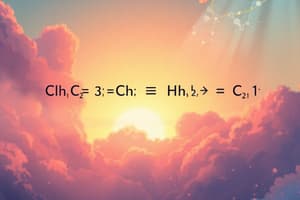Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is a chemical equation?
What is a chemical equation?
- A scientific theory explaining the behavior of chemicals
- A written formula that shows the physical state of the reactants and products in a chemical reaction (correct)
- A physical change that involves rearrangement of atoms to form new substances
- The transformation of one chemical into another without any visual representation
What do the reactants represent in a chemical equation?
What do the reactants represent in a chemical equation?
- The state of matter of the products
- Substances that form after the reaction
- Substances that undergo a change (correct)
- Numbers indicating relative proportions
What is stoichiometry?
What is stoichiometry?
- The visual representation of a chemical reaction
- The physical change of substances in a chemical process
- The study of the quantitative relationships between reactants and products in a chemical reaction (correct)
- The rearrangement of atoms to form new substances
In a chemical equation, what do stoichiometric coefficients represent?
In a chemical equation, what do stoichiometric coefficients represent?
What does the arrow in a chemical equation represent?
What does the arrow in a chemical equation represent?
What do the coefficients in a balanced chemical equation represent?
What do the coefficients in a balanced chemical equation represent?
In a balanced chemical equation, what does it mean if there are the same number of atoms of each element on both sides?
In a balanced chemical equation, what does it mean if there are the same number of atoms of each element on both sides?
Why do chemists balance chemical equations?
Why do chemists balance chemical equations?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Chemical Reaction and Equation
A chemical reaction is a transformation of one set of chemical substances into another through a chemical process. It involves rearrangement of atoms to form new substances with different chemical properties. Central to understanding chemical reactions is the chemical equation, which helps describe the reactants and products involved in a chemical reaction.
Chemical Equations
Chemical equations are visual representations of chemical reactions. They consist of the reactants (the substances that undergo a change) listed on the left side of the equation, joined by an arrow that typically faces to the right. On the right side of the equation, the products (the substances that form after the reaction) are listed. An equation also specifies the quantity of each reactant and product involved, often expressed in terms of moles or masses.
For instance, consider the combustion of methane ((CH_4)):
[CH_4 (g) + 2 O_2 (g) \rightarrow CO_2 (g) + 2 H_2O (g) \tag{1}]
In this equation, one molecule of methane reacts with two molecules of oxygen to produce one molecule of carbon dioxide and two molecules of water. Symbols like (g) indicate the state of matter, and the stoichiometric coefficients (numbers written next to the elements) denote the relative proportions of reactants and products.
Stoichiometry
Stoichiometry is the study of the quantitative relationships between reactants and products in a chemical reaction. The coefficients in a balanced chemical equation represent these stoichiometric ratios. For example, in Eq. (1), there are two hydrogen atoms on the left and two on the right, indicating that the reaction conserves the relative number of hydrogen atoms. Similarly, there are three oxygen atoms on the left and six on the right, demonstrating that the reaction consumes three times as many oxygen atoms as it produces.
Balancing Equations
When confronted with an unknown reaction, chemists start by identifying the reactants and products. Then they write a preliminary unbalanced equation based on their knowledge of the general type of reaction. Finally, they adjust the coefficients until the equation is balanced, meaning the numbers of each type of atom and the overall charges are the same on both sides of the equation.
Consider the combustion of n-heptane:
[C_7H_{16}(l) + O_2(g) \rightarrow CO_2(g) + H_2O(g) \tag{2}]
This equation is unbalanced because the initial n-heptane has 7 carbons, 16 hydrogens, and 2 oxygens, while the final products consist of 1 carbon, 2 hydrogens, and 3 oxygens. The correct balanced equation for this reaction is:
[7 C_7H_{16}(l) + O_2(g) \rightarrow 7 CO_2(g) + 7 H_2O(g) \tag{3}]
Balancing ensures that the reactants and products match in terms of the atoms they contain and the charges they carry.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.