Podcast
Questions and Answers
What are the 3 main parts of the cestode body?
What are the 3 main parts of the cestode body?
- Proboscis, stipe, holdfast
- Mouth, body, tail
- Scolex, neck, strobila (correct)
- Head, thorax, abdomen
What is the head of a cestode called?
What is the head of a cestode called?
- Bothrium
- Capitulum
- Rostellum
- Scolex (correct)
What are the 2 types of attachment organs found on a cestode's head?
What are the 2 types of attachment organs found on a cestode's head?
- Suckers and bothria (correct)
- Tentacles and pedicels
- Fins and claspers
- Hooks and spines
Are cestodes hermaphroditic?
Are cestodes hermaphroditic?
Do cestodes have an alimentary canal?
Do cestodes have an alimentary canal?
What type of life cycle do cestodes have?
What type of life cycle do cestodes have?
How many intermediate hosts are in the life cycle of a Cyclophyllidea cestode?
How many intermediate hosts are in the life cycle of a Cyclophyllidea cestode?
What does the egg of a Cyclophyllidea cestode contain?
What does the egg of a Cyclophyllidea cestode contain?
How many intermediate hosts are in the life cycle of a Pseudophyllidea cestode?
How many intermediate hosts are in the life cycle of a Pseudophyllidea cestode?
What are the attachment organs of a Pseudophyllidea cestode called?
What are the attachment organs of a Pseudophyllidea cestode called?
What is the name given to the body segments of cestodes?
What is the name given to the body segments of cestodes?
What is the mature segment of the cestode body called and where is it located?
What is the mature segment of the cestode body called and where is it located?
What are the reproductive organs found in the cestode proglottid?
What are the reproductive organs found in the cestode proglottid?
What is the function of the vitelline glands?
What is the function of the vitelline glands?
What are the hooks on the cestode scolex called?
What are the hooks on the cestode scolex called?
What is the name of the structure that can be present or absent on the scolex?
What is the name of the structure that can be present or absent on the scolex?
What are the 2 variations of this structure called?
What are the 2 variations of this structure called?
What are the 4 different types of larval stages of cestodes?
What are the 4 different types of larval stages of cestodes?
What is the purpose of the larval stage of the cestode?
What is the purpose of the larval stage of the cestode?
What is the final host of Taenia solium?
What is the final host of Taenia solium?
What is the intermediate host of Taenia solium?
What is the intermediate host of Taenia solium?
What are the clinical signs of Taenia solium in the final host?
What are the clinical signs of Taenia solium in the final host?
What larval stage of Taenia solium is found in the intermediate host?
What larval stage of Taenia solium is found in the intermediate host?
What is the result of a human consuming Taenia Solium eggs in feces?
What is the result of a human consuming Taenia Solium eggs in feces?
What are the 4 key characteristics of nematodes?
What are the 4 key characteristics of nematodes?
What are the 5 larval stages of nematodes?
What are the 5 larval stages of nematodes?
Do nematodes multiply within the host?
Do nematodes multiply within the host?
What are the 2 types of nematode life cycles?
What are the 2 types of nematode life cycles?
Describe the general nematode life cycle.
Describe the general nematode life cycle.
What is the infective larval stage of nematodes?
What is the infective larval stage of nematodes?
What are 4 ways that nematodes ensure survival?
What are 4 ways that nematodes ensure survival?
What is hypobiosis?
What is hypobiosis?
What morphological features aid in the identification of nematodes?
What morphological features aid in the identification of nematodes?
What are the primary clinical signs of Ancylostoma caninum?
What are the primary clinical signs of Ancylostoma caninum?
What are the primary modes of infection of Ancylostoma caninum?
What are the primary modes of infection of Ancylostoma caninum?
What are the hosts of Ancylostoma caninum?
What are the hosts of Ancylostoma caninum?
Where do adult Ancylostoma caninum reside?
Where do adult Ancylostoma caninum reside?
What do adult Ancylostoma caninum eat?
What do adult Ancylostoma caninum eat?
Describe the life cycle of Ancylostoma caninum.
Describe the life cycle of Ancylostoma caninum.
What are the clinical signs of an acute Ancylostoma caninum infection?
