Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of the central nervous system (CNS)?
What is the primary function of the central nervous system (CNS)?
- To connect the brain and spinal cord
- To carry sensory messages from the CNS to muscles
- To process sensory information and coordinate responses (correct)
- To regulate blood vessel activity
Which area is responsible for speech comprehension?
Which area is responsible for speech comprehension?
- Precentral gyrus
- Broca area
- Cerebellum
- Wernicke area (correct)
Which layer of the meninges is the outermost and most protective?
Which layer of the meninges is the outermost and most protective?
- Arachnoid mater
- Subarachnoid space
- Pia mater
- Dura mater (correct)
What is the role of myelin in the nervous system?
What is the role of myelin in the nervous system?
What structure connects the left and right cerebral hemispheres?
What structure connects the left and right cerebral hemispheres?
Which part of the CNS is primarily responsible for motor coordination and equilibrium balance?
Which part of the CNS is primarily responsible for motor coordination and equilibrium balance?
Which of the following structures is NOT part of the brainstem?
Which of the following structures is NOT part of the brainstem?
What is the primary sensory area of the cerebral cortex?
What is the primary sensory area of the cerebral cortex?
What is the primary function of somatic fibers?
What is the primary function of somatic fibers?
Which cranial nerve is responsible for smell?
Which cranial nerve is responsible for smell?
What type of cranial nerve is the Vagus nerve?
What type of cranial nerve is the Vagus nerve?
What role do autonomic fibers primarily serve?
What role do autonomic fibers primarily serve?
At what stage do infants gain motor control according to the myelination process?
At what stage do infants gain motor control according to the myelination process?
What is a sign of CNS dysfunction in infants?
What is a sign of CNS dysfunction in infants?
As a person ages, what happens to the volume of the brain?
As a person ages, what happens to the volume of the brain?
Which cranial nerve allows for lateral movement of the eye?
Which cranial nerve allows for lateral movement of the eye?
What decreases in older adults, leading to slower reaction times?
What decreases in older adults, leading to slower reaction times?
What sensory function is associated with the Glossopharyngeal nerve?
What sensory function is associated with the Glossopharyngeal nerve?
Which cranial nerve is NOT involved in mixed functions?
Which cranial nerve is NOT involved in mixed functions?
Which number indicates the lumbar spinal nerves in the human body?
Which number indicates the lumbar spinal nerves in the human body?
What is the primary function of the facial nerve?
What is the primary function of the facial nerve?
What does the mnemonic FACE stand for in the recognition of stroke symptoms?
What does the mnemonic FACE stand for in the recognition of stroke symptoms?
Which of the following is NOT a modifiable risk factor for stroke?
Which of the following is NOT a modifiable risk factor for stroke?
For which group is the risk of stroke generally higher than for women?
For which group is the risk of stroke generally higher than for women?
What is the first action recommended when someone shows symptoms of a TIA?
What is the first action recommended when someone shows symptoms of a TIA?
Which of the following nonmodifiable risk factors is mentioned as contributing to a higher prevalence of stroke?
Which of the following nonmodifiable risk factors is mentioned as contributing to a higher prevalence of stroke?
Which medical condition significantly contributes to the risk of non–pregnancy-related ischemic stroke in women?
Which medical condition significantly contributes to the risk of non–pregnancy-related ischemic stroke in women?
Which of the following is NOT included as a risk factor for stroke?
Which of the following is NOT included as a risk factor for stroke?
Which of the following lifestyle changes is recommended for stroke prevention?
Which of the following lifestyle changes is recommended for stroke prevention?
What symptom might indicate a potential stroke that requires immediate medical attention?
What symptom might indicate a potential stroke that requires immediate medical attention?
Which of the following factors has NOT been associated with a higher risk for stroke among certain ethnic groups?
Which of the following factors has NOT been associated with a higher risk for stroke among certain ethnic groups?
Which of the following health history questions would help assess potential stroke risk?
Which of the following health history questions would help assess potential stroke risk?
What is the primary purpose of the frontal lobe?
What is the primary purpose of the frontal lobe?
What acronym can be used to remember the immediate steps to take in stroke recognition?
What acronym can be used to remember the immediate steps to take in stroke recognition?
Damage to which area of the brain primarily affects the ability to produce language?
Damage to which area of the brain primarily affects the ability to produce language?
What is the relationship between age and stroke risk?
What is the relationship between age and stroke risk?
Which part of the brain acts as the main relay station for sensory pathways?
Which part of the brain acts as the main relay station for sensory pathways?
Which condition is NOT classified as a cardiac condition related to stroke risk?
Which condition is NOT classified as a cardiac condition related to stroke risk?
Which part of the central nervous system is primarily responsible for coordinating motor movements?
Which part of the central nervous system is primarily responsible for coordinating motor movements?
What is the unique characteristic of crossed representation in the nervous system?
What is the unique characteristic of crossed representation in the nervous system?
What type of sensations does the spinothalamic tract primarily transmit?
What type of sensations does the spinothalamic tract primarily transmit?
Where is the primary auditory reception center located in the brain?
Where is the primary auditory reception center located in the brain?
What results when Wernicke’s area is damaged in the dominant hemisphere?
What results when Wernicke’s area is damaged in the dominant hemisphere?
The hypothalamus plays a crucial role in regulating which of the following functions?
The hypothalamus plays a crucial role in regulating which of the following functions?
What is primarily housed in the basal ganglia?
What is primarily housed in the basal ganglia?
Which area of the brain would most likely be damaged if a person cannot perceive sensations?
Which area of the brain would most likely be damaged if a person cannot perceive sensations?
Which structure is NOT part of the brainstem?
Which structure is NOT part of the brainstem?
What does paresis refer to in neurological terms?
What does paresis refer to in neurological terms?
In which part of the brain do pyramidal decussation occur?
In which part of the brain do pyramidal decussation occur?
How does the cerebrospinal fluid travel through the spinal cord?
How does the cerebrospinal fluid travel through the spinal cord?
Which of the following could be considered an aura before a seizure?
Which of the following could be considered an aura before a seizure?
Dysarthria refers to which of the following problems?
Dysarthria refers to which of the following problems?
What might trigger seizures in some individuals?
