes related to adipocytes?
Childhood obesity can involve what processes related to adipocytes?
Where is brown adipose tissue primarily located in newborns?
Where is brown adipose tissue primarily located in newborns?
What characteristic gives brown adipose tissue its color?
What characteristic gives brown adipose tissue its color?
What structural feature is more delineated in brown adipose tissue compared to white adipose tissue?
What structural feature is more delineated in brown adipose tissue compared to white adipose tissue?
Nonshivering thermogenesis, the main function of multilocular adipose cells, enables what?
Nonshivering thermogenesis, the main function of multilocular adipose cells, enables what?
What triggers nerve impulses to liberate norepinephrine into brown adipose tissue?
What triggers nerve impulses to liberate norepinephrine into brown adipose tissue?
Unlike white fat, in brown fat liberated fatty acids are not released but are quickly what?
Unlike white fat, in brown fat liberated fatty acids are not released but are quickly what?
What protein, found in high levels in the inner mitochondrial membrane of brown fat cells, facilitates heat production?
What protein, found in high levels in the inner mitochondrial membrane of brown fat cells, facilitates heat production?
What process does thermogenin (UCP-1) permit in brown fat mitochondria?
What process does thermogenin (UCP-1) permit in brown fat mitochondria?
During cold adaptation in adults, how does the number of brown adipocytes typically change?
During cold adaptation in adults, how does the number of brown adipocytes typically change?
Besides stimulating thermogenesis, autonomic nerves also promote what activity in brown fat cells?
Besides stimulating thermogenesis, autonomic nerves also promote what activity in brown fat cells?
Which of the following is the most accurate description of white adipose tissue's role regarding heat?
Which of the following is the most accurate description of white adipose tissue's role regarding heat?
What is the fate of glycerol, released during lipolysis, in adipose tissue?
What is the fate of glycerol, released during lipolysis, in adipose tissue?
Which statement accurately contrasts the roles of white and brown adipose tissue in response to overfeeding?
Which statement accurately contrasts the roles of white and brown adipose tissue in response to overfeeding?
Imagine a scenario where a drug selectively inhibits the action of lipoprotein lipase exclusively in adipose tissue. What direct effect would this have?
Imagine a scenario where a drug selectively inhibits the action of lipoprotein lipase exclusively in adipose tissue. What direct effect would this have?
A researcher discovers a novel hormone primarily secreted by adipocytes that strongly inhibits appetite and increases insulin sensitivity via direct action on the brain and muscle tissue. Which of the following is most likely true regarding this hormone's mechanism of action?
A researcher discovers a novel hormone primarily secreted by adipocytes that strongly inhibits appetite and increases insulin sensitivity via direct action on the brain and muscle tissue. Which of the following is most likely true regarding this hormone's mechanism of action?
A pharmaceutical company is developing a drug to combat obesity by increasing the activity of brown adipose tissue in adults. Which of the following mechanisms would be the MOST effective target for this drug?
A pharmaceutical company is developing a drug to combat obesity by increasing the activity of brown adipose tissue in adults. Which of the following mechanisms would be the MOST effective target for this drug?
Flashcards
Other Tissue Types
Other Tissue Types
Tissue mainly consisting of cells, such as epithelium, muscle and nerve.
Extracellular Matrix (ECM)
Extracellular Matrix (ECM)
The major component of connective tissue, made up of protein fibers and ground substance.
Protein Fibers
Protein Fibers
Components of extracellular matrices like collagen, elastic fibers, and ground substance.
