Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the main characteristic of the hydrocarbon chains in the cell membrane's structure?
What is the main characteristic of the hydrocarbon chains in the cell membrane's structure?
- They can be charged and hydrophilic.
- They are nonpolar and hydrophobic. (correct)
- They are polar and hydrophilic.
- They are exclusively found on the membrane's outer layer.
What role does cholesterol play in the cell membrane?
What role does cholesterol play in the cell membrane?
- It forms integral proteins within the membrane.
- It acts as a charged head group.
- It contributes to the asymmetry of oligosaccharide chains.
- It provides structural stability and fluidity. (correct)
Which statement accurately describes integral proteins in the plasma membrane?
Which statement accurately describes integral proteins in the plasma membrane?
- They span the membrane and may protrude from both sides. (correct)
- They exclusively function on the outer membrane surface.
- They are loosely associated with the membrane surfaces.
- They are only found in the cytoplasm.
How do integrins function within the cell membrane?
How do integrins function within the cell membrane?
What defines the trilaminar appearance of cellular membranes?
What defines the trilaminar appearance of cellular membranes?
What is the primary function of organelle-specific membrane proteins?
What is the primary function of organelle-specific membrane proteins?
What does the fluid mosaic model describe?
What does the fluid mosaic model describe?
How do peripheral proteins differ from integral proteins?
How do peripheral proteins differ from integral proteins?
What is the primary role of the glycocalyx in cells?
What is the primary role of the glycocalyx in cells?
Which process is best described as 'cell eating'?
Which process is best described as 'cell eating'?
What distinguishes receptor-mediated endocytosis from other types of endocytosis?
What distinguishes receptor-mediated endocytosis from other types of endocytosis?
Which of the following mechanisms is NOT a way molecules can cross the cell membrane?
Which of the following mechanisms is NOT a way molecules can cross the cell membrane?
What is a characteristic feature of all cell membranes?
What is a characteristic feature of all cell membranes?
What is the function of the phagosome in phagocytosis?
What is the function of the phagosome in phagocytosis?
Which transport mechanism is characterized by the bulk uptake of materials?
Which transport mechanism is characterized by the bulk uptake of materials?
How does pinocytosis differ from phagocytosis?
How does pinocytosis differ from phagocytosis?
What is the primary role of cholesterol in cell membranes?
What is the primary role of cholesterol in cell membranes?
What is the appearance of sex chromatin in female cells?
What is the appearance of sex chromatin in female cells?
How does the X chromosome in male cells differ from that in female cells?
How does the X chromosome in male cells differ from that in female cells?
How does cholesterol affect the permeability of cell membranes?
How does cholesterol affect the permeability of cell membranes?
In what way does cholesterol respond to cold temperatures?
In what way does cholesterol respond to cold temperatures?
Where is the nucleolus primarily located?
Where is the nucleolus primarily located?
What is synthesized in the nucleolus?
What is synthesized in the nucleolus?
What structural feature of cholesterol contributes to its function in membranes?
What structural feature of cholesterol contributes to its function in membranes?
Why is cholesterol essential for certain membrane proteins?
Why is cholesterol essential for certain membrane proteins?
What are the components of nucleoplasm?
What are the components of nucleoplasm?
Which of the following describes cholesterol's distribution in the cell membrane?
Which of the following describes cholesterol's distribution in the cell membrane?
Which phase of the cell cycle involves the synthesis of macromolecules for DNA duplication?
Which phase of the cell cycle involves the synthesis of macromolecules for DNA duplication?
What occurs during the S phase of the cell cycle?
What occurs during the S phase of the cell cycle?
What effect would the lack of cholesterol have on cell membranes?
What effect would the lack of cholesterol have on cell membranes?
Cholesterol molecules interact with which portion of the cell membrane?
Cholesterol molecules interact with which portion of the cell membrane?
What is the functional significance of the association between heterochromatin and the nucleolus?