What might trigger seizures in some individuals?
What describes dysphagia?
What describes dysphagia?
Which condition involves an inability to control the range of motion of the muscles?
Which condition involves an inability to control the range of motion of the muscles?
What is an example of an environmental hazard that could affect cognitive development in children?
What is an example of an environmental hazard that could affect cognitive development in children?
Which of the following symptoms is indicative of an early sign of muscular dystrophy in children?
Which of the following symptoms is indicative of an early sign of muscular dystrophy in children?
What is the significance of the postictal phase following a seizure?
What is the significance of the postictal phase following a seizure?
What is the primary sensory function of the dorsal columns?
What is the primary sensory function of the dorsal columns?
What does the term 'paraesthesia' refer to?
What does the term 'paraesthesia' refer to?
Where do sensory fibers from the dorsal columns cross to the opposite side of the body?
Where do sensory fibers from the dorsal columns cross to the opposite side of the body?
What is primarily assessed when asking about environmental and occupational hazards?
What is primarily assessed when asking about environmental and occupational hazards?
Which cortex is responsible for full interpretation of sensory messages?
Which cortex is responsible for full interpretation of sensory messages?
Which of the following statements best defines tremors?
Which of the following statements best defines tremors?
Which aspect of a child's development is monitored through reflexes?
Which aspect of a child's development is monitored through reflexes?
What is the role of the corticospinal tract?
What is the role of the corticospinal tract?
What might indicate that an adult is at a higher risk of falls?
What might indicate that an adult is at a higher risk of falls?
What is a characteristic of the cortical homunculus?
What is a characteristic of the cortical homunculus?
What does referred pain mean?
What does referred pain mean?
Which system is responsible for maintaining muscle tone and controlling gross movements?
Which system is responsible for maintaining muscle tone and controlling gross movements?
How do upper motor neurons influence lower motor neurons?
How do upper motor neurons influence lower motor neurons?
Which of the following is an example of an upper motor neuron disease?
Which of the following is an example of an upper motor neuron disease?
Where are the lower motor neurons predominantly located?
Where are the lower motor neurons predominantly located?
What kind of movements does the cerebellar system primarily coordinate?
What kind of movements does the cerebellar system primarily coordinate?
What structure is primarily responsible for the exchange of sensory and motor information?
What structure is primarily responsible for the exchange of sensory and motor information?
How do proprioceptors function in the sensory pathway?
How do proprioceptors function in the sensory pathway?
What do the extrapyramidal tracts primarily regulate?
What do the extrapyramidal tracts primarily regulate?
What is a common physical change observed in older adults as they age?
What is a common physical change observed in older adults as they age?
What is the primary risk associated with older adults getting up too quickly?
What is the primary risk associated with older adults getting up too quickly?
Which demographic is shown to have a higher rate of strokes as compared to the general population?
Which demographic is shown to have a higher rate of strokes as compared to the general population?
What is the leading cause of adult disability in Canada?
What is the leading cause of adult disability in Canada?
Which of the following is NOT a common symptom of stroke?
Which of the following is NOT a common symptom of stroke?
What should not be ignored after experiencing symptoms that disappear within an hour?
What should not be ignored after experiencing symptoms that disappear within an hour?
What contributes significantly to the elevated death rate due to strokes in certain populations?
What contributes significantly to the elevated death rate due to strokes in certain populations?
Which type of stroke is the most common?
Which type of stroke is the most common?
What is a critical factor in the initial assessment of a stroke?
What is a critical factor in the initial assessment of a stroke?
How does socioeconomic status influence stroke risk?
How does socioeconomic status influence stroke risk?
Which of the following describes a transient ischemic attack (TIA)?
Which of the following describes a transient ischemic attack (TIA)?
What often contributes to a lack of recognition of stroke symptoms among Canadians?
What often contributes to a lack of recognition of stroke symptoms among Canadians?
What health issue is linked to racism and impacts stroke risk among specific populations?
What health issue is linked to racism and impacts stroke risk among specific populations?
What should be assessed when testing the muscles of mastication?
What should be assessed when testing the muscles of mastication?
What physical characteristic may older adults display while walking, indicating cautiousness?
What physical characteristic may older adults display while walking, indicating cautiousness?
Which cranial nerve is primarily involved in the corneal reflex?
Which cranial nerve is primarily involved in the corneal reflex?
What indicates decreased strength of the muscles of facial expression?
What indicates decreased strength of the muscles of facial expression?
Which action tests cranial nerves IX and X?
Which action tests cranial nerves IX and X?
What does the presence of atrophy in a muscle indicate?
What does the presence of atrophy in a muscle indicate?
Which of the following best describes the normal range of findings for the tongue during evaluation?
Which of the following best describes the normal range of findings for the tongue during evaluation?
What symptom suggests a dysfunction in cranial nerve VII?
What symptom suggests a dysfunction in cranial nerve VII?
Which test assesses the sensory function of the trigeminal nerve?
Which test assesses the sensory function of the trigeminal nerve?
What is a common finding in individuals who have worn contact lenses related to the corneal reflex?
What is a common finding in individuals who have worn contact lenses related to the corneal reflex?
Which assessment technique is used to evaluate cranial nerve XI?
Which assessment technique is used to evaluate cranial nerve XI?
What does the presence of nasal twang in a patient's voice indicate?
What does the presence of nasal twang in a patient's voice indicate?
What does normal muscle tone demonstrate when a passive ROM test is conducted?
What does normal muscle tone demonstrate when a passive ROM test is conducted?
Which of the following conditions can result in facial muscle weakness?
Which of the following conditions can result in facial muscle weakness?
How can dizziness impact a person's ability to drive?
How can dizziness impact a person's ability to drive?
What is micturition syncope?
What is micturition syncope?
Which of the following changes may indicate a decline in cognitive function?
Which of the following changes may indicate a decline in cognitive function?
What factors can exacerbate tremors experienced by a patient?
What factors can exacerbate tremors experienced by a patient?
What is a critical finding that necessitates immediate medical attention?
What is a critical finding that necessitates immediate medical attention?
Which cranial nerves are involved in assessing eye movement?
Which cranial nerves are involved in assessing eye movement?
Which condition is associated with a sudden and severe headache?
