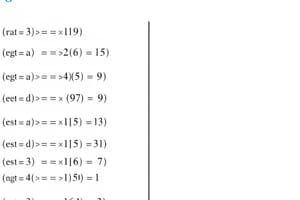Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the final true value of the octal number 21772?
What is the final true value of the octal number 21772?
- 9210
- 921010 (correct)
- 91020
- 9120
Radix conversion only involves changing binary numbers into decimal numbers.
Radix conversion only involves changing binary numbers into decimal numbers.
False (B)
What is the base of the hexadecimal number system?
What is the base of the hexadecimal number system?
16
The octal number system is also known as base ____.
The octal number system is also known as base ____.
How is the final value of a binary number calculated?
How is the final value of a binary number calculated?
Match the numeral system with its radix:
Match the numeral system with its radix:
What is the weight of the first digit from the right in the octal number 21772?
What is the weight of the first digit from the right in the octal number 21772?
The weight of a digit in any numeral system is determined by its position.
The weight of a digit in any numeral system is determined by its position.
What is the result of the hexadecimal addition 1B16 + F16?
What is the result of the hexadecimal addition 1B16 + F16?
The hexadecimal number system uses a base of 16.
The hexadecimal number system uses a base of 16.
What is the decimal result of the binary addition 110112 + 11112?
What is the decimal result of the binary addition 110112 + 11112?
The octal number system uses a base of _____.
The octal number system uses a base of _____.
What is the decimal result of 628 – 268?
What is the decimal result of 628 – 268?
Match the following operations with their results.
Match the following operations with their results.
In hexadecimal multiplication, if the quotient is 3, after carrying over, the next operand becomes _____ before division.
In hexadecimal multiplication, if the quotient is 3, after carrying over, the next operand becomes _____ before division.
What is the result of the octal operation 1100102 - 101102?
What is the result of the octal operation 1100102 - 101102?
What is the correct binary representation of the decimal number 156?
What is the correct binary representation of the decimal number 156?
The fractional part of a decimal can be converted to binary by dividing by 2 until the result becomes 0.
The fractional part of a decimal can be converted to binary by dividing by 2 until the result becomes 0.
What is the greatest power of 2 that fits into 156?
What is the greatest power of 2 that fits into 156?
To convert the integer part to binary, repeatedly divide by 2 until the quotient becomes _____ .
To convert the integer part to binary, repeatedly divide by 2 until the quotient becomes _____ .
Match the following steps with their corresponding descriptions:
Match the following steps with their corresponding descriptions:
Which of the following describes the process of converting the fractional part of a decimal to binary?
Which of the following describes the process of converting the fractional part of a decimal to binary?
What is the final true value of the decimal number 21998?
What is the final true value of the decimal number 21998?
What sequence of operations do you perform to convert the integer part to binary?
What sequence of operations do you perform to convert the integer part to binary?
Hexadecimal numbers use the digits from 0 to 9 and include letters A to F.
Hexadecimal numbers use the digits from 0 to 9 and include letters A to F.
When converting a decimal number to binary, you write down '0' for each power of 2 that cannot fit into the current dividend.
When converting a decimal number to binary, you write down '0' for each power of 2 that cannot fit into the current dividend.
What is the base (radix) of octal numbers?
What is the base (radix) of octal numbers?
To convert a hexadecimal number to decimal, each digit is multiplied by the weight of the radix (______)
To convert a hexadecimal number to decimal, each digit is multiplied by the weight of the radix (______)
What is the value of the binary number 11001 in decimal?
What is the value of the binary number 11001 in decimal?
In octal numbers, the exponent for the fractional part starts from -1.
In octal numbers, the exponent for the fractional part starts from -1.
What digits do octal numbers use?
What digits do octal numbers use?
Match the following number systems with their bases:
Match the following number systems with their bases:
What is the minimum unit that represents a binary state in computers?
What is the minimum unit that represents a binary state in computers?
In computers, a byte consists of 16 bits.
In computers, a byte consists of 16 bits.
How many different states can be represented with 3 bits?
How many different states can be represented with 3 bits?
The unit of processing inside computers that consists of multiple bits is called a _____
The unit of processing inside computers that consists of multiple bits is called a _____
Match the following data units with their respective sizes:
Match the following data units with their respective sizes:
Which of the following statements about bits and bytes is true?
Which of the following statements about bits and bytes is true?
The information amount that can be represented with 2 bits is 2 types.
The information amount that can be represented with 2 bits is 2 types.
What are two states represented by electric signals in data representation?
What are two states represented by electric signals in data representation?
What is the first step in converting an n-adic number into a decimal number?
What is the first step in converting an n-adic number into a decimal number?
When converting a decimal number to an n-adic number, the fractional part is handled by dividing by n repeatedly.
When converting a decimal number to an n-adic number, the fractional part is handled by dividing by n repeatedly.
What procedure is used to convert the integer part of a decimal number into an n-adic number?
What procedure is used to convert the integer part of a decimal number into an n-adic number?
When converting a decimal number like (0.2)10 to binary, the result may lead to a ______.
