Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the basic unit of life?
What is the basic unit of life?
Cell
Robert Hooke discovered cells in 1665.
Robert Hooke discovered cells in 1665.
True (A)
Who is known as the 'Father of Microscopy'?
Who is known as the 'Father of Microscopy'?
- Rudolf Virchow
- Robert Hooke
- Robert Brown
- Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek (correct)
What term did Robert Hooke coin when describing cells?
What term did Robert Hooke coin when describing cells?
Cells are often called the building blocks of _____
Cells are often called the building blocks of _____
Red blood cells contain a nucleus.
Red blood cells contain a nucleus.
What substance in red blood cells carries oxygen?
What substance in red blood cells carries oxygen?
Which scientist is associated with the statement 'Omnis cellula e cellula'?
Which scientist is associated with the statement 'Omnis cellula e cellula'?
What is the study of cells called?
What is the study of cells called?
The scientist who discovered 'animalcules' was _____
The scientist who discovered 'animalcules' was _____
Match the following scientists with their contributions:
Match the following scientists with their contributions:
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Cell Theory and Discovery
- Cell Definition: The basic structural and functional unit of life, derived from the Latin word "cella" meaning "small room."
- Biotic vs. Abiotic: Biotic refers to living entities, while abiotic encompasses non-living factors such as sunlight and air.
- Cytology: Branch of science focused on the study of cells.
Historical Scientists in Cell Biology
- Robert Hooke:
- English scientist who discovered cells in 1665 by observing cork under a crude microscope.
- Coined the term "cellula" due to the room-like structures he observed.
- Antonie van Leeuwenhoek:
- Dutch naturalist known as the Father of Microscopy.
- Discovered "animalcules" (bacteria) in pond water, significantly contributing to microbiology.
- Robert Brown:
- Scottish botanist who described the nucleus in detail in 1831.
- Extended cell theory to animals by identifying the nucleus as a key cell component.
- Rudolf Virchow:
- German physician who articulated the idea that "Omnis cellula e cellula," meaning all cells come from pre-existing cells.
- Known as the father of modern pathology.
Cell Types and Functions
- Red Blood Cells:
- Oval biconcave discs that lack a nucleus; most abundant cells in the body.
- Contain hemoglobin, a protein that transports oxygen.
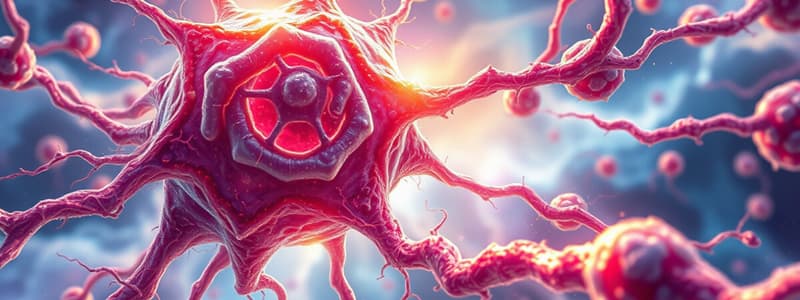
- Nerve Cells:
- Fundamental units of the nervous system with a star-like shape.
- Feature dendrites (short projections) and axons (long single branches) for transmitting information.
Common Characteristics of Cells
- Cell Membrane Composition: Essential for maintaining the integrity of the cell.
- Metabolic Activities: All cells perform various metabolic activities vital for sustaining life.
Important Concepts
- Classic Cell Theory: Asserts that cells are the building blocks of all living organisms, arising from pre-existing cells.
- Protoplasm: Term introduced by Felix Dujardin, referring to the living part of the cell.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.