Which condition is associated with a sudden and severe headache?
What should be done when a patient shows signs of neurological dysfunction?
What should be done when a patient shows signs of neurological dysfunction?
How should olfactory nerve function be evaluated?
How should olfactory nerve function be evaluated?
What might unilateral loss of smell indicate?
What might unilateral loss of smell indicate?
What is the recommended action if a patient reports sudden vision changes?
What is the recommended action if a patient reports sudden vision changes?
What does increased intracranial pressure often cause regarding pupil response?
What does increased intracranial pressure often cause regarding pupil response?
What is a common finding in senile tremor?
What is a common finding in senile tremor?
What is the expected finding when assessing joint resistance during movement?
What is the expected finding when assessing joint resistance during movement?
What does an inability to tandem walk indicate?
What does an inability to tandem walk indicate?
Which of the following demonstrates an abnormal finding in the Romberg Test?
Which of the following demonstrates an abnormal finding in the Romberg Test?
What indicates that a patient is fully alert?
What indicates that a patient is fully alert?
What type of movement is described as dysdiadochokinesia?
What type of movement is described as dysdiadochokinesia?
What is the first method to increase stimulation for a patient who is not fully alert?
What is the first method to increase stimulation for a patient who is not fully alert?
Which command can be used to check voluntary movement of the patient's extremities?
Which command can be used to check voluntary movement of the patient's extremities?
Which test assesses lower extremity coordination by running the heel down the opposite shin?
Which test assesses lower extremity coordination by running the heel down the opposite shin?
Which of the following is NOT a method to assess a patient's response to stimuli?
Which of the following is NOT a method to assess a patient's response to stimuli?
In a healthy patient, what should be observed during the finger-to-nose test?
In a healthy patient, what should be observed during the finger-to-nose test?
Which finding indicates abnormal gait during a walking test?
Which finding indicates abnormal gait during a walking test?
What facial movements should be noted to assess cranial nerve VII?
What facial movements should be noted to assess cranial nerve VII?
What role do lower motor neurons play in the nervous system?
What role do lower motor neurons play in the nervous system?
Which of the following is not classified as a lower motor neuron disease?
Which of the following is not classified as a lower motor neuron disease?
What does the presence of spasticity indicate during a movement assessment?
What does the presence of spasticity indicate during a movement assessment?
What are the major motor pathways mentioned?
What are the major motor pathways mentioned?
How should a normal finding appear during rapid alternating movements?
How should a normal finding appear during rapid alternating movements?
Which cranial nerves are involved in supplying the head and neck?
Which cranial nerves are involved in supplying the head and neck?
Which condition is associated with an absence of proprioception while performing a Romberg Test?
Which condition is associated with an absence of proprioception while performing a Romberg Test?
What characterizes deep tendon reflexes?
What characterizes deep tendon reflexes?
What does a positive finding for involuntary movements indicate?
What does a positive finding for involuntary movements indicate?
What is a common symptom that may accompany an inability to perform a shallow knee bend?
What is a common symptom that may accompany an inability to perform a shallow knee bend?
Where do peripheral nerves carry sensory and motor information?
Where do peripheral nerves carry sensory and motor information?
Which of the following is NOT a component of the deep tendon reflex?
Which of the following is NOT a component of the deep tendon reflex?
What is often tested to assess skin sensitivity in a patient?
What is often tested to assess skin sensitivity in a patient?
What does a reflex arc consist of?
What does a reflex arc consist of?
What is the function of spinal nerves in the body?
What is the function of spinal nerves in the body?
Which function describes the role of the vagus nerve?
Which function describes the role of the vagus nerve?
Which dermatomes correspond to the thumb, middle finger, and fifth finger?
Which dermatomes correspond to the thumb, middle finger, and fifth finger?
What distinguishes somatic from autonomic nerve fibers?
What distinguishes somatic from autonomic nerve fibers?
What happens when a tendon is tapped during a reflex test?
What happens when a tendon is tapped during a reflex test?
Which of the following options describes the flow of the corticospinal crossed tract?
Which of the following options describes the flow of the corticospinal crossed tract?
What does the inability to recognize a traced number or letter on the palm indicate?
What does the inability to recognize a traced number or letter on the palm indicate?
What is the most sensitive area for two-point discrimination testing?
What is the most sensitive area for two-point discrimination testing?
Which statement about extinction testing is accurate?
Which statement about extinction testing is accurate?
What should be observed to obtain an adequate response during deep tendon reflex testing?
What should be observed to obtain an adequate response during deep tendon reflex testing?
How are reflex responses graded?
How are reflex responses graded?
What tests should be administered when a patient displays neurological symptoms?
What tests should be administered when a patient displays neurological symptoms?
How should the sensory testing be conducted to avoid suggestion?
How should the sensory testing be conducted to avoid suggestion?
What could cause hyperreflexia during a reflex test?
What could cause hyperreflexia during a reflex test?
If a patient demonstrates reduced reflex functioning, what does this indicate?
If a patient demonstrates reduced reflex functioning, what does this indicate?
What is the purpose of letting at least 2 seconds elapse between each stimulus during pain testing?
What is the purpose of letting at least 2 seconds elapse between each stimulus during pain testing?
Which muscle response indicates a normal biceps reflex?
Which muscle response indicates a normal biceps reflex?
Which of the following sensations is assessed using a tuning fork?
Which of the following sensations is assessed using a tuning fork?
What does hyperalgesia refer to?
What does hyperalgesia refer to?
What technique can enhance a reflex response during testing?
What technique can enhance a reflex response during testing?
What procedure is used to test the ability to recognize an object through touch?
What procedure is used to test the ability to recognize an object through touch?
When testing the triceps reflex, where should the hammer strike?
When testing the triceps reflex, where should the hammer strike?
Which reflex is specifically associated with segments L2 to L4?
Which reflex is specifically associated with segments L2 to L4?
To effectively map decreased sensation, which approach should be taken?
To effectively map decreased sensation, which approach should be taken?
What element is critical to accurately assess the stretch reflex?
What element is critical to accurately assess the stretch reflex?
How should temperature sensation testing be conducted?
How should temperature sensation testing be conducted?
What does clonus indicate during a reflex assessment?