What are the clinical signs of an acute Ancylostoma caninum infection?
What are the clinical signs of a chronic Ancylostoma caninum infection?
What are the clinical signs of a chronic Ancylostoma caninum infection?
Are hookworms zoonotic? If so, what is the disease called?
Are hookworms zoonotic? If so, what is the disease called?
Define a facultative parasite and give an example.
Define a facultative parasite and give an example.
Define an opportunistic infection.
Define an opportunistic infection.
Define parasitism.
Define parasitism.
Give 2 examples of ectoparasites.
Give 2 examples of ectoparasites.
Give 2 examples of endoparasites.
Give 2 examples of endoparasites.
What is commensalism? Give an example.
What is commensalism? Give an example.
What is mutualism?
What is mutualism?
What is virulence?
What is virulence?
What is pathogenicity?
What is pathogenicity?
What is a direct life cycle? What is another name for it?
What is a direct life cycle? What is another name for it?
What is an indirect life cycle? What is another name for it?
What is an indirect life cycle? What is another name for it?
What is a paratenic host?
What is a paratenic host?
What is an aberrant host? What is another name for it?
What is an aberrant host? What is another name for it?
Name the 3 classes in the phylum Platyhelminthes.
Name the 3 classes in the phylum Platyhelminthes.
Are Monogenea endoparasites or ectoparasites?
Are Monogenea endoparasites or ectoparasites?
Where are Monogenea typically found?
Where are Monogenea typically found?
Describe the life cycle of Monogenea.
Describe the life cycle of Monogenea.
Give 2 examples of Monogenea.
Give 2 examples of Monogenea.
What is the common name for Acanthocephala?
What is the common name for Acanthocephala?
Where are adult Acanthocephala found?
Where are adult Acanthocephala found?
Describe the life cycle of Acanthocephala.
Describe the life cycle of Acanthocephala.
What is the intermediate host of Oncicola venezuelensis? What is its definitive host?
What is the intermediate host of Oncicola venezuelensis? What is its definitive host?
What is the name of the larval stage of Oncicola venezuelensis found in the mongoose and monkey?
What is the name of the larval stage of Oncicola venezuelensis found in the mongoose and monkey?
What other phylum are Myxozoa related to?
What other phylum are Myxozoa related to?
What are the 2 hosts in the Myxozoa life cycle?
What are the 2 hosts in the Myxozoa life cycle?
What is the clinical sign of Myxobolus cerebralis?
What is the clinical sign of Myxobolus cerebralis?
What is the most optimum temperature for development of major trichostrongylid species?
What is the most optimum temperature for development of major trichostrongylid species?
What are the key characteristics of protozoa?
What are the key characteristics of protozoa?
How do protozoa move?
How do protozoa move?
Describe schizogony.
Describe schizogony.
Give 3 examples of protozoa.
Give 3 examples of protozoa.
Name 3 important flagellated protozoa.
Name 3 important flagellated protozoa.
How is Giardia transmitted?
How is Giardia transmitted?
What animals are affected by Histomoniasis?
What animals are affected by Histomoniasis?
How is Histomonas transmitted?
How is Histomonas transmitted?
Give an example of a ciliate protozoan.
Give an example of a ciliate protozoan.
Name 2 Apicomplexa protozoa.
Name 2 Apicomplexa protozoa.
What is an oocyst?
What is an oocyst?
Flashcards
What are the 3 main parts of a cestode body?
What are the 3 main parts of a cestode body?
Scolex (head), neck, and strobila (segmented body)
What is the head of a cestode called?
What is the head of a cestode called?
Scolex
What are the 2 types of attachment organs on a cestode's Scolex?
What are the 2 types of attachment organs on a cestode's Scolex?
Suckers and bothria OR hooks and spines
Are cestodes hermaphroditic?
Are cestodes hermaphroditic?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Do cestodes have an alimentary canal?
Do cestodes have an alimentary canal?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What type of life cycle do cestodes have?
What type of life cycle do cestodes have?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How many intermediate hosts are in the life cycle of a Cyclophyllidea cestode?