Adipose Tissue
Adipose Tissue
Signup and view all the flashcards
Adipocytes
Adipocytes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Adipose Tissue in Men
Adipose Tissue in Men
Signup and view all the flashcards
Adipocytes Function
Adipocytes Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Adipocytes Activity
Adipocytes Activity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Adipose Tissue Functions
Adipose Tissue Functions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue
Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue
Signup and view all the flashcards
White Adipose Tissue
White Adipose Tissue
Signup and view all the flashcards
Brown Adipose Tissue
Brown Adipose Tissue
Signup and view all the flashcards
Long-term energy storage
Long-term energy storage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Unilocular
Unilocular
Signup and view all the flashcards
Signet-ring appearance
Signet-ring appearance
Signup and view all the flashcards
White Adipocyte
White Adipocyte
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vimentin
Vimentin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lobules
Lobules
Signup and view all the flashcards
Reticular Fibers
Reticular Fibers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Adipose Tissue Color
Adipose Tissue Color
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fatty Acids and Glycerol
Fatty Acids and Glycerol
Signup and view all the flashcards
Adipocytes Role
Adipocytes Role
Signup and view all the flashcards
Visceral Deposits
Visceral Deposits
Signup and view all the flashcards
Unilocular Adipocytes Change
Unilocular Adipocytes Change
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mesenchymal Cells
Mesenchymal Cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Obesity
Obesity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hypertrophic Obesity
Hypertrophic Obesity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hyperplastic Obesity
Hyperplastic Obesity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Brown Adipose Tissue Weight
Brown Adipose Tissue Weight
Signup and view all the flashcards
Brown Adipose Color
Brown Adipose Color
Signup and view all the flashcards
Multilocular
Multilocular
Signup and view all the flashcards
Polygonal Cells
Polygonal Cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Brown Fat
Brown Fat
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thermogenesis
Thermogenesis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fat Hydrolysis
Fat Hydrolysis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thermogenin
Thermogenin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Brown Adipose Tissue Development
Brown Adipose Tissue Development
Signup and view all the flashcards
Brown Adipocytes
Brown Adipocytes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
- Adipose tissue is a type of connective tissue studied by Seda Karabulut, PhD.
- Other tissue types like epithelium, muscle, and nerve consist mainly of cells.
- Connective tissue's major component is the extracellular matrix (ECM).
- The extracellular matrix comprise protein fibers, such as collagens and elastic fibers, combined with ground substance.
Structure of Connective Tissue
- Connective tissue contains cells, fibers, and ground substance.
- Cells include fibroblasts, macrophages, mast cells, plasma cells, lymphocytes, leukocytes, and adipose cells.
- Types of fibers in connective tissue are reticular, elastic, and collagen.
- The ground substance contains macromolecules and multiadhesive glycoproteins.
About Adipose Tissue
- Connective tissue in which adipocytes or fat cells are predominant is called adipose tissue.
- These large cells occur in small groups within loose or dense connective tissue, but can form large masses like adipose tissue or fat in body regions.
- Adipose tissue location is throughout the human body and represents normally 15%-20% of men body weight, somewhat more in women.
- Besides storing neutral fats (triglycerides), adipocytes regulate the body's overall energy metabolism.
- Obesity, diabetes, and heart ailment links mean adipocytes and tissues are a major area of medical research.
- Energy balance, nutrient transport, blood pressure, insulin sensitivity, glucose homeostasis, angiogenesis, lipid metabolism, and vascular hemostasis are key for the study of adipose tissue.
- Adipocytes are metabolically active and respond to nervous and hormonal stimuli.
- Adipose tissue releases hormones and other substances, which marks it as an important endocrine tissue.
- PAI-1, Adipisn, Adiponectin, Resistin,Leptin, and Angiotensin are released by adipose tissue.
- Adipose tissue insulates the body, cushions other tissues/organs, and helps shape the body surface, acting as shock absorbers in the soles and palms.
Types of Adipose Tissue
- Types of adipose tissue exist with different locations, structures, appearances, and pathologic characteristics.
- White adipose tissue is the more common type, that contain a large droplet of whitish-yellow fat to their cytoplasm, once fully developed
- Brown adipose tissue contains multiple lipid droplets interspersed among abundant mitochondria, giving the cells a darker appearance.
- Both types of adipose tissue have a substantial blood supply.
Adipose Tissue Processes
- Lipolysis and Lipogenesis are key processes in adipose tissue.