What does clonus indicate during a reflex assessment?
What is the primary purpose of comparing sensations on symmetrical parts of the body?
What is the primary purpose of comparing sensations on symmetrical parts of the body?
Where is loss of vibration sense often first detected in peripheral neuropathy?
Where is loss of vibration sense often first detected in peripheral neuropathy?
How is sensation typically localized with a sensory cortex lesion?
How is sensation typically localized with a sensory cortex lesion?
When assessing position sense, how should the examination be conducted?
When assessing position sense, how should the examination be conducted?
What does a deficiency in tactile discrimination indicate?
What does a deficiency in tactile discrimination indicate?
Which of the following conditions reflects a loss in position sense?
Which of the following conditions reflects a loss in position sense?
What term describes the absence of pain sensation?
What term describes the absence of pain sensation?
What reflex involves an infant extending the arm and leg on the same side where the head is turned?
What reflex involves an infant extending the arm and leg on the same side where the head is turned?
At what age does the Babinski reflex typically begin to disappear?
At what age does the Babinski reflex typically begin to disappear?
Which reflex is characterized by the infant demonstrating a symmetrical 'hugging' motion when startled?
Which reflex is characterized by the infant demonstrating a symmetrical 'hugging' motion when startled?
Which reflex indicates potential severe CNS injury if absent in a newborn?
Which reflex indicates potential severe CNS injury if absent in a newborn?
When does the Tonic Neck Reflex typically decrease in infants?
When does the Tonic Neck Reflex typically decrease in infants?
What abnormal sign is indicated by the persistence of the Moro reflex after 5 months of age?
What abnormal sign is indicated by the persistence of the Moro reflex after 5 months of age?
What does the Placing Reflex test in infants assess?
What does the Placing Reflex test in infants assess?
What indicates a concern when observing a child's ability to rise from a supine position?
What indicates a concern when observing a child's ability to rise from a supine position?
At what age should children normally be able to balance on one foot for about 5 seconds?
At what age should children normally be able to balance on one foot for about 5 seconds?
What assessment tool is recommended for screening gross and fine motor skills in children?
What assessment tool is recommended for screening gross and fine motor skills in children?
What is the typical response of an infant when the dorsal aspect of their foot touches the underside of a table during the Placing Reflex?
What is the typical response of an infant when the dorsal aspect of their foot touches the underside of a table during the Placing Reflex?
What movement indicates a possible lower spinal cord problem in an infant?
What movement indicates a possible lower spinal cord problem in an infant?
Normal development in children includes the ability to hop by what age?
Normal development in children includes the ability to hop by what age?
At what age can children typically start to have their sensory systems tested similarly to adults?
At what age can children typically start to have their sensory systems tested similarly to adults?
What action indicates a normal response when testing for spasticity in infants?
What action indicates a normal response when testing for spasticity in infants?
What is the recommended method for testing deep tendon reflexes (DTRs) in children under 5 years?
What is the recommended method for testing deep tendon reflexes (DTRs) in children under 5 years?
At what age does purposeful release of objects typically develop in infants?
At what age does purposeful release of objects typically develop in infants?
Which of the following conditions may lead to hyperactivity of deep tendon reflexes (DTRs)?
Which of the following conditions may lead to hyperactivity of deep tendon reflexes (DTRs)?
What is a common sign of cerebral palsy in infants?
What is a common sign of cerebral palsy in infants?
What are common signs of neurological deterioration that should be monitored closely in hospitalized patients?
What are common signs of neurological deterioration that should be monitored closely in hospitalized patients?
Which reflex is assessed by brushing the infant’s cheek?
Which reflex is assessed by brushing the infant’s cheek?
Which position indicates an abnormal finding in an infant after a breech delivery?
Which position indicates an abnormal finding in an infant after a breech delivery?
Which reflex is often found to be absent in older adults?
Which reflex is often found to be absent in older adults?
What should be observed at 4 months regarding head control?
What should be observed at 4 months regarding head control?
What is a common age-related change in older adults regarding sensory perception?
What is a common age-related change in older adults regarding sensory perception?
When does the palmar grasp reflex typically disappear?
When does the palmar grasp reflex typically disappear?
What characteristic distinguishes senile tremors from parkinsonism tremors?
What characteristic distinguishes senile tremors from parkinsonism tremors?
What does persistent one-hand preference in infants younger than 18 months indicate?
What does persistent one-hand preference in infants younger than 18 months indicate?
When conducting an abbreviated neurological examination, which of the following is assessed first?
When conducting an abbreviated neurological examination, which of the following is assessed first?
Which sensory aspect is usually not tested in children younger than 6 years?
Which sensory aspect is usually not tested in children younger than 6 years?
What does head lag in an infant over 6 months suggest?
What does head lag in an infant over 6 months suggest?
Which of the following indicates hyperaesthesia in an infant?
Which of the following indicates hyperaesthesia in an infant?
In order to assess a patient's orientation, which of the following questions would be inappropriate?
In order to assess a patient's orientation, which of the following questions would be inappropriate?
What does the Landau reflex indicate in infants when absent?
What does the Landau reflex indicate in infants when absent?
Which of the following conditions is usually associated with a loss of the ankle jerk reflex in older adults?
Which of the following conditions is usually associated with a loss of the ankle jerk reflex in older adults?
What sign may indicate brain damage in an infant?
What sign may indicate brain damage in an infant?
What sensory changes can be expected in older adults regarding pain and light touch?
What sensory changes can be expected in older adults regarding pain and light touch?
The sucking reflex is strongest in which age range?
The sucking reflex is strongest in which age range?
How should you approach testing deep tendon reflexes in older adults who find it challenging to relax?
How should you approach testing deep tendon reflexes in older adults who find it challenging to relax?
During a sensory examination of a newborn, how should the infant typically respond to a strong stimulus?
During a sensory examination of a newborn, how should the infant typically respond to a strong stimulus?
What is the expected response when testing the Achilles reflex?
What is the expected response when testing the Achilles reflex?
Which position is appropriate for testing the clonus reflex?
Which position is appropriate for testing the clonus reflex?
A positive Babinski sign is indicated by which response?
A positive Babinski sign is indicated by which response?
