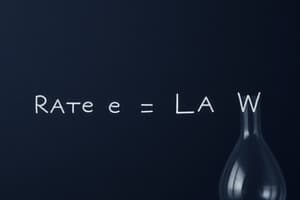Podcast
Questions and Answers
Explain the difference between zero-order and first-order reactions in terms of the reaction rate and reactant concentration.
Explain the difference between zero-order and first-order reactions in terms of the reaction rate and reactant concentration.
Zero-order reactions have a reaction rate independent of reactant concentration, while first-order reactions have a reaction rate directly proportional to reactant concentration.
Describe the role of a catalyst in a chemical reaction.
Describe the role of a catalyst in a chemical reaction.
A catalyst increases the reaction rate without being consumed in the reaction.
How does temperature affect reaction rates?
How does temperature affect reaction rates?
Higher temperatures generally lead to faster reaction rates.
Explain the significance of reaction mechanisms in predicting reaction rates.
Explain the significance of reaction mechanisms in predicting reaction rates.
Define chemical kinetics.
Define chemical kinetics.
What factors influence reaction rates in gas-phase reactions?
What factors influence reaction rates in gas-phase reactions?
What is reaction rate in the context of chemical kinetics?
What is reaction rate in the context of chemical kinetics?
How does increasing the surface area of a solid reactant affect the reaction rate?
How does increasing the surface area of a solid reactant affect the reaction rate?
Explain the concept of rate law in chemical kinetics.
Explain the concept of rate law in chemical kinetics.
What is the formula for the rate law in chemical kinetics?
What is the formula for the rate law in chemical kinetics?
Why is rate law considered an essential tool in chemical kinetics?
Why is rate law considered an essential tool in chemical kinetics?
How is reaction speed typically described in chemical kinetics?
How is reaction speed typically described in chemical kinetics?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Chemical Kinetics: Unraveling the Pace of Chemical Reactions
Chemical kinetics is the branch of chemistry that deals with the rates of chemical reactions and the factors influencing these rates. It's a fundamental aspect of understanding and predicting how substances interact, transform, and combine in various chemical processes. In this article, we'll explore the basics of chemical kinetics, the fundamental concepts, and the factors that influence reaction rates.
Reaction Rate
A chemical reaction's rate is the speed at which reactant molecules collide, react, and form products. It's typically described using the following terms:
-
Reaction speed: The rate at which a reaction proceeds, measured in terms of the concentration of reactants or products changing over time.
-
Rate law: A mathematical expression that relates the reaction rate to the concentrations of reactants raised to their respective exponential powers.
Rate Law
The rate law is an essential tool in chemical kinetics because it helps predict the reaction rate for any combination of reactant concentrations. The rate law is given by:
[ \text{Rate} = k \left[ \text{A} \right]^m \left[ \text{B} \right]^n \cdots ]
where ( k ) is the rate constant, ( m ) and ( n ) are the reaction orders with respect to reactants A and B, and [A] and [B] are the concentrations of the reactants.
Reaction Orders
A reaction's order with respect to a reactant is the exponent in the rate law expression for that reactant. There are two types of reaction orders:
- Zero order: The reaction rate is independent of the reactant concentration.
- First order: The reaction rate is directly proportional to the concentration of the reactant.
- Second order and higher orders: The reaction rate is proportional to the concentration of the reactant raised to a power greater than one.
Reaction Mechanisms
A chemical reaction mechanism is a step-by-step description of how reactants form products, illustrating the intermediates and transition states involved in the reaction. It helps predict the reaction rate and the order of the reaction. A typical reaction mechanism is a concise sequence of elementary steps, also known as elementary reactions.
Factors Influencing Reaction Rates
Several factors influence reaction rates:
- Temperature: Higher temperatures generally lead to faster reaction rates due to increased molecular motion and collision frequency.
- Concentration: Increasing reactant concentrations typically lead to faster reaction rates.
- Pressure (for gas-phase reactions): Higher pressures can increase reaction rates if the reaction involves gases.
- Surface area: Increasing the surface area of a solid reactant can increase the reaction rate.
- Catalysts: Catalysts are substances that increase the reaction rate without being consumed during the reaction.
In summary, chemical kinetics is an essential field of chemistry that helps us understand and predict the rates of chemical reactions. It provides insights into reaction mechanisms and the factors that influence reaction rates. With this knowledge, we can design more efficient chemical processes and develop a better understanding of the natural world around us.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.