Podcast
Questions and Answers
What part of the anatomy is primarily involved in Cervical Facet Syndrome?
What part of the anatomy is primarily involved in Cervical Facet Syndrome?
- Thoracic spine
- Lumbar spine
- Sacral spine
- Cervical spine (correct)
Which of the following nerves are highlighted in the illustration of Cervical Facet Syndrome?
Which of the following nerves are highlighted in the illustration of Cervical Facet Syndrome?
- Cranial nerves
- Thoracic nerves
- Lumbar nerves
- Cervical nerves (correct)
What is a common feature depicted in illustrations of Cervical Facet Syndrome?
What is a common feature depicted in illustrations of Cervical Facet Syndrome?
- Disc herniation in the thoracic spine
- Nerves emerging from the cervical spine (correct)
- Muscle spasms in the sacral area
- Inflamed ligaments in the lumbar region
What pathological feature is most associated with Cervical Facet Syndrome?
What pathological feature is most associated with Cervical Facet Syndrome?
In an image illustrating Cervical Facet Syndrome, which anatomical structures are likely to be emphasized?
In an image illustrating Cervical Facet Syndrome, which anatomical structures are likely to be emphasized?
Which cervical vertebrae is predominantly responsible for the rotation of the head?
Which cervical vertebrae is predominantly responsible for the rotation of the head?
What is the primary function of the facet joints in the cervical spine?
What is the primary function of the facet joints in the cervical spine?
Which of the following is NOT a likely consequence of the degeneration of facet joints?
Which of the following is NOT a likely consequence of the degeneration of facet joints?
Facet joint degeneration commonly occurs in which region of the spine?
Facet joint degeneration commonly occurs in which region of the spine?
How does the degeneration of facet joints primarily affect the spine?
How does the degeneration of facet joints primarily affect the spine?
Which specific type of pain is associated with the posterior c-spine region?
Which specific type of pain is associated with the posterior c-spine region?
What movement limitations are noted during activities of daily living (ADLs) with this clinical presentation?
What movement limitations are noted during activities of daily living (ADLs) with this clinical presentation?
Which of the following can become a chronic condition?
Which of the following can become a chronic condition?
During which movements is posterior c-spine neck pain noted?
During which movements is posterior c-spine neck pain noted?
What may cause difficulty with grasping activities?
What may cause difficulty with grasping activities?
What type of fracture is indicated by a break in the spinous process of a cervical vertebra?
What type of fracture is indicated by a break in the spinous process of a cervical vertebra?
Which part of the cervical spine is most likely to experience a compression fracture?
Which part of the cervical spine is most likely to experience a compression fracture?
If a patient has a fracture in the vertebral body of the cervical spine, what type of fracture might this be?
If a patient has a fracture in the vertebral body of the cervical spine, what type of fracture might this be?
Which specific type of fracture involves the vertebral body in the cervical spine?
Which specific type of fracture involves the vertebral body in the cervical spine?
Which fracture type is not commonly associated with the cervical spine?
Which fracture type is not commonly associated with the cervical spine?
Which of the following is a potential cause for a cervical vertebra fracture?
Which of the following is a potential cause for a cervical vertebra fracture?
Which mechanism is least likely to be associated with cervical vertebra fractures?
Which mechanism is least likely to be associated with cervical vertebra fractures?
What pathological condition could directly result in a cervical vertebra fracture?
What pathological condition could directly result in a cervical vertebra fracture?
What type of trauma is most commonly associated with cervical vertebra fractures?
What type of trauma is most commonly associated with cervical vertebra fractures?
Falls can cause fractures in which part of the vertebral column?
Falls can cause fractures in which part of the vertebral column?
Which type of fractures typically require surgical fusion with HALO immobilization?
Which type of fractures typically require surgical fusion with HALO immobilization?
Which of the following is a potential consequence of surgical fusion at a cervical spine level?
Which of the following is a potential consequence of surgical fusion at a cervical spine level?
What is the primary diagnostic imaging method mentioned for assessing spinal issues?
What is the primary diagnostic imaging method mentioned for assessing spinal issues?
Which surgical procedure is used for repairing fractures of the vertebral body?
Which surgical procedure is used for repairing fractures of the vertebral body?
Why might surgical cervical fusion with bracing be required for certain C-spine segments?
Why might surgical cervical fusion with bracing be required for certain C-spine segments?
Which of the following is NOT listed as an impairment in the clinical presentation?
Which of the following is NOT listed as an impairment in the clinical presentation?
Which condition could directly cause decreased ROM?
Which condition could directly cause decreased ROM?