Which reflex is not routinely tested in adults?
Which reflex is not routinely tested in adults?
What response indicates a problem in the pyramidal tract when assessing superficial reflexes?
What response indicates a problem in the pyramidal tract when assessing superficial reflexes?
The normal response to an abdominal reflex test should show what?
The normal response to an abdominal reflex test should show what?
What happens to superficial reflexes in cases of upper motor neuron lesions?
What happens to superficial reflexes in cases of upper motor neuron lesions?
How can you confirm the proper functioning of cranial nerves in an infant?
How can you confirm the proper functioning of cranial nerves in an infant?
Which developmental milestone is typically observed by 4 months of age?
Which developmental milestone is typically observed by 4 months of age?
How is muscle tone assessed in infants during a neurological examination?
How is muscle tone assessed in infants during a neurological examination?
What characterizes a normal response when testing for clonus?
What characterizes a normal response when testing for clonus?
What is a sign of CNS damage in infants regarding their cry?
What is a sign of CNS damage in infants regarding their cry?
At what age should you expect a baby to recognize their parent's face?
At what age should you expect a baby to recognize their parent's face?
What would indicate a delay in motor activity during an infant's exam?
What would indicate a delay in motor activity during an infant's exam?
Flashcards
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Central Nervous System (CNS)
The CNS is made up of the brain and spinal cord. It's the control center for your body.
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
The PNS includes all nerves outside the CNS. It connects the CNS to the rest of your body.
What are Sensory (Afferent) Messages?
What are Sensory (Afferent) Messages?
They carry information from your senses (sight, touch, etc.) to the CNS.
What are Motor (Efferent) Messages?
What are Motor (Efferent) Messages?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are Autonomic Messages?
What are Autonomic Messages?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cerebral Cortex
Cerebral Cortex
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Myelin?
What is Myelin?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the Brainstem?
What is the Brainstem?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Left Hemisphere Dominance
Left Hemisphere Dominance
Signup and view all the flashcards
Frontal Lobe
Frontal Lobe
Signup and view all the flashcards
Precentral gyrus
Precentral gyrus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Parietal Lobe
Parietal Lobe
Signup and view all the flashcards
Postcentral gyrus
Postcentral gyrus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Occipital Lobe
Occipital Lobe
Signup and view all the flashcards
Temporal Lobe
Temporal Lobe
Signup and view all the flashcards
Wernicke's Area
Wernicke's Area
Signup and view all the flashcards
Broca's Area
Broca's Area
Signup and view all the flashcards
Basal Ganglia
Basal Ganglia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thalamus
Thalamus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hypothalamus
Hypothalamus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cerebellum
Cerebellum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Brainstem
Brainstem
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sensory Cortex
Sensory Cortex
Signup and view all the flashcards
Posterior Columns
Posterior Columns
Signup and view all the flashcards
Proprioception
Proprioception
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stereognosis
Stereognosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Referred Pain
Referred Pain
Signup and view all the flashcards
Motor Cortex
Motor Cortex
Signup and view all the flashcards
Corticospinal Tract
Corticospinal Tract
Signup and view all the flashcards
Somatotopic Organization
Somatotopic Organization
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pyramidal Decussation
Pyramidal Decussation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Extrapyramidal Tracts
Extrapyramidal Tracts
Signup and view all the flashcards
Upper Motor Neuron
Upper Motor Neuron
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lower Motor Neuron
Lower Motor Neuron
Signup and view all the flashcards
Final Common Pathway
Final Common Pathway
Signup and view all the flashcards
Somatic Nervous System
Somatic Nervous System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Autonomic Nervous System
Autonomic Nervous System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cranial Nerves
Cranial Nerves
Signup and view all the flashcards
Olfactory Nerve
Olfactory Nerve
Signup and view all the flashcards
Optic Nerve
Optic Nerve
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oculomotor Nerve
Oculomotor Nerve
Signup and view all the flashcards
Trochlear Nerve
Trochlear Nerve
Signup and view all the flashcards
Trigeminal Nerve
Trigeminal Nerve
Signup and view all the flashcards
Abducens Nerve
Abducens Nerve
Signup and view all the flashcards
Facial Nerve
Facial Nerve
Signup and view all the flashcards
Acoustic Nerve (Vestibulocochlear Nerve)
Acoustic Nerve (Vestibulocochlear Nerve)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glossopharyngeal Nerve
Glossopharyngeal Nerve
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vagus Nerve
Vagus Nerve
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spinal Accessory Nerve
Spinal Accessory Nerve
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hypoglossal Nerve
Hypoglossal Nerve
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spinal Nerves
Spinal Nerves
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sensory Afferent Fibers
Sensory Afferent Fibers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Motor Efferent Fibers
Motor Efferent Fibers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Reflex Arc
Reflex Arc
Signup and view all the flashcards
Deep Tendon Reflexes (Myotatic)
Deep Tendon Reflexes (Myotatic)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Superficial Reflexes
Superficial Reflexes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Visceral (Organic) Reflexes
Visceral (Organic) Reflexes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pathological Reflexes
Pathological Reflexes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dermatome
Dermatome
Signup and view all the flashcards
TIA
TIA
Signup and view all the flashcards
Why is seeking medical attention important after a TIA?
Why is seeking medical attention important after a TIA?
