Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of the heart in the circulatory system?
What is the primary function of the heart in the circulatory system?
- To filter waste from the blood
- To absorb nutrients from food
- To produce hormones
- To circulate blood throughout the body (correct)
Which structure in the small intestine is primarily responsible for nutrient absorption?
Which structure in the small intestine is primarily responsible for nutrient absorption?
- Pancreas
- Stomach
- Villi and microvilli (correct)
- Large intestine
What role do valves play in the heart's function?
What role do valves play in the heart's function?
- To prevent backflow of blood (correct)
- To pump blood stronger
- To prevent blood clotting
- To enhance nutrient absorption
What is the main waste product managed by the excretory system?
What is the main waste product managed by the excretory system?
What type of vessels carry blood back to the heart?
What type of vessels carry blood back to the heart?
How does the integumentary system help in temperature regulation?
How does the integumentary system help in temperature regulation?
Which organ is primarily responsible for detoxifying the blood?
Which organ is primarily responsible for detoxifying the blood?
What is the outer layer of the skin called?
What is the outer layer of the skin called?
Which system is primarily responsible for producing gametes?
Which system is primarily responsible for producing gametes?
What is the primary function of the lymphatic system?
What is the primary function of the lymphatic system?
Which type of muscle tissue is responsible for moving bones?
Which type of muscle tissue is responsible for moving bones?
Where does gas exchange primarily occur in the respiratory system?
Where does gas exchange primarily occur in the respiratory system?
Which part of the nervous system includes the brain and spinal cord?
Which part of the nervous system includes the brain and spinal cord?
What type of cells in the immune system are responsible for producing antibodies?
What type of cells in the immune system are responsible for producing antibodies?
What is the total number of bones in an adult human skeletal system?
What is the total number of bones in an adult human skeletal system?
Which structure helps regulate bodily functions and responses within the nervous system?
Which structure helps regulate bodily functions and responses within the nervous system?
Flashcards
What is the function of the circulatory system?
What is the function of the circulatory system?
The circulatory system is responsible for circulating blood throughout the body, carrying oxygen, nutrients, and removing waste products.
What is the main organ of the circulatory system?
What is the main organ of the circulatory system?
The heart, a powerful pump, is the main organ of the circulatory system. It has four chambers: right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, and left ventricle.
What is the difference between arteries and veins?
What is the difference between arteries and veins?
Arteries carry blood away from the heart, while veins carry blood back to the heart.
What is the function of the digestive system?
What is the function of the digestive system?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the function of the endocrine system?
What is the function of the endocrine system?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the function of the excretory system?
What is the function of the excretory system?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What role does the liver play in the excretory system?
What role does the liver play in the excretory system?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the function of the integumentary system?
What is the function of the integumentary system?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lymphatic System
Lymphatic System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lymph
Lymph
Signup and view all the flashcards
Immune System
Immune System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Muscular System
Muscular System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nervous System
Nervous System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Reproductive System
Reproductive System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Respiratory System
Respiratory System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Skeletal System
Skeletal System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
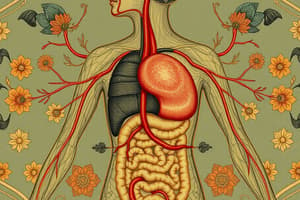
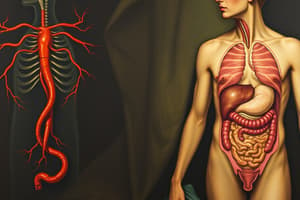
Circulatory System
- The circulatory system transports oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients, and blood throughout the body.
- The heart, the main organ, pumps blood.
- The heart has four chambers: right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, and left ventricle.
- Valves prevent backflow of blood.
- Arteries carry blood away from the heart.
- Veins carry blood back to the heart.
- Capillaries connect arteries and veins.
- Blood's color varies slightly based on oxygen content.
- Blood is red, regardless of oxygen level.
Digestive System
- The digestive system breaks down food and absorbs nutrients.
- Digestion begins in the mouth with saliva enzymes.
- The stomach uses acid and enzymes for further digestion.
- Most nutrient absorption occurs in the small intestine via villi and microvilli.
- The large intestine reabsorbs water.
- Waste is expelled through the anus.
- The digestive system includes accessory structures.
Endocrine System
- The endocrine system consists of glands secreting hormones.
- Hormones act as messengers, triggering actions in target cells.
- Hormones regulate growth, metabolism, and other bodily functions.
Excretory System
- The excretory system maintains osmotic balance and removes metabolic wastes.
- Metabolic wastes include carbon dioxide and nitrogenous waste (urea).
- The excretory system includes liver, skin, lungs, and urinary system.
- The liver detoxifies blood and processes urea.
- The skin excretes through sweat.
- The lungs excrete carbon dioxide.
- The urinary system (kidneys, bladder, ureters, urethra) filters blood and eliminates urine.
- Kidney failure can require dialysis.
- Nephrons are the functional units within kidneys.
Integumentary System
- The integumentary system includes the skin, the body's largest organ.
- Skin protects, regulates temperature, and prevents water loss.
- The skin has three layers: epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis.
- The epidermis' outer layer has cornified cells that are constantly shed and replaced.
- The integumentary system has hair, nails, and sebaceous glands.
Lymphatic and Immune System
- The lymphatic system collects, filters, and returns lymph fluid to the blood.
- Lymph is a clear fluid derived from blood plasma, surrounding cells.
- The lymphatic system supports immune function, protecting against pathogens.
- The immune system includes lymph nodes, thymus, spleen, tonsils, and bone marrow.
- Specialized white blood cells combat pathogens.
- Antibodies bind to pathogens, marking them for macrophage ingestion.
Muscular System
- The muscular system enables movement.
- Skeletal muscle moves bones.
- Muscle tissues include skeletal, smooth, and cardiac.
Nervous System
- The nervous system controls bodily actions, voluntary and involuntary.
- It includes the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS).
- The CNS includes the brain and spinal cord.
- The PNS includes nerves throughout the body.
- The PNS transmits sensory information to the CNS.
- Neurons and glia transmit messages.
Reproductive System
- The reproductive system is responsible for reproduction.
- The reproductive system has internal and external structures.
- Gonads produce gametes: egg cells (female) and sperm cells (male).
- Ovaries produce egg cells.
- Testes produce sperm cells.
Respiratory System
- The respiratory system takes in oxygen and releases carbon dioxide.
- Structures include the trachea and lungs.
- Alveolar sacs contain alveoli, where gas exchange occurs.
- Alveoli have thin walls and a large surface area for efficient gas exchange with capillaries.
Skeletal System
- The skeletal system supports, protects organs, and produces blood cells.
- Humans have 206 bones, developed from fused fetal bones.
- The skeletal system includes axial (skull, vertebrae, ribcage) and appendicular (limbs, girdles) skeletons.
- Bone marrow produces blood cells.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.