What is the functional significance of the association between heterochromatin and the nucleolus?
What is the primary function of the nuclear pores?
What is the primary function of the nuclear pores?
Which of the following describes the structure of chromatin?
Which of the following describes the structure of chromatin?
What is the size limit for ions and molecules to pass freely through the nuclear pore?
What is the size limit for ions and molecules to pass freely through the nuclear pore?
What is the term used to describe a gradual reduction in drug responsiveness due to repeated administration?
What is the term used to describe a gradual reduction in drug responsiveness due to repeated administration?
What structure is the nucleus primarily made up of?
What structure is the nucleus primarily made up of?
How are larger molecules transported through the nuclear pore?
How are larger molecules transported through the nuclear pore?
Which term describes an acute, rapidly developed tolerance occurring after quick succession of doses?
Which term describes an acute, rapidly developed tolerance occurring after quick succession of doses?
What type of RNA is synthesized and processed within the nucleus?
What type of RNA is synthesized and processed within the nucleus?
What does the term 'hypersensitivity reaction' refer to?
What does the term 'hypersensitivity reaction' refer to?
Which part of the nucleus is primarily involved in assembling ribosomal RNA?
Which part of the nucleus is primarily involved in assembling ribosomal RNA?
What signifies the complete loss of effectiveness to antibiotics or anticancer agents?
What signifies the complete loss of effectiveness to antibiotics or anticancer agents?
What connects the nuclear envelope to the endoplasmic reticulum?
What connects the nuclear envelope to the endoplasmic reticulum?
Which term is used for the exaggerated response to a drug that can lead to symptoms like syncope?
Which term is used for the exaggerated response to a drug that can lead to symptoms like syncope?
What condition arises when withdrawal symptoms appear after the cessation of drug administration?
What condition arises when withdrawal symptoms appear after the cessation of drug administration?
What is the result of a genetic defect leading to abnormal drug reactions?
What is the result of a genetic defect leading to abnormal drug reactions?
What indicates a loss of therapeutic efficacy without complete drug ineffectiveness?
What indicates a loss of therapeutic efficacy without complete drug ineffectiveness?
Flashcards
Cell Membrane Structure
Cell Membrane Structure
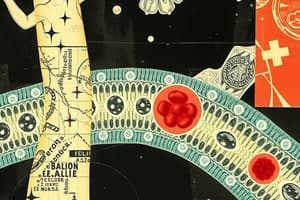
The cell membrane is a bilayer of phospholipids with hydrophobic tails facing inward and hydrophilic heads facing outward.
Phospholipid Bilayer
Phospholipid Bilayer
Two layers of phospholipids forming the basic structure of the cell membrane.
Hydrophobic Tails
Hydrophobic Tails
The nonpolar, water-fearing parts of the phospholipid, which face the interior of the membrane.
