Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is anaemia?
What is anaemia?
A reduction in the number of erythrocytes, indicated by decreased red blood cell count, haemoglobin concentration, and/or haematocrit.
Which of the following is most likely to significantly affect the results of our data when investigating anaemia?
Which of the following is most likely to significantly affect the results of our data when investigating anaemia?
- Age of patient
- Lipaemic sample
- Size of patient
- A clot in the sample (correct)
What tests would you perform first to investigate a dog's anaemia?
What tests would you perform first to investigate a dog's anaemia?
Take blood sample in EDTA, perform an automated analysis, evaluate machine generated values, and examine blood smear.
Haemoglobin is the most accurate way of measuring the ability to carry oxygen.
Haemoglobin is the most accurate way of measuring the ability to carry oxygen.
What does MCV stand for?
What does MCV stand for?
A decrease in MCHC usually causes hypochromasia.
A decrease in MCHC usually causes hypochromasia.
Match the causes of icterus to their classifications:
Match the causes of icterus to their classifications:
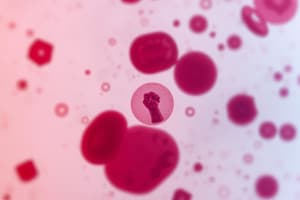
How many platelets are there on average per high power field in this image?
How many platelets are there on average per high power field in this image?
What is anisocytosis?
What is anisocytosis?
What is macrocytosis?
What is macrocytosis?
What does MCV stand for?
What does MCV stand for?
What indicates macrocytosis?
What indicates macrocytosis?
Microcytosis is indicative of iron deficiency anemia.
Microcytosis is indicative of iron deficiency anemia.
What can cause false decrease in cell size in blood samples?
What can cause false decrease in cell size in blood samples?
What characterizes polychromasia?
What characterizes polychromasia?
Hypochromasia is a condition with increased cell staining.
Hypochromasia is a condition with increased cell staining.
What should be done to ensure accurate results from machine-generated values?
What should be done to ensure accurate results from machine-generated values?
What is one of the learning objectives from Week Two, Lesson One of Clinical Pathology?
What is one of the learning objectives from Week Two, Lesson One of Clinical Pathology?
Which breeds are mentioned to recognize familial macrocytosis?
Which breeds are mentioned to recognize familial macrocytosis?
Which of the following conditions are associated with hypochromasia? (Select all that apply)
Which of the following conditions are associated with hypochromasia? (Select all that apply)
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Learning Objectives
- Understand the investigative approach to anaemia.
- Master the preparation, staining, and examination of blood smears for precise analysis.
Introduction to Anaemia
- Anaemia is suspected from patient history and clinical examinations.
- Acute anaemia can cause symptoms like pallor, tachycardia, and shock; chronic anaemia may lead to a more compensated, normal appearance.
Definition and Classification of Anaemia
- Defined as a reduction in erythrocytes indicated by decreased RBC count, haemoglobin, or haematocrit.
- Feline RBCs may overlap in size with platelets, possibly leading to false readings.
- Haemoglobin concentration reflects oxygen-carrying capacity but may be affected by lipaemia and haemolysis.
- Haematocrit is a calculated value, differing slightly from PCV.
- Anaemia can be classified morphologically by red cell indices such as MCV, MCH, and MCHC.
Diagnostic Blood Smear
- Blood smear examination is crucial to identify morphological changes that automated analysers may miss.
- Snapshot of patient health; provides insights into red and white blood cell structure.
- Examination technique includes starting at low magnification, progressing to oil immersion for detailed analysis of RBC morphology and estimates of WBC and platelet counts.
Red Cell Indices
- MCV (Mean Cell Volume): Assesses average red cell size; can be normocytic, macrocytic, or microcytic.
- MCH (Mean Corpuscular Haemoglobin): Indicates average haemoglobin per red cell.
- MCHC (Mean Corpuscular Haemoglobin Concentration): Average haemoglobin concentration; hypochromasia suggests a decrease.
Importance of Blood Smear Examination
- Identifies errors from automated results, aiding in clinical decision-making.
- Errors from clots or sample issues can significantly compromise data integrity.
Making a Diagnostic Blood Smear
- A diagnostic smear must include clear patient identification, even and consistent smear length, and stainable visibility.
- Use techniques for optimal smear creation, focusing on controlling blood drop size and smooth spreading.
Troubleshooting Blood Smear Issues
- Strategies to address common problems such as smeared length and thickness for consistent results.
Examining and Interpretating a Blood Smear
- Systematic examination includes assessing RBC size, shape, color, and inclusions, determining white blood cell types, and estimating platelet counts.
Anisocytosis and Morphological Changes
- Anisocytosis: Variation in red cell size; can indicate various conditions.
- Macrocytosis: Larger than average RBCs; suggests regeneration or possible disease.
- Microcytosis: Smaller than typical RBCs; often associates with iron deficiency.
- Polychromasia: Presence of immature cell forms indicating regenerative activity or stress responses.
Importance of Platelet Counts
- Validates automated analyzer results; small, round structures with variable sizes pose identification challenges, especially in cats.
Conclusion
- Blood smear examination provides vital insights into anaemia and other blood disorders by identifying subtle cellular abnormalities that automated tests might overlook.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.