Which impairment is most likely to affect a person's ability to perform daily activities involving lifting objects?
Which impairment is most likely to affect a person's ability to perform daily activities involving lifting objects?
What is the direct impact of decreased muscle length on physical function?
What is the direct impact of decreased muscle length on physical function?
Limitation in which aspect is specifically mentioned as impacting activities of daily living (ADLs)?
Limitation in which aspect is specifically mentioned as impacting activities of daily living (ADLs)?
What is the recommended duration for immobilization following surgery?
What is the recommended duration for immobilization following surgery?
Which activity is recommended for the upper extremities (UE) while braced post-surgery?
Which activity is recommended for the upper extremities (UE) while braced post-surgery?
When can stretching, range of motion, and strengthening exercises for the cervical spine be introduced?
When can stretching, range of motion, and strengthening exercises for the cervical spine be introduced?
What is the duration of restriction for spine precautions post-surgery?
What is the duration of restriction for spine precautions post-surgery?
What type of therapeutic exercises are recommended for the lower extremities (LE) while braced?
What type of therapeutic exercises are recommended for the lower extremities (LE) while braced?
Which activity is permitted for patients under spine precautions?
Which activity is permitted for patients under spine precautions?
Which position should be avoided post-operatively according to the spine precautions?
Which position should be avoided post-operatively according to the spine precautions?
What specific movement is restricted to prevent stress on the spine post-operatively?
What specific movement is restricted to prevent stress on the spine post-operatively?
Which action should be avoided especially for patients with lumbar spinal precautions?
Which action should be avoided especially for patients with lumbar spinal precautions?
Which of the following restrictions is NOT included in post-operative spine precautions?
Which of the following restrictions is NOT included in post-operative spine precautions?
Study Notes
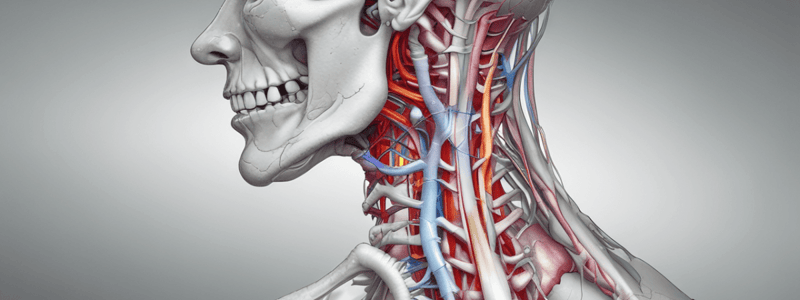
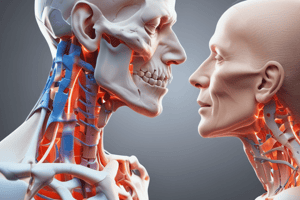
Cervical Facet Syndrome
- Degeneration of facet joints in the cervical spine causes pain and stiffness
- Facet joints are located in the back of the spine and provide stability and movement
Clinical Presentation
- Pain in the posterior cervical spine area
- Pain worsens with cervical spine extension and/or rotation
- Can become a chronic pain condition
- Posterior neck stiffness
- May have radicular signs (e.g. numbness, tingling, or weakness in arms or legs)
- Limited cervical active range of motion (AROM) during daily activities
- Difficulty with grasping if radicular signs are present
Fractures
- Fracture of the vertebral body (compression fracture)
- Fracture of the spinous process
- Fracture of any part of cervical vertebrae due to falls, trauma, or pathological conditions
Clinical Presentation (Fractures)
- Pain
- Decreased muscle length
- Decreased muscle strength
- Decreased ROM
- Limited AROM during daily activities
Medical Management
- Diagnostic imaging: X-ray
- Surgical procedures:
- Unstable fractures require surgical stabilization
- C1 or C2 fractures require surgical fusion plus immobilization with HALO
- Other C-spine segments with fracture may require surgical cervical fusion with bracing
- Vertebroplasty may be used to repair vertebral body fractures
Post-Operative Management
- Immobilization for 6-12 weeks
- Patient education regarding spine precautions and duration of restriction (6-8 weeks)
- Therapeutic exercises for lower extremities while braced
- Open chain therapeutic exercises of upper extremities to 90 degrees at shoulder
- Introduce stretching, ROM, strengthening, and modalities of C-spine after bracing and spine precautions are discontinued
- Patients follow spine precautions to avoid exacerbating the condition
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Description
Understand the pathophysiology of cervical facet syndrome through an illustration of the neck and its nerves. Learn about the anatomy of the cervical spine and its relation to this condition.