Signup and view all the flashcards
FACE mnemonic for stroke
FACE mnemonic for stroke
Signup and view all the flashcards
Modifiable risk factors for stroke
Modifiable risk factors for stroke
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nonmodifiable risk factors for stroke
Nonmodifiable risk factors for stroke
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stroke prevention for high-risk individuals
Stroke prevention for high-risk individuals
Signup and view all the flashcards
Subjective data for stroke assessment
Subjective data for stroke assessment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Health History: Headache
Health History: Headache
Signup and view all the flashcards
Health History: Head injury
Health History: Head injury
Signup and view all the flashcards
Health History: Dizziness or Vertigo
Health History: Dizziness or Vertigo
Signup and view all the flashcards
Health History: Seizures
Health History: Seizures
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pre-eclampsia and stroke risk
Pre-eclampsia and stroke risk
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oral contraceptives and stroke risk
Oral contraceptives and stroke risk
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ethnocultural background and stroke risk
Ethnocultural background and stroke risk
Signup and view all the flashcards
Genetic disorders and stroke risk
Genetic disorders and stroke risk
Signup and view all the flashcards
Postictal Phase
Postictal Phase
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tremor
Tremor
Signup and view all the flashcards
Paresis
Paresis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dysmetria
Dysmetria
Signup and view all the flashcards
Paraesthesia
Paraesthesia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dysphagia
Dysphagia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dysarthria
Dysarthria
Signup and view all the flashcards
Aphasia
Aphasia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Congenital Defect
Congenital Defect
Signup and view all the flashcards
Maternal Health
Maternal Health
Signup and view all the flashcards
Neonatal Period
Neonatal Period
Signup and view all the flashcards
Apgar Score
Apgar Score
Signup and view all the flashcards
Developmental Milestones
Developmental Milestones
Signup and view all the flashcards
Risk for Falls
Risk for Falls
Signup and view all the flashcards
Motor System Changes with Aging
Motor System Changes with Aging
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cerebral Blood Flow and Aging
Cerebral Blood Flow and Aging
Signup and view all the flashcards
Falls in Older Adults
Falls in Older Adults
Signup and view all the flashcards
Walking Changes in Older Adults
Walking Changes in Older Adults
Signup and view all the flashcards
Social Determinants of Health and Stroke
Social Determinants of Health and Stroke
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stroke Disparities by Income
Stroke Disparities by Income
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stroke Disparities in Indigenous Populations
Stroke Disparities in Indigenous Populations
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stroke Disparities in African Heritage Populations
Stroke Disparities in African Heritage Populations
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stroke: Leading Cause of Disability and Death
Stroke: Leading Cause of Disability and Death
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stroke Risk Factors
Stroke Risk Factors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Types of Stroke
Types of Stroke
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stroke Symptoms
Stroke Symptoms
Signup and view all the flashcards
Importance of Early Stroke Detection
Importance of Early Stroke Detection
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stroke Symptoms vs. Other Conditions
Stroke Symptoms vs. Other Conditions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Importance of Recognizing TIA (Mini-Stroke)
Importance of Recognizing TIA (Mini-Stroke)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dizziness Impact
Dizziness Impact
Signup and view all the flashcards
Home Safety Modifications
Home Safety Modifications
Signup and view all the flashcards
Micturition Syncope
Micturition Syncope
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cognitive Decline
Cognitive Decline
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sudden vs. Gradual Cognitive Changes
Sudden vs. Gradual Cognitive Changes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tremor Triggers
Tremor Triggers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tremor and Daily Life
Tremor and Daily Life
Signup and view all the flashcards
Senile Tremor
Senile Tremor
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sudden Vision Changes
Sudden Vision Changes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vision Change and Weakness
Vision Change and Weakness
Signup and view all the flashcards
Critical Findings
Critical Findings
Signup and view all the flashcards
Neurological Examination
Neurological Examination
Signup and view all the flashcards
Range of Motion (ROM)
Range of Motion (ROM)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Flaccidity
Flaccidity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spasticity
Spasticity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Rigidity
Rigidity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Involuntary Movement
Involuntary Movement
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tandem Walking
Tandem Walking
Signup and view all the flashcards
Romberg Test
Romberg Test
Signup and view all the flashcards
Positive Romberg Sign
Positive Romberg Sign
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dysdiadochokinesia
Dysdiadochokinesia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Finger-to-Nose Test
Finger-to-Nose Test
Signup and view all the flashcards
Heel-to-Shin Test
Heel-to-Shin Test
Signup and view all the flashcards
Levels of Consciousness
Levels of Consciousness
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stimulus Response
Stimulus Response
Signup and view all the flashcards
Motor Function
Motor Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cranial Nerve VII
Cranial Nerve VII
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nasolabial Folds
Nasolabial Folds
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cranial Nerve V: Trigeminal Nerve
Cranial Nerve V: Trigeminal Nerve
Signup and view all the flashcards
Trigeminal Nerve - Motor Function
Trigeminal Nerve - Motor Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Trigeminal Nerve - Sensory Function
Trigeminal Nerve - Sensory Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Corneal Reflex
Corneal Reflex
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cranial Nerve VII: Facial Nerve
Cranial Nerve VII: Facial Nerve
Signup and view all the flashcards
Facial Nerve - Motor Function
Facial Nerve - Motor Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Facial Nerve - Sensory Function
Facial Nerve - Sensory Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cranial Nerve VIII: Acoustic (Vestibulocochlear) Nerve
Cranial Nerve VIII: Acoustic (Vestibulocochlear) Nerve
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cranial Nerves IX and X: Glossopharyngeal and Vagus Nerves
Cranial Nerves IX and X: Glossopharyngeal and Vagus Nerves
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glossopharyngeal and Vagus Nerves - Motor Function
Glossopharyngeal and Vagus Nerves - Motor Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glossopharyngeal and Vagus Nerves - Sensory Function
Glossopharyngeal and Vagus Nerves - Sensory Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cranial Nerve XI: Spinal Accessory Nerve
Cranial Nerve XI: Spinal Accessory Nerve
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spinal Accessory Nerve - Function
Spinal Accessory Nerve - Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cranial Nerve XII: Hypoglossal Nerve
Cranial Nerve XII: Hypoglossal Nerve