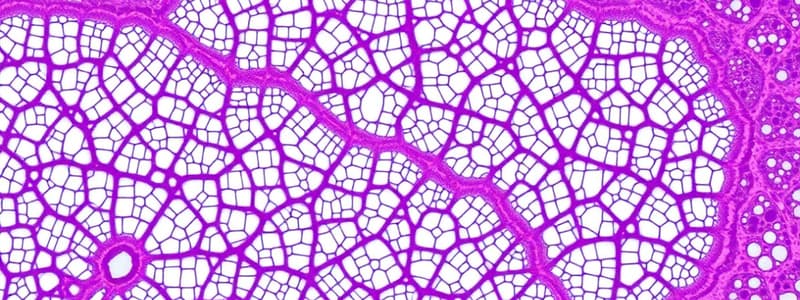
- Adipocytes of white tissue store energy long term, appear spherical when isolated but polyhedral within closely packed in situ.
- White adipose tissue cells are very large, ranging between 50 and 150 µm in diameter
- Within the cells are single, huge droplet of lipid that fills almost entire cell.
- White adipocytes are unilocular because triglycerides are stored in only one large droplet
- These cells have a signet-ring appearance, since their lipid droplet displaces and flattens the nucleus.
- The membrane and thin cytoplasm rim shrink, collapse, or rupture upon removal of the triglycerides - distorting the tissue structure.
- Removed lipid is due to xylene or other solvents used in routine histological techniques, unilocular adipocytes appear empty in standard light microscope preparations.
- The cytoplasm of a white adipocyte surrounds nucleus and carries mitochondria, a small Golgi apparatus, some RER cisternae, and free polyribosomes.
- Most adipocytes, notably immature cells, have minute lipid droplets aside from any single large droplet seen with the light microscope.
- The lipid droplet-cytoplasm interface is reinforced by intermediate filaments of vimentin.
- Adipocytes are surrounded by a thin external lamina containing type IV collagen, instead of other connective tissue cells.
- White adipose tissue is subdivided into incomplete lobules by connective tissue partitions, with a vascular bed and nerve network.
- White tissue contains fibroblasts and macrophages, which account for about half the cell total.
- Reticular fibers support individual fat cells by forming an interwoven network that interconnects them.
Adipose Tissue Facts
- Almost all adipose tissue in adults is unilocular and found within many organs throughout the body.
- Tissue distribution varies in childhood and adult life and relates in part to sex hormones
- White adipose tissue, when dissected fresh, shows its color based on someone's diet, which ranges from white to yellow based on dissolved carotenoids levels in the lipid.
- When stimulated by nerves or hormones, stored lipids are mobilized inside adipocytes causing fatty acids and glycerol to go inside the bloodstream.
- The released fatty acids travels across the membranes of the adipocyte and the capillary endothelium by binding to protein albumin carriers in blood.
- Liberated glycerol remains free inside the body and goes to the liver.
- White adipose tissue functions serve as an important endocrine organ.
- Adipocytes are the sole source of leptin which is "satiety factor" and targets their cells inside the hypothalamus and also other organs.
- Leptin helps regulate appetite in normal conditions and plays a key role in the formation of new adipose tissue.
- Variations in gene expression have been noted for visceral deposits (in the abdomen) and subcutaneous deposits of white fat, even though white adipose tissue appears histologically similar.
- Differences may indicate medical risks with obesity.
- It is well-researched that increased visceral adipose tissue increases the risk of diabetes and cardiovascular diseases, but not heightened subcutaneous fat.
- Lipids are mobilized rather uniformly in all body parts, regarding body needs with few exceptions
- Adipose tissue in palms, soles, and retro-orbital fat pads resists even long periods of starvation.
- During starvation, cells of unilocular adipocytes lose nearly all their fat and become polyhedral or spindle shapes carrying some small lipid droplets.
Histogenesis of White Adipose Tissue
- Adipocytes, like the fiber-producing cells of connective tissue - differentiate from embryonic mesenchymal cells.
- The differentiation is first seen with the appearance of preadipocytes.
