Podcast
Questions and Answers
A patient with cholelithiasis is experiencing pruritus. What physiological process is most likely causing this symptom?
A patient with cholelithiasis is experiencing pruritus. What physiological process is most likely causing this symptom?
- Accumulation of bilirubin in the skin. (correct)
- Increased cholesterol levels in the bloodstream.
- Inflammation of the gallbladder.
- Vitamin deficiency due to malabsorption.
Following a cholecystectomy, a patient reports significant pain due to gas. Which nursing intervention is most appropriate to address this?
Following a cholecystectomy, a patient reports significant pain due to gas. Which nursing intervention is most appropriate to address this?
- Applying a heating pad to the incision site.
- Encouraging early ambulation. (correct)
- Administering an antiemetic medication.
- Administering a high-fat meal to stimulate bowel activity.
A patient presents with right upper quadrant pain, dark urine, and clay-colored stools. Which diagnostic test would be most useful in initially confirming cholelithiasis?
A patient presents with right upper quadrant pain, dark urine, and clay-colored stools. Which diagnostic test would be most useful in initially confirming cholelithiasis?
- Liver Biopsy
- Abdominal X-ray
- Ultrasound of the gallbladder (correct)
- Blood Culture
Which combination of risk factors significantly increases an individual's susceptibility to developing cholesterol-based cholelithiasis?
Which combination of risk factors significantly increases an individual's susceptibility to developing cholesterol-based cholelithiasis?
A patient is being discharged after a cholecystectomy. Which of the following instructions is most important to include in the patient's discharge teaching?
A patient is being discharged after a cholecystectomy. Which of the following instructions is most important to include in the patient's discharge teaching?
Flashcards
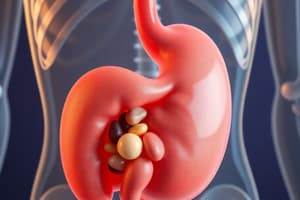
Cholelithiasis
Cholelithiasis
The presence of stones in the gallbladder; most common biliary disorder.
Risk Factors
Risk Factors
Factors increasing likelihood for cholelithiasis: obesity, women, high-fat diet, genetics, age, diabetes.
Clinical Manifestations
Clinical Manifestations
Symptoms of cholelithiasis include pain, jaundice, itching, dark urine, and clay-colored stool.
Diagnosis Methods
Diagnosis Methods
Signup and view all the flashcards
Post-Surgical Care
Post-Surgical Care
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Cholelithiasis (Gallstones)
- Gallstones are hard deposits that form inside the gallbladder, a small organ that stores bile.
- This is the most common disorder of the biliary system.
- Not all gallstones require removal.
Pathophysiology
- Gallstones are categorized into pigment stones (10-25%) and cholesterol stones.
Risk Factors
- Obesity
- Female gender
- High-fat diet
- Genetics
- Age
- Diabetes (often remembered as the "Fat, Forty, Female" risk factors)
Clinical Manifestations
- Pain, often described as biliary colic (a squeezing and releasing sensation)
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Itching (pruritis) potentially from uremic frost.
- Changes in urine color (dark, tea-colored)
- Changes in stool color (light, clay-colored due to bile duct blockage)
- Vitamin deficiencies (leading to unhealthy hair and nails)
- Pain under the rib cage that can be referred to the shoulder blade.
Diagnostics
- Ultrasound (rapid and accurate)
- X-ray of the abdomen (stones rarely visible)
- Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)
Blood Chemistry Findings
- Elevated white blood cell count (WBCs)
- Increased bilirubin levels
- Increased levels of liver enzymes (AST, LDH, ALP)
- Increased cholesterol (greater than 200mg/dL)
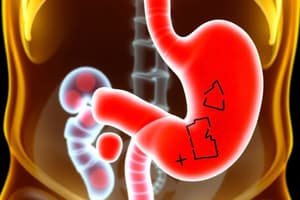
Medical Management
- Cholecystectomy (surgical removal of the gallbladder)
- Dietary management (low-fat, low-cholesterol diet)
Nursing Care
- Post-operative gas is a common source of discomfort.
- Encouraging ambulation shortly after surgery helps reduce gas pain.
- Deep breathing and coughing exercises are important.
Patient Education
- Report a temperature above 100.5°F/38°C.
- Note any drainage from the incision.
- Report any wound opening.
- Follow a bland diet for 7-10 days
- Proper wound care (soap and water)
- Use an incentive spirometer (to improve lung function).
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.