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hypoglossal Nerve - Function
Hypoglossal Nerve - Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Newborn Flexion
Newborn Flexion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Breech Delivery Position
Breech Delivery Position
Signup and view all the flashcards
Frog Position
Frog Position
Signup and view all the flashcards
Opisthotonos
Opisthotonos
Signup and view all the flashcards
Extension of Limbs
Extension of Limbs
Signup and view all the flashcards
Asymmetry of Limbs
Asymmetry of Limbs
Signup and view all the flashcards
Head Control
Head Control
Signup and view all the flashcards
Landau Reflex
Landau Reflex
Signup and view all the flashcards
Muscle Strength Assessment
Muscle Strength Assessment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hypoaesthesia
Hypoaesthesia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Rooting Reflex
Rooting Reflex
Signup and view all the flashcards
Palmar Grasp
Palmar Grasp
Signup and view all the flashcards
Plantar Grasp
Plantar Grasp
Signup and view all the flashcards
Graphaesthesia
Graphaesthesia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Two-Point Discrimination
Two-Point Discrimination
Signup and view all the flashcards
Extinction
Extinction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Point Location
Point Location
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stretch (Deep Tendon) Reflexes
Stretch (Deep Tendon) Reflexes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Reflex Grading Scale
Reflex Grading Scale
Signup and view all the flashcards
Clonus
Clonus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hyperreflexia
Hyperreflexia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hyporeflexia
Hyporeflexia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Reinforcement Technique
Reinforcement Technique
Signup and view all the flashcards
Biceps Reflex
Biceps Reflex
Signup and view all the flashcards
Triceps Reflex
Triceps Reflex
Signup and view all the flashcards
Brachioradialis Reflex
Brachioradialis Reflex
Signup and view all the flashcards
Quadriceps (Patellar) Reflex
Quadriceps (Patellar) Reflex
Signup and view all the flashcards
Babinski Reflex
Babinski Reflex
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tonic Neck Reflex
Tonic Neck Reflex
Signup and view all the flashcards
Moro Reflex
Moro Reflex
Signup and view all the flashcards
Placing Reflex
Placing Reflex
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stepping Reflex
Stepping Reflex
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gower's Sign
Gower's Sign
Signup and view all the flashcards
Wide-Based Gait
Wide-Based Gait
Signup and view all the flashcards
Knock-Kneed Walk
Knock-Kneed Walk
Signup and view all the flashcards
Balance on One Foot
Balance on One Foot
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hopping
Hopping
Signup and view all the flashcards
Staggering and Falling
Staggering and Falling
Signup and view all the flashcards
Weakness Climbing Stairs
Weakness Climbing Stairs
Signup and view all the flashcards
Broad-Based Gait
Broad-Based Gait
Signup and view all the flashcards
Scissor Gait
Scissor Gait
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sensory Testing: When is it necessary?
Sensory Testing: When is it necessary?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sensory Testing: What to test?
Sensory Testing: What to test?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sensory Testing: Compare what?
Sensory Testing: Compare what?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sensory Testing: Mapping out the deficit
Sensory Testing: Mapping out the deficit
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sensory Testing: Glove-and-Stocking Distribution
Sensory Testing: Glove-and-Stocking Distribution
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sensory Testing: Avoiding Leading Questions
Sensory Testing: Avoiding Leading Questions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sensory Testing: Closed Eyes
Sensory Testing: Closed Eyes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spinothalamic Tract: What does it test?
Spinothalamic Tract: What does it test?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spinothalamic Tract: Testing Pain Sensation
Spinothalamic Tract: Testing Pain Sensation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spinothalamic Tract: Terms for Abnormal Pain
Spinothalamic Tract: Terms for Abnormal Pain
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spinothalamic Tract: Temperature Testing
Spinothalamic Tract: Temperature Testing
Signup and view all the flashcards
Posterior Column Tract: Testing Vibration
Posterior Column Tract: Testing Vibration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Posterior Column Tract: Interpreting Vibration Loss
Posterior Column Tract: Interpreting Vibration Loss
Signup and view all the flashcards
Posterior Column Tract: Testing Position Sense (Kinaesthesia)
Posterior Column Tract: Testing Position Sense (Kinaesthesia)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tactile Discrimination: Stereognosis
Tactile Discrimination: Stereognosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tactile Discrimination: Graphaesthesia
Tactile Discrimination: Graphaesthesia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Light Touch Test
Light Touch Test
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vibrational Sense
Vibrational Sense
Signup and view all the flashcards
Position Sense
Position Sense
Signup and view all the flashcards
Deep Tendon Reflexes (DTRs)
Deep Tendon Reflexes (DTRs)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hyperactive DTRs
Hyperactive DTRs
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hypoactive DTRs
Hypoactive DTRs
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dyskinesias
Dyskinesias
Signup and view all the flashcards
Orientation Assessment
Orientation Assessment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Neurological Re-check
Neurological Re-check
Signup and view all the flashcards
Achilles Reflex
Achilles Reflex
Signup and view all the flashcards
Abdominal Reflexes
Abdominal Reflexes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cremasteric Reflex
Cremasteric Reflex
Signup and view all the flashcards
Babinski Sign
Babinski Sign
Signup and view all the flashcards
Primitive Reflexes in Infants
Primitive Reflexes in Infants
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nipissing District Developmental Screen (NDDS)
Nipissing District Developmental Screen (NDDS)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Muscle Tone in Infants
Muscle Tone in Infants
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lethargy, Hyporeactivity, Hyperirritability in Infants
Lethargy, Hyporeactivity, Hyperirritability in Infants
Signup and view all the flashcards
Developmental Delays in Infants
Developmental Delays in Infants
Signup and view all the flashcards
Persistence of Reflex Behavior Beyond Normal Time
Persistence of Reflex Behavior Beyond Normal Time
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cry Assessment in Infants
Cry Assessment in Infants
Signup and view all the flashcards
Smoothness and Symmetry of Movement in Infants
Smoothness and Symmetry of Movement in Infants
Signup and view all the flashcards
Delayed Motor Activity in Infants
Delayed Motor Activity in Infants
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Nervous System Structure and Function
- Nervous System Division: The nervous system is divided into the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS).
- CNS Components: The CNS includes the brain and spinal cord.
- PNS Components: The PNS includes cranial nerves (12 pairs), spinal nerves (31 pairs), and their branches.
- PNS Functions: The PNS transmits sensory (afferent) messages to the CNS, motor (efferent) messages from the CNS to muscles and glands, and autonomic messages regulating internal organs and blood vessels.
- Meninges: Protective membranes (dura, arachnoid, pia mater) surrounding the CNS. Cerebrospinal fluid also protects CNS.