How many intermediate hosts are in the life cycle of a Cyclophyllidea cestode?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does the egg of a Cyclophyllidea cestode contain?
What does the egg of a Cyclophyllidea cestode contain?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How many intermediate hosts are in the life cycle of a Pseudophyllidea cestode?
How many intermediate hosts are in the life cycle of a Pseudophyllidea cestode?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the name given to the body segments of cestodes?
What is the name given to the body segments of cestodes?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Where is the mature segment of the cestode body located?
Where is the mature segment of the cestode body located?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What reproductive organs are found in the cestode proglottid?
What reproductive organs are found in the cestode proglottid?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the function of the vitelline glands?
What is the function of the vitelline glands?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the hooks on the cestode scolex called?
What are the hooks on the cestode scolex called?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the name of the structure that can be present or absent on the scolex?
What is the name of the structure that can be present or absent on the scolex?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the 2 variations of the rostellum structure called?
What are the 2 variations of the rostellum structure called?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the 4 different types of larval stages of cestodes?
What are the 4 different types of larval stages of cestodes?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the purpose of the larval stage of the cestode?
What is the purpose of the larval stage of the cestode?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Define opportunistic infection.
Define opportunistic infection.
Signup and view all the flashcards
Define parasitism.
Define parasitism.
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hosts of Taenia solium?
Hosts of Taenia solium?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Taenia solium clinical signs?
Taenia solium clinical signs?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Taenia solium larval stage?
Taenia solium larval stage?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nematode characteristics?
Nematode characteristics?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nematode larval stages?
Nematode larval stages?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Do nematodes multiply in host?
Do nematodes multiply in host?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Types of nematode life cycles?
Types of nematode life cycles?
Signup and view all the flashcards
General life cycle of nematode?
General life cycle of nematode?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Infective larval stage of nematodes?
Infective larval stage of nematodes?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nematode survival adaptations?
Nematode survival adaptations?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is hypobiosis?
What is hypobiosis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nematode identification features?
Nematode identification features?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ancylostoma caninum signs?
Ancylostoma caninum signs?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How is Ancylostoma transmitted?
How is Ancylostoma transmitted?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hosts of Ancylostoma caninum?
Hosts of Ancylostoma caninum?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Where does adult Ancylostoma reside?
Where does adult Ancylostoma reside?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What do adult dog hookworms eat?
What do adult dog hookworms eat?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Are hookworms zoonotic?
Are hookworms zoonotic?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Define: facultative parasite
Define: facultative parasite
Signup and view all the flashcards
Define virulence.
Define virulence.
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
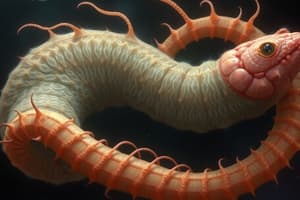
Cestodes (Tapeworms)
- The three main parts of the cestode body are the scolex, neck, and strobila
- The head of a cestode is called the scolex
- Two types of attachment organs on a cestode's head are suckers and bothria
- Cestodes are hermaphroditic
- Cestodes do not have an alimentary canal
- Cestodes have an indirect life cycle
- A Cyclophyllidea cestode has one intermediate host in its life cycle
- The egg of a Cyclophyllidea cestode contains an oncosphere
- A Pseudophyllidea cestode has two intermediate hosts in its life cycle
- Attachment organs of a Pseudophyllidea cestode are called bothria
- Body segments of cestodes are called proglottids
- The mature segment of the cestode body is located posterior and is called proglottid.
