Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary consideration for placing the lowest electronegativity element in a Lewis structure?
What is the primary consideration for placing the lowest electronegativity element in a Lewis structure?
- It should be placed on the outside.
- It should be placed in the center. (correct)
- It should only bond with hydrogen.
- It should be avoided completely.
In a molecule's Lewis structure, how should H and F be positioned?
In a molecule's Lewis structure, how should H and F be positioned?
- Both H and F should be placed at the center.
- H should be in the center, while F is outside.
- H should be on the outside, and F should be on the outside. (correct)
- H should be placed with double bonds, while F should be on the outside.
What is the correct first step in determining the number of electron pairs for a molecule?
What is the correct first step in determining the number of electron pairs for a molecule?
- Determine the molecular geometry.
- Count the number of valence electrons and divide by 2. (correct)
- Add up total protons.
- Predict the polarity of the bonds.
According to the octet rule, what should be done if one atom has enough electrons while another has too few?
According to the octet rule, what should be done if one atom has enough electrons while another has too few?
What does VSEPR stand for and what does it help to predict?
What does VSEPR stand for and what does it help to predict?
What is true regarding polar bonds when atoms of unequal electronegativity are involved?
What is true regarding polar bonds when atoms of unequal electronegativity are involved?
What is the effect of molecular geometry on substances?
What is the effect of molecular geometry on substances?
What should be avoided when constructing a Lewis structure for a molecule?
What should be avoided when constructing a Lewis structure for a molecule?
What is the primary characteristic of ionic bonding compared to covalent bonding?
What is the primary characteristic of ionic bonding compared to covalent bonding?
Which type of elements typically engage in ionic bonding?
Which type of elements typically engage in ionic bonding?
What does lattice energy measure in ionic compounds?
What does lattice energy measure in ionic compounds?
What happens to lattice energy as the distance between ions increases?
What happens to lattice energy as the distance between ions increases?
Which compound would likely have the highest lattice energy?
Which compound would likely have the highest lattice energy?
In which scenario do ionic compounds conduct electricity?
In which scenario do ionic compounds conduct electricity?
What type of bonding is characterized by two elements having very similar electronegativities?
What type of bonding is characterized by two elements having very similar electronegativities?
Which Lewis dot structure represents the greatest number of valence electrons shared in a bond?
Which Lewis dot structure represents the greatest number of valence electrons shared in a bond?
What property characterizes ionic compounds at room temperature?
What property characterizes ionic compounds at room temperature?
Which of the following represents a molecular bond as opposed to an ionic bond?
Which of the following represents a molecular bond as opposed to an ionic bond?
Flashcards
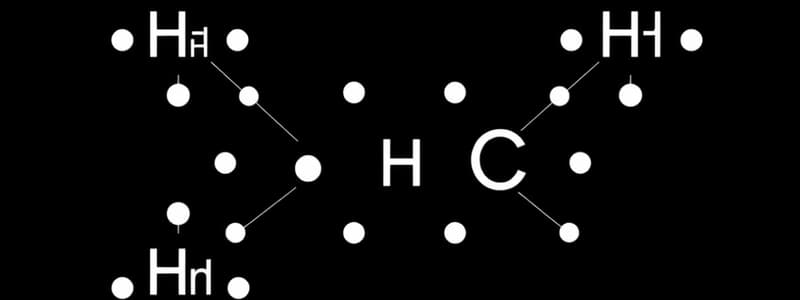
Lewis Dot Structure
Lewis Dot Structure
A diagram that shows the bonding between atoms in a molecule, representing valence electrons as dots.
Octet Rule
Octet Rule
The tendency of atoms to gain, lose, or share electrons to achieve a stable configuration with eight electrons in their outermost shell.
Formal Charge
Formal Charge
The charge an atom would have if all the electrons in the bond were shared equally between the atoms.
