Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which structure is primarily responsible for allowing the passage of ions and non-polar molecules through the cell membrane?
Which structure is primarily responsible for allowing the passage of ions and non-polar molecules through the cell membrane?
- Receptor Proteins
- Cell Recognition Proteins
- Transport Proteins (correct)
- Enzymatic Proteins
What role do receptor proteins play in cellular communication?
What role do receptor proteins play in cellular communication?
- Assisting in cell-to-cell adhesion
- Facilitating signal exchange by changing shape (correct)
- Forming tunnels for material export
- Providing structural support to the cell
Which type of proteins primarily aid in the recognition of cells and enable them to distinguish self from non-self?
Which type of proteins primarily aid in the recognition of cells and enable them to distinguish self from non-self?
- Transport Proteins
- Junction Proteins
- Cell Recognition Proteins (correct)
- Channel Proteins
What is the main role of cholesterol in the cell membrane?
What is the main role of cholesterol in the cell membrane?
How do junction proteins contribute to cellular function?
How do junction proteins contribute to cellular function?
Which of the following is NOT a function of enzymatic proteins?
Which of the following is NOT a function of enzymatic proteins?
Which structure is composed mainly of polysaccharide cellulose and is found only in plant cells?
Which structure is composed mainly of polysaccharide cellulose and is found only in plant cells?
What is the primary composition of cytosol within the cytoplasm?
What is the primary composition of cytosol within the cytoplasm?
Which type of organelles are ribosomes classified as?
Which type of organelles are ribosomes classified as?
What characteristic feature distinguishes the cell walls of fungi from those of plants?
What characteristic feature distinguishes the cell walls of fungi from those of plants?
Study Notes
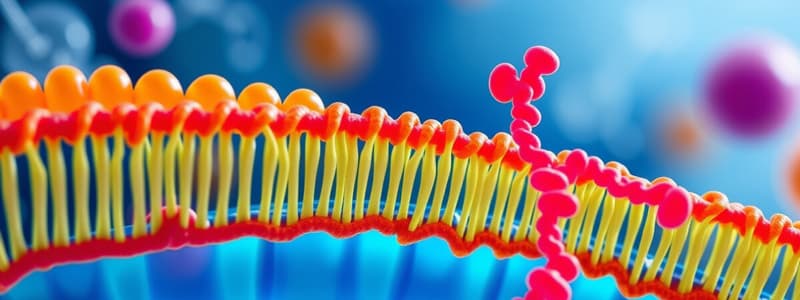
Structures Embedded In Cell Membrane
- Plant cells and prokaryotic bacteria possess unique structures, with plants and algae primarily utilizing polysaccharide cellulose, while fungi utilize chitin.
- Cellulose is rigid and impedes the free passage of molecules; hence, plants and algae have openings that facilitate diffusion.
Transport Proteins
- Transport proteins form channels allowing ions and non-polar molecules to traverse the cell membrane freely.
Channel Proteins
- These proteins create tunnels for the import and export of materials and waste products within the cell.
Cell Recognition Proteins
- Essential for identifying self from non-self, enabling cells to recognize their own type versus foreign entities.
Junction Proteins
- Facilitate adhesion and communication between adjacent cells, enhancing tissue integrity and function.
Receptor Proteins
- Change shape to bind specific molecules (ligands), enabling the exchange of signals between cells.
Enzymatic Proteins
- Involved in metabolic processes, including degradation and synthesis necessary for cell survival and function.
Chains
- Act as identification markers for cell recognition proteins, playing a role in cellular communication.
Cholesterol
- Enhances membrane strength and flexibility while reducing fluidity, making the membrane less permeable to water-soluble substances.
Cytoplasm
- A jellylike substance within the cell membrane, consisting of organelles (excluding the nucleus) and cytosol.
- Cytosol serves as the liquid component, primarily composed of water.
- Organelles are specialized structures that enhance efficiency and allow complex metabolic reactions in localized areas.
Membranous Organelles
- Include the Golgi body, lysosomes, smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum, vesicles, vacuoles, nucleus, mitochondria, and plastids.
Non-membranous Organelles
- Comprise ribosomes and centrioles, which lack surrounding membranes.
Cell Wall
- Provides an additional protective boundary outside the cell membrane, contributing to structural support and overall protection.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Description
Explore the various structures embedded in cell membranes, including transport, channel, and receptor proteins. Understand how these proteins facilitate communication, transport, and cellular recognition. This quiz will test your knowledge on the essential components that support cellular integrity and function.