- Reproductive organs in the cestode proglottid include both male and female organs
- Vitelline glands function to produce yolk
- Hooks on the cestode scolex are called rostellar hooks
- The rostellum is a structure that can be present or absent on the scolex
- The variations of the rostellum are called armed and unarmed
- Four different types of larval stages of cestodes are cysticercus, hydatid cyst, coenurus, and strobilocercus
- The larval stage's purpose is dispersal
- The final host of Taenia solium is humans
- The intermediate host of Taenia solium is pigs
- Clinical signs of Taenia solium in the final host include an itchy rear end
- The larval stage of Taenia solium found in the intermediate host is cysticercus
- The result of a human consuming Taenia solium eggs in feces is cysticercosis
Nematodes (Roundworms)
- Nematodes have the following key characteristics: elongate/cylindrical shape, an alimentary canal, sexes usually separate, and are egg-laying
- The five larval stages of nematodes are L1-L5
- Nematodes do not multiply within the host
- Nematode life cycles are direct and indirect
- A general nematode life cycle is Egg -> L1 -> L2 -> L3 -> L4 -> L5 -> Adult
- The infective larval stage of nematodes is L3
- Nematodes ensure survival through survival of eggs with larva, paratenic hosts, transmammary, and transplacental
- Hypobiosis is arrested development
- Identification of nematodes is aided by observing male bursa, vulva, mouth (shape, teeth), esophagus, and size
- Primary clinical signs of Ancylostoma caninum include anemia and lassitude
- Primary modes of infection of Ancylostoma caninum include percutaneous or penetration of oral mucosa, per os, paratenic hosts, transplacental, and transmammary
- Hosts of Ancylostoma caninum are dogs
- Adult Ancylostoma caninum reside in the small intestine
- Adult Ancylostoma caninum eat blood
- The life cycle of Ancylostoma caninum: Adults in the intestine lay eggs -> eggs hatch -> larvae penetrate skin or ingested -> adults develop in the intestine
- Clinical signs of an acute Ancylostoma caninum infection include anemia and lassitude, respiratory disease, and diarrhea (blood and mucus)
- Clinical signs of a chronic Ancylostoma caninum infection include weight loss and poor hair coat
- Hookworms are zoonotic, and the disease is called cutaneous larval migrans
General Parasitology
- A facultative parasite may become parasitic but does not require a host, for example, fungi
- An opportunistic infection is an infection that takes advantage of a weakened immune system
- Parasitism is defined as an organism deriving food from a living organism of another species
- Fleas and copepods are examples of ectoparasites
- Cestodes and trematodes are examples of endoparasites
- Commensalism is a relationship where one organism benefits and the other is unaffected; flagellates feeding on bacteria on the surface of fish
- Mutualism is a relationship where both organisms benefit
- Virulence is the degree of pathology caused by the organism
- Pathogenicity is the ability of an organism to cause disease
- A direct life cycle involves only one host; monoxenous
- An indirect life cycle involves more than one host; heteroxenous
- A paratenic host is a non-required host in which no development occurs
- An aberrant host is a host in which the parasite cannot complete its development; dead-end host
Other Taxa
- Three classes in the phylum Platyhelminthes are Cestoda, Trematoda, and Monogenea
- Monogenea are ectoparasites
- Monogenea are typically found on the skin, fins, and gills of fish
- Monogenea have a direct life cycle involving one host
- Two examples of Monogenea: Gyrodactylus, Benedenia seriolae
- The common name for Acanthocephala is thorny-headed worms
- Adult Acanthocephala are found in the intestine
- Acanthocephala has an indirect life cycle involving two or more hosts
- Termites are the intermediate host of Oncicola venezuelensis; ocelots are the definitive host
- The larval stage of Oncicola venezuelensis found in the mongoose and monkey is cystacanth
- The phylum Myxozoa is related to the phylum Cnidaria
- Fish and annelids are the 2 hosts in the Myxozoa life cycle
- A clinical sign of Myxobolus cerebralis is cartilage destruction and erratic tail chasing behavior ("whirling disease")
- The optimum temperature for the development of major trichostrongylid species is 20 degrees C
Protozoa
- Protozoa are unicellular, eukaryotic, may have a "pseudo-mouth", and may form cysts
- Protozoa move with flagella, cilia, and pseudopodia
- Schizogony is asexual reproduction with multiple divisions of the nucleus and cell
- Eimeria, Neospora, and Balantidium are examples of protozoa
- Important flagellated protozoa are Giardia, Histomonas, and Trypanosoma
- Giardia is transmitted through contamination of water, food, or hands/fomites with infective cysts
- Histomoniasis affects poultry
- Histomonas is transmitted fecal-orally
- Balantidium is an example of a ciliate protozoan
- Eimeria and Toxoplasma are Apicomplexa protozoa
- An oocyst is a cyst containing a zygote
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.