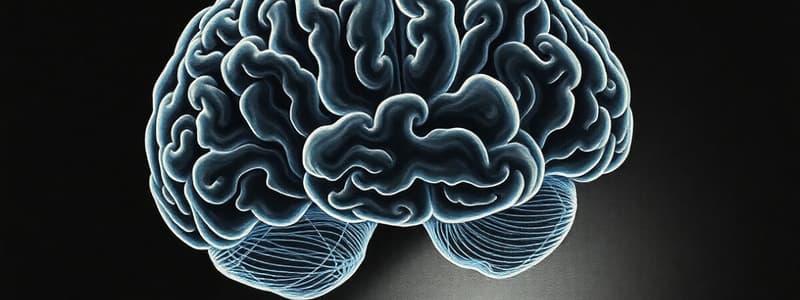
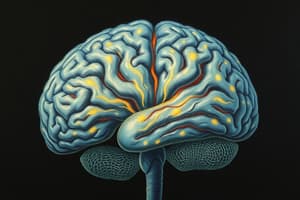
Cerebral Cortex
- Structure: The outermost layer of the cerebrum, composed of nerve cell bodies without myelin ("grey matter"). Myelin increases nerve impulse speed.
- Function (General): Centre for higher functions: thought, memory, reasoning, sensation, and voluntary movement.
- Hemispheric Dominance: Left hemisphere dominates in most right-handers and many left-handers.
- Lobes and Functions:
- Frontal Lobe: Personality, behavior, emotions, intellectual functions.
- Precentral Gyrus: Initiates voluntary movement.
- Parietal Lobe: Primary sensory centre (postcentral gyrus).
- Occipital Lobe: Primary visual receptor centre.
- Temporal Lobe: Primary auditory reception, taste, smell, Wernicke's area (language comprehension). Damage causes receptive aphasia (hearing without meaning). Broca's area (motor speech) in frontal lobe; damage causes expressive aphasia (understanding with garbled speech).
- Damage Effects: Loss of function (motor weakness, paralysis, sensory loss, language impairment) due to blood supply interruption (occluded artery, bleeding, vasospasm).
Basal Ganglia
- Location: Deep within the cerebral hemispheres.
- Function: Subcortical associated motor system. Controls automatic associated movements (e.g., arm swing during walking).
Thalamus
- Function: Main relay station for sensory pathways from spinal cord and brainstem to cerebrum.
Hypothalamus
- Function: Major control center for vital functions like temperature, heart rate, blood pressure, sleep, pituitary gland regulation, autonomic nervous system and emotional response.
Cerebellum
- Location: Under the occipital lobe.
- Function: Coordinates voluntary movements, maintains equilibrium, and muscle tone; does not initiate movement but refines and smoothes it.
Brainstem
- Structure: Central core of the brain, primarily nerve fibers.
- Midbrain: Anterior, basic tubular structure, merges into thalamus and hypothalamus, contains many motor neurons and tracts.
- Pons: Enlarged area with ascending and descending fiber tracts.
- Medulla: Continuation of spinal cord, contains ascending and descending fiber tracts connecting brain and spinal cord, controls vital autonomic centers (respiratory, cardiac, gastrointestinal functions), and nuclei for cranial nerves VIII–XII (Pyramidal decussation).
Spinal Cord
- Structure: Long cylindrical structure of nervous tissue, occupying upper two-thirds of vertebral canal from medulla to lumbar vertebrae L1/L2.
- Function: Main pathway for ascending and descending fiber tracts connecting brain and spinal nerves; mediates reflexes. Grey matter in butterfly shape with anterior and posterior "horns," containing nerve cell bodies.
Pathways of the CNS
- Crossed Representation: Left cerebral cortex interacts with right body, and vice versa.
Sensory Pathways
- Sensory Receptors: Extensive network in skin, mucous membranes, muscles, tendons, and viscera. Monitor conscious sensations, internal organ functions, body positions, and reflexes.
- Spinothalamic Tract: Transmits pain, temperature, and crude/light touch sensations.
- Posterior (Dorsal) Columns: Conduct sensations of position, vibration, and finely localized touch. (Proprioception, vibration, stereognosis)
Motor Pathways
- Corticospinal (Pyramidal) Tract: Initiates voluntary movements, especially skilled, discrete movements. Originates in motor cortex.
- Extrapyramidal Tracts: Older motor system outside pyramidal tract (muscle tone maintenance, gross automatic movements, such as walking).
- Cerebellar System: Coordinates movement, maintains equilibrium and posture by receiving position and motor messages; subconscious level.
Upper and Lower Motor Neurons
- Upper Motor Neurons: Located entirely within the CNS; influence lower motor neurons; examples include corticospinal, corticobulbar, and extrapyramidal tracts: cerebral vascular accidents, cerebral palsy, multiple sclerosis.
- Lower Motor Neurons: Located mostly in the PNS, cell body in spinal cord, nerve fiber extends to muscle, the final common pathway
Peripheral Nervous System
- Nerves: Bundles of fibers outside the CNS. Carry input (sensory) and output (motor).
- Reflex Arc: Basic defense mechanisms; involuntary reactions for painful stimuli—deep tendon, superficial, visceral, pathological.
- Components: Sensory nerve (afferent), synapse in spinal cord, motor nerve (efferent), neuromuscular junction, competent muscle.
- Cranial Nerves: 12 pairs, mostly supply head and neck.
- Spinal Nerves: 31 pairs, mixed nerves (sensory and motor fibers). Originate from the length of the spinal cord. Innervate body (each nerve segments body part-dermatome).
- Somatic & Autonomic Fibers: Somatic: skeletal muscles; Autonomic: smooth muscles, glands, heart; mediates unconscious activity (maintaining homeostasis).
Developmental Considerations
- Infants: Neurological systems are not fully developed at birth, motor, and sensory systems are rudimentary. Development proceeds in a cephalocaudal (head to tail) and proximal-to-distal (center to extremities) order. Primitive reflexes present at birth normally fade with development.
- Older Adults: Aging causes atrophy, neuron loss, decrease in brain weight and volume, thinning cortex, reduced subcortical structures, and ventricular enlargement. Slowed nerve conduction, decreased sensation (touch, pain, taste, smell). Motor system showing slowing, decrease in muscle bulk and strength. Stroke risk increased.
Social Determinants of Health Considerations
- Socioeconomic status: Stroke more prevalent in socioeconomically disadvantaged populations, impacting short/long-term outcomes.
- Cultural/Ethnic background: Indigenous people, people of African or South Asian descent, demonstrate higher stroke death rates due to underlying factors like higher hypertension and diabetes.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.