Hydrophilic Heads
Hydrophilic Heads
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fluid Mosaic Model
Fluid Mosaic Model
Signup and view all the flashcards
Integral Proteins
Integral Proteins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Peripheral Proteins
Peripheral Proteins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Transmembrane Proteins
Transmembrane Proteins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cholesterol
Cholesterol
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glycocalyx
Glycocalyx
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cell Recognition
Cell Recognition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Passive Transport
Passive Transport
Signup and view all the flashcards
Facilitated Diffusion
Facilitated Diffusion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Active Transport
Active Transport
Signup and view all the flashcards
Endocytosis
Endocytosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Exocytosis
Exocytosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Phagocytosis
Phagocytosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pinocytosis
Pinocytosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis
Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cholesterol in Membranes
Cholesterol in Membranes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Amphipathic Molecule
Amphipathic Molecule
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cholesterol's Effect on Fluidity
Cholesterol's Effect on Fluidity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cholesterol and Protein Placement
Cholesterol and Protein Placement
Signup and view all the flashcards
High Cholesterol and Glycosphingolipids
High Cholesterol and Glycosphingolipids
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cell Membrane Fluidity
Cell Membrane Fluidity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Membrane Permeability
Membrane Permeability
Signup and view all the flashcards
Therapeutic Window
Therapeutic Window
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tolerance
Tolerance
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tachyphylaxis
Tachyphylaxis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Refractoriness
Refractoriness
Signup and view all the flashcards
Resistance
Resistance
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hyper-susceptibility
Hyper-susceptibility
Signup and view all the flashcards
Idiosyncrasy
Idiosyncrasy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hypersensitivity Reaction
Hypersensitivity Reaction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dependence
Dependence
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cell Cycle
Cell Cycle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chromatin
Chromatin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nuclear Envelope Components
Nuclear Envelope Components
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nuclear Pores
Nuclear Pores
Signup and view all the flashcards
Small Molecules Movement
Small Molecules Movement
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chromatin Composition
Chromatin Composition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nucleosome
Nucleosome
Signup and view all the flashcards
Protein Synthesis Location (Nucleus)
Protein Synthesis Location (Nucleus)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Protein Import into Nucleus
Protein Import into Nucleus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nucleus Shape
Nucleus Shape
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nucleus Staining
Nucleus Staining
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nuclear Envelope and Endoplasmic Reticulum
Nuclear Envelope and Endoplasmic Reticulum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sex Chromatin
Sex Chromatin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nucleolus
Nucleolus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nucleoplasm
Nucleoplasm
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cell Cycle
Cell Cycle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Interphase
Interphase
Signup and view all the flashcards
G1 Phase
G1 Phase
Signup and view all the flashcards
S Phase
S Phase
Signup and view all the flashcards
G2 Phase
G2 Phase
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sex Chromatin Appearance
Sex Chromatin Appearance
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Cell Membrane & Vesicular Transport
- Cell membranes are composed of phospholipids, cholesterol, proteins, and oligosaccharides
- Phospholipids are amphipathic, with a hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tails
- Glycerophospholipids (phosphoglycerides) have glycerol backbones
- Sphingophospholipids have sphingosine backbones
- Cholesterol controls membrane fluidity
- Proteins in membranes include integral (spanning the bilayer), peripheral (loosely associated), and those specific to organelles
- Carbohydrates are attached to lipids (glycolipids) or proteins (glycoproteins) on the outer surface, creating a glycocalyx
- Membrane function includes transport and communication with the environment
- Transport methods include passive (diffusion), active (pumps, cotransport), and bulk transport (endocytosis, exocytosis)
- Endocytosis includes phagocytosis (cell eating), pinocytosis (cell drinking), and receptor-mediated endocytosis (specific uptake of molecules via receptors)
Endocytosis
- Mechanisms of endocytosis include:
- Phagocytosis: engulfment of large particles
- Pinocytosis: engulfment of fluid
- Receptor-mediated endocytosis: selective uptake via receptors
Lipid Structure & Functions in Biomembranes
- Phospholipids are the primary lipids in cell membranes
- There are two main types of phospholipids, phosphoglycerides and sphingophospholipids
- Steroid lipid cholesterol is important for membrane fluidity and structural stability
- Cholesterol helps control membrane fluidity
- Cholesterol helps secure important proteins in the membrane
Nucleus and phases of cell cycle
- The nucleus contains the cell's genetic material (DNA) and the machinery for making RNA and proteins.
- Chromatin is composed of DNA and proteins (specifically histones). Two types of chromatin exist: condensed heterochromatin and less condensed euchromatin.
- Nucleolus is a region within the nucleus that produces ribosomes.
- The nuclear envelope is a double membrane that surrounds the nucleus, containing nuclear pores that allow molecules to pass in and out.
- Cell cycle phases include:
- Interphase (G1, S, G2): growth, DNA replication, and preparation for mitosis
- Mitosis: division of the nucleus (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase)
- Cytokinesis: division of the cytoplasm
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.