When converting a decimal number like (0.2)10 to binary, the result may lead to a ______.
Match the following processes with their correct descriptions:
Match the following processes with their correct descriptions:
Why is it sometimes easier to convert from decimal to binary before converting to octal or hexadecimal?
Why is it sometimes easier to convert from decimal to binary before converting to octal or hexadecimal?
The result of converting a fractional number that has no finite representation is treated as an exact value in computations.
The result of converting a fractional number that has no finite representation is treated as an exact value in computations.
What happens when applying radix conversion to a decimal number that gets into a loop?
What happens when applying radix conversion to a decimal number that gets into a loop?
Flashcards
Bit
Bit
The smallest unit of data in a computer, representing either a 0 or a 1.
Byte
Byte
A group of 8 bits, forming a fundamental unit for storing data.
Word
Word
A unit of data processed by a computer, typically consisting of 16, 32, or 64 bits.
Information Amount
Information Amount
Signup and view all the flashcards
Binary System
Binary System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Radix Conversion
Radix Conversion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Arithmetic Operations
Arithmetic Operations
Signup and view all the flashcards
Precision
Precision
Signup and view all the flashcards
Octal Number System
Octal Number System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Octal Number Weight
Octal Number Weight
Signup and view all the flashcards
Octal Number Value
Octal Number Value
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hexadecimal Number System
Hexadecimal Number System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hexadecimal Number Weight
Hexadecimal Number Weight
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hexadecimal Number Value
Hexadecimal Number Value
Signup and view all the flashcards
Number of Digits
Number of Digits
Signup and view all the flashcards
Decimal Weights
Decimal Weights
Signup and view all the flashcards
Binary Weights
Binary Weights
Signup and view all the flashcards
Binary to Decimal Conversion
Binary to Decimal Conversion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Octal Weights
Octal Weights
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hexadecimal Weights
Hexadecimal Weights
Signup and view all the flashcards
Radix Point
Radix Point
Signup and view all the flashcards
Radix (Base)
Radix (Base)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Converting n-adic to Decimal
Converting n-adic to Decimal
Signup and view all the flashcards
Converting Decimal to n-adic
Converting Decimal to n-adic
Signup and view all the flashcards
Non-Terminating Fraction
Non-Terminating Fraction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Recurring Fraction
Recurring Fraction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Approximation in Computers
Approximation in Computers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Decimal to Octal/Hexadecimal Conversion
Decimal to Octal/Hexadecimal Conversion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Decimal to Binary Conversion (Integer Part)
Decimal to Binary Conversion (Integer Part)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Decimal to Binary Conversion (Fractional Part)
Decimal to Binary Conversion (Fractional Part)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Shortcut method for Decimal to Binary Conversion
Shortcut method for Decimal to Binary Conversion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Greatest Power of 2
Greatest Power of 2
Signup and view all the flashcards
Subtracting the Greatest Power of 2
Subtracting the Greatest Power of 2
Signup and view all the flashcards
New Number
New Number
Signup and view all the flashcards
Binary Answer
Binary Answer
Signup and view all the flashcards
Base 2 Table
Base 2 Table
Signup and view all the flashcards
Radix
Radix
Signup and view all the flashcards
Number System Conversion
Number System Conversion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hexadecimal Multiplication
Hexadecimal Multiplication
Signup and view all the flashcards
Binary Addition
Binary Addition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Binary Subtraction
Binary Subtraction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Octal Addition
Octal Addition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Computer Science Fundamentals - Basic Theory on Discrete Mathematics (Part 1)
- Objectives:
- Understand how computers represent numerical values, including base systems (radix), converting between bases, and arithmetic operations.
- Understand the rules and techniques for sets, logical operations, and Karnaugh maps.
Data Representation in Computers
- Unit of Representation: Computers store data as electrical signals represented by two states: current flowing (high voltage) or not flowing (low voltage).
- Bit: The smallest unit of data in computers, representing 0 or 1.
- Byte: A collection of 8 bits, forming a larger unit of data.
- Word: A collection of bits larger than a byte (e.g., 16 bits, 32 bits, 64 bits). Longer words allow for faster processing of larger amounts of data.
Information Amount
- The number of possible combinations of 0s and 1s determines the amount of information.
- n bits can represent 2n possible values.
- 1 bit = 2 values
- 2 bits = 4 values
- 8 bits (1 byte) = 256 values
- 16 bits (1 word) = 65,536 values
Radix Systems
- Radix (base) is the number of digits used in a numerical system.
- Common radix systems include:
- Decimal (base 10)
- Binary (base 2)
- Octal (base 8)
- Hexadecimal (base 16)
- Prefixes are used to represent very large or very small numbers (e.g., Kilo (k) = 103, Mega(M) = 106, etc.)
- Note that these values in computer science often correspond or are close to 2x values.
Radix Conversion
- Converting between different radix systems (e.g., binary to decimal, decimal to hexadecimal)
- Integer parts converted through division and remainders
- Fractional parts using multiplication.
- These processes handle the conversion of integers and fractional parts individually.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.