- These cells appear the same as fibroblasts but accumulate lipid droplets in the cytoplasm.
- Lipid accumulations are isolated at first, but fuse and form single huge droplet, which is typical of cells in unilocular adipose tissue.
- Excessive fatty tissue formation, which brings to obesity, happens when energy intake goes further beyond energy expenditure - a very increasingly common matter in sedentary lifestyles.
- Adult-onset obesity relates mainly to the raised size of existing adipocytes (hypertrophic obesity), even though adipocytes are able to differentiate from mesenchymal stem cells at any point.
- Childhood obesity is because of the increased rate of adipocyte size and numbers due to the differentiation of more preadipocytes from mesenchymal stem cells, which is hyperplastic obesity.
- Hypertrophy (SIZE) is true to Adults and children, while Hyperplasia (NUMBER) is related to several things
- Hyperplasia is related to the patient's Last-Trimester during Pregnancy ,the diet choices of the Mother, the first year of their life and whether 9 to 13yr or more
- Hyperplasia is also relevant to obese patients
Details about Brown Adipose Tissue
- Brown adipose tissue accounts for 2% to 5% of the newborn weight, it resides mainly in the back, neck, and shoulders
- Levels are reduced more during childhood and adolescence.
- In adults, this tissue is is scattered areas located especially around the kidneys, adrenal glands, aorta, and mediastinum.
- Brown or brown adipose tissue gains its color from abundant mitochondria which has cytochrome pigment spread among the lipid droplets of the fat cells, also from the blood capillaries within.
- Brown fat adipocytes contain small lipid inclusions, meaning it is multilocular.
- These small lipid droplets, abundant mitochondria, all mediate this tissue's function of heat production.
- Brown adipose tissue cells appear polygonal and they area smaller than white adipocytes
- Cytoplasm contains many lipid droplets of varying dimensions alongside nuclei are located centrally
- Brown fat adipocytes are often closely packed around large capillaries.
- Tissue is subdivided by connective tissue partitions into lobules that are delineated well compared to the ones found in white adipose tissue.
- Cells of this tissue directly receive sympathetic innervation.
- Main function of multilocular adipose cells is to create heat via nonshivering thermogenesis (generation of body heat in warm-blooded animals).
- The physiology of multilocular adipose tissue is best understood from studies of the tissue in hibernating species.
- When animals conclude hibernation, nerve impulses release norepinephrine - this also applies to newborn humans exposed to cooler environments than inside the uterus.
- As in white fat, this neurotransmitter activates adipocyte hormone-sensitive lipase and promotes triglyceride hydrolysis into fatty acids and glycerol.
- Unlike the white fat process, liberated fatty acids of multilocular adipocytes aren't released, they are metabolized for increased in oxygen consumption and heat production.
- This process warms the locally circulating blood and distributes heat throughout the body.
- Heat output increases in these cells since there are more thermogenin, or thermouncoupling protein (UCP-1) in a cell's mitochondria in its inside membrane.
- Thermogenin enables protons to backflow after being transported through without engaging with ATP-synthetase complexes.
- Proton flow dissipates energy as heat, which heats up the blood.
Histogenesis of Brown Adipose Tissue
- Brown adipose tissue forms with embryonic mesenchyme, its cells emerge more quickly than white fat during fetal development. These cells grow as growing preadipocytes.
- In humans, the quantity of brown fat peaks relative to overall body weight at the time a baby is born. Its job is to provide heat, which means thermogenesis, then gets slowly removed through cell death from apoptosis as the patient enters childhood.
- Adults with leaner builds contain more brown fat and more activity of the fat.
- Number of brown adipocytes grows as a result of cold adaptation for adults, and appears in areas which typically include groups of multilocular cells surrounded by white adipose tissue.
- This can indicate proliferation and differentiation of modern adipocytes, also alteration into already differentiated white adipoctyes.
- Besides stirring up thermogenic activity, autonomic nerves boost brown adipose tissue differentiation and forestall cell death (apoptosis) around older brown fatt cells
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.