Resonance Structures
Resonance Structures
Signup and view all the flashcards
VSEPR Theory
VSEPR Theory
Signup and view all the flashcards
Electron Domain
Electron Domain
Signup and view all the flashcards
Polar Bond
Polar Bond
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nonpolar Bond
Nonpolar Bond
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ionic Bonding
Ionic Bonding
Signup and view all the flashcards
Covalent Bonding
Covalent Bonding
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lewis Dot Symbols
Lewis Dot Symbols
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lattice Energy
Lattice Energy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Factors affecting Lattice Energy
Factors affecting Lattice Energy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Melting Point
Melting Point
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ionic Compounds and Conductivity
Ionic Compounds and Conductivity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Covalent Bond Lengths
Covalent Bond Lengths
Signup and view all the flashcards
Electronegativity (EN)
Electronegativity (EN)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Predicting Bond Type
Predicting Bond Type
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Chemical Bonding
- Chemical bonding is the joining of atoms to form molecules or compounds
- Two main types of bonds are ionic and covalent bonds
- Ionic bonds form between a metal and nonmetal or polyatomic ions
- Ionic bonding involves a transfer of electrons, creating positive and negative ions that are held together by electrostatic attraction
- Covalent bonds form between two nonmetals
- Covalent bonding involves sharing of electrons between atoms
- Electronegativity (EN) is a measure of an atom's ability to attract shared electrons
- Different EN values between atoms lead to different types of bonds
Lewis Dot Symbols
- Gilbert Lewis developed Lewis dot symbols to track valence electrons
- Valence electrons are the outermost electrons in an atom and are the main actors in bonding
- Lewis dot symbols show the elemental symbol and valence electrons as dots around the symbol
- Atoms combine to achieve a more stable electron configuration, often isoelectronic with a noble gas
- Stability is achieved by fulfilling the octet rule, where atoms tend to have eight valence electrons
Ionic Compounds
- Ionic compounds form lattices, a repeating three-dimensional pattern of ions
- The strength of this lattice is described by lattice energy, which is the energy required to completely separate one mole of solid ionic compound into gaseous ions
- The lattice energy depends on the charges of the ions and the distance between them
- Ionic compounds are typically solids at room temperature with high melting points and boiling points
- Ionic compounds conduct electricity when dissolved or molten
Lattice Energy
- Lattice energy is the energy needed to break apart an ionic compound into its component ions
- Lattice energy is directly proportional to the product of the ionic charges (q₁q₂) and inversely proportional to the distance (r) between the ions
- Larger charges will result in a higher lattice energy
- Larger distances will result in a lower lattice energy
Covalent Bond Lengths
- Covalent bond lengths impact the properties of molecules
- Single bonds are longer than double bonds, and double bonds are longer than triple bonds
- This difference in length is due to the varying number of shared pairs of electrons in each bond
- Multiple bonds are more stable
Electronegativity
- Electronegativity is the measure of an atom's ability to attract shared electrons in a covalent bond
- Electronegativity is periodic
- Differences in electronegativity between atoms determine the polarity of the bond and molecule
Drawing Lewis Dot Structures
- Place the least electronegative atom at the centre
- Add up the total valence electrons
- Place single bonds around the central atom first, then add non-bonding pairs to complete the octet of each atom
- Multiple bonds are formed to complete the octet only if needed
Molecular Geometries (VSEPR)
- Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) theory describes molecular shapes by considering electron repulsions between electron domains
- Electron domains include bonding electron pairs and lone electron pairs (non-bonding)
- Electron domains are arranged as far apart as possible to minimize repulsion
- Experimentally determined bond lengths and angles determine molecular geometries which impact properties (melting point, boiling point, density, types of reactions)
Polar and Nonpolar Molecules
- Polarity, either of a bond or a molecule, is determined by the difference in electronegativity of the bonded atoms or the vector sum of all bond dipoles
- Nonpolar molecules exhibit no dipole moment, meaning the centers of positive and negative charge coincide
- Polar molecules have a permanent dipole moment resulting from an asymmetric arrangement of polar bonds
- Bond polarity is determined by the difference in electronegativity of the two atoms in a bond; the larger the difference, the more polar the bond; atoms with large electronegativity values attract shared electrons more strongly
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.