Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the distance between the centers of two bonded atoms called?
What is the distance between the centers of two bonded atoms called?
- Bond strength
- Bond length (correct)
- Atomic radius
- Bond angle
Chemical bonds are always rigid and cannot bend or stretch.
Chemical bonds are always rigid and cannot bend or stretch.
False (B)
What model visually represents atoms as balls and bonds as sticks?
What model visually represents atoms as balls and bonds as sticks?
Ball-and-stick model
Quartz is made of silicon dioxide and is represented chemically as ______.
Quartz is made of silicon dioxide and is represented chemically as ______.
Match the following terms with their descriptions:
Match the following terms with their descriptions:
Which of the following describes a property of compounds with network structures?
Which of the following describes a property of compounds with network structures?
What term describes the angle formed between two bonds to the same atom?
What term describes the angle formed between two bonds to the same atom?
What feature of chemical bonds allows them to bend, stretch, and rotate?
What feature of chemical bonds allows them to bend, stretch, and rotate?
In a space-filling model, what do the spheres represent?
In a space-filling model, what do the spheres represent?
Which compound is an example of a network structure?
Which compound is an example of a network structure?
What primarily determines a compound's properties?
What primarily determines a compound's properties?
What is bond length defined as?
What is bond length defined as?
Study Notes
Chemical Compounds and Bonds
- Compounds form when two or more elements chemically combine.
- Chemical bonds are the forces that hold these elements together.
- Bond length refers to the distance between the nuclei of two bonded atoms.
- Bond angle is the angle formed between two bonds connecting to the same atom.
Models Representing Molecules
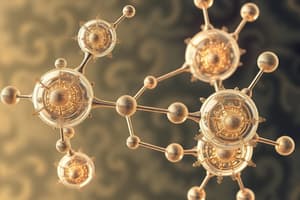
- Ball-and-stick models depict atoms as balls and chemical bonds as sticks.
- Real chemical bonds are flexible, capable of bending, stretching, and rotating.
- Space-filling models illustrate the actual space atoms occupy within a molecule.
Structure and Properties of Compounds
- A compound's chemical structure significantly influences its properties.
- Compounds with network structures, such as quartz, tend to be strong solids.
- Quartz consists of silicon dioxide (SiO₂), where each silicon atom is bonded to four oxygen atoms.
Types of Bonds and Interactions
- Network structures may consist of bonded ions or molecules.
- The strength of attraction between molecules can vary, affecting the physical characteristics of compounds.
Chemical Compounds and Bonds
- Compounds form when two or more elements chemically combine.
- Chemical bonds are the forces that hold these elements together.
- Bond length refers to the distance between the nuclei of two bonded atoms.
- Bond angle is the angle formed between two bonds connecting to the same atom.
Models Representing Molecules
- Ball-and-stick models depict atoms as balls and chemical bonds as sticks.
- Real chemical bonds are flexible, capable of bending, stretching, and rotating.
- Space-filling models illustrate the actual space atoms occupy within a molecule.
Structure and Properties of Compounds
- A compound's chemical structure significantly influences its properties.
- Compounds with network structures, such as quartz, tend to be strong solids.
- Quartz consists of silicon dioxide (SiO₂), where each silicon atom is bonded to four oxygen atoms.
Types of Bonds and Interactions
- Network structures may consist of bonded ions or molecules.
- The strength of attraction between molecules can vary, affecting the physical characteristics of compounds.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Description
Explore the fundamentals of chemical compounds and bonds in this quiz. Learn about the models representing molecules, the influence of structure on properties, and the types of bonds and interactions that characterize various compounds. Test your knowledge on key concepts including bond lengths, angles, and different structural models.