Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following lipid types is the primary component forming the structural backbone of biological membranes?
Which of the following lipid types is the primary component forming the structural backbone of biological membranes?
- Phospholipids (correct)
- Glycolipids
- Lipoproteins
- Sterols
Extrinsic proteins are embedded within the phospholipid bilayer, spanning from one side of the membrane to the other.
Extrinsic proteins are embedded within the phospholipid bilayer, spanning from one side of the membrane to the other.
False (B)
What property of phospholipids allows them to spontaneously form bilayers in aqueous solutions?
What property of phospholipids allows them to spontaneously form bilayers in aqueous solutions?
amphipathic
The fluidity of a biological membrane is influenced by temperature; membranes are in a(n) _ state at higher temperatures and a solid state at lower temperatures.
The fluidity of a biological membrane is influenced by temperature; membranes are in a(n) _ state at higher temperatures and a solid state at lower temperatures.
Match each membrane component with its primary function:
Match each membrane component with its primary function:
Which of the following is NOT considered a primary function of membrane proteins?
Which of the following is NOT considered a primary function of membrane proteins?
The distribution of proteins within a biological membrane is typically symmetrical, ensuring uniform functionality across the membrane surface.
The distribution of proteins within a biological membrane is typically symmetrical, ensuring uniform functionality across the membrane surface.
What is the approximate thickness range, in nanometers (nm), of a typical biological membrane?
What is the approximate thickness range, in nanometers (nm), of a typical biological membrane?
The _ model describes the biological membrane as a dynamic structure with proteins embedded within a fluid lipid bilayer.
The _ model describes the biological membrane as a dynamic structure with proteins embedded within a fluid lipid bilayer.
Which component of the cell membrane is most directly involved in maintaining membrane permeability and stability?
Which component of the cell membrane is most directly involved in maintaining membrane permeability and stability?
Flashcards
Composition chimic del membranas
Composition chimic del membranas
Componentes basic del membranas biologic include proteinas, lipides, e glucides.
Bistrato de Phospholipides
Bistrato de Phospholipides
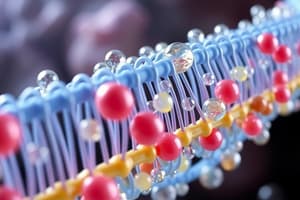
Le skeleton del membranas es formate per un bistrato de phospholipides, con le capites hydrophilic al exterior e le caudas hydrophobic al interior.
Proteinas Extrinsec
Proteinas Extrinsec
Proteinas que es attachate al superficie del membrana.
Proteinas Intrinsec
Proteinas Intrinsec
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fluiditate de membranas
Fluiditate de membranas
Signup and view all the flashcards
Effecto del temperatura
Effecto del temperatura
Signup and view all the flashcards
Modello de Mosaico Fluide
Modello de Mosaico Fluide
Signup and view all the flashcards
Compartimentation Cellular
Compartimentation Cellular
Signup and view all the flashcards
Functiones de proteinas
Functiones de proteinas
Signup and view all the flashcards
Permeabilitate del membranas
Permeabilitate del membranas
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
- Le componentes basic del membrana biologic es proteinas, lipides, e saccharides.
- Proteinas representa 30%-40%, lipides 40%-60%, e saccharides 10%-20% del composition del membrana.
Componentes del Membrana
- Proteinas in le membrana include glycoproteinas e lipoproteinas, que functiona in structura, transporto, e transmission de information.
- Le componentes principal de lipides es phospholipides, inclusive phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylserine, phosphatidylglycerol, e phosphatidylinositol.
- Phospholipides es amphipathic, significa que illos ha un extremitate polar hydrophilic ("capite") e un extremitate nonpolar hydrophobic ("cauda").
- Phospholipides forma le structura basic de membranas e pote regular varie functiones cellular.
- Membranas thylakoidic contine un quantitate significative de glycolipides, principalmente galactosyl diglyceride e digalactosyl diglyceride.
- Steroles es etiam presente in membranas, intermixte inter phospholipides, pro mantener le permeabilitate e stabilitate del membrana.
Structura del Membrana
- Membranas es fluide, non static, e adapta se al crescimento e activitates del cellula, como evidentiate per lor capacitate a mover, rumper, recombinar, e formar vesiculas.
- Le fluiditate del membrana es relate al movimento relative de moleculas de phospholipides.
- Membranas existe in un phase liquide a temperaturas plus alte e transita a un phase solide a temperaturas plus basse.
- Le modello de mosaico fluide, proponite per S.J. Singer e G.L. Nicolson in 1972, describe le characteristicas structural basic del membranas biologic.
- Membranas es typicalmente composte de un bilayer de phospholipides con proteinas incastonate.
- Le "capites" hydrophilic de moleculas de phospholipides es situate al superficie del membrana, durante que le "caudas" hydrophobic es locate in le interior del membrana.
- Proteinas pote esser associate con le superficie del membrana (proteinas extrinsic o peripheric) o incastonate inter phospholipides, a transverso del membrana (proteinas intrinsic o integral).
- Le distribution irregular de proteinas in le membrana resulta in un structura asymmetric.
- Alcun proteinas es ligate a polysaccharides.
- Lipides de membrana e proteinas de membrana pote mover se.
- Le spissor del membrana es de 7-10nm.
- Membranas biologic compartimenta areas cellular (con differentias in pH, potential electric, systemas enzymatic e reactantes) conducente a reactiones metabolic ordinate.
- Le bilayer lipidic face que le membrana ha un permeabilitate debile.
- Proteinas in le membrana es associate con functiones physiologic cellular, inclusive enzimas que catalysa reactiones chimic; proteinas de transporto que exequia transporto de iones transmembrana; vectores que facilita le movimento de iones in cellulas o organellos; e moleculas receptorial que transmitte signales chimic.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.