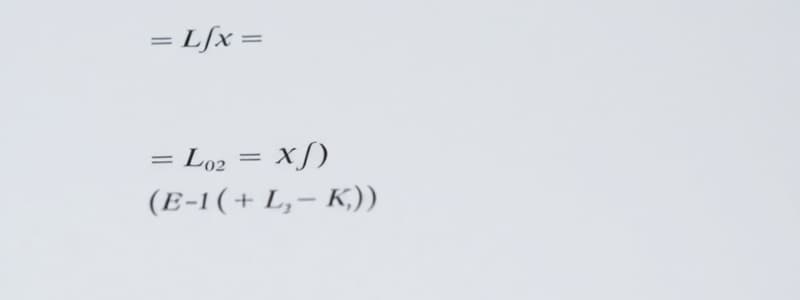Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the value of the integral $\int_0^3 (5 - x) \ dx$?
What is the value of the integral $\int_0^3 (5 - x) \ dx$?
- 9
- 6
- 7.5 (correct)
- 10.5
What is the instantaneous velocity of the ball at $t = 1$ from the height equation $s(t) = -16t^2 + 50t + 36$?
What is the instantaneous velocity of the ball at $t = 1$ from the height equation $s(t) = -16t^2 + 50t + 36$?
- 50 ft/s
- 18 ft/s (correct)
- 14 ft/s
- 34 ft/s
What is the limit of the function as $x$ approaches $b$ indicated in the integral $\lim_{x \to b} \int_3^x (x^4 + 5) \ dx$?
What is the limit of the function as $x$ approaches $b$ indicated in the integral $\lim_{x \to b} \int_3^x (x^4 + 5) \ dx$?
- Undefined
- 50 (correct)
- 7/5
- 25
How is the area enclosed by the curve $y = x^2 + 3x + 2$ and the x-axis determined?
How is the area enclosed by the curve $y = x^2 + 3x + 2$ and the x-axis determined?
What is the average value of $y = x^2$ over the interval $[-1, 5]$?
What is the average value of $y = x^2$ over the interval $[-1, 5]$?
Which of the following represents the left-endpoint Riemann sum for the function $f(x)$ over $[0, 5]$ with 5 subintervals?
Which of the following represents the left-endpoint Riemann sum for the function $f(x)$ over $[0, 5]$ with 5 subintervals?
In the integral $\int \sin \theta \cos \theta \ d\theta$, what substitution might simplify the integration process?
In the integral $\int \sin \theta \cos \theta \ d\theta$, what substitution might simplify the integration process?
What is the result of the integral $\int (1 + \sin x) \ dx$?
What is the result of the integral $\int (1 + \sin x) \ dx$?
What is the limit of the expression as $x$ approaches 2 in the function $
rac{x + 3}{x - 1}$?
What is the limit of the expression as $x$ approaches 2 in the function $ rac{x + 3}{x - 1}$?
What is the result of the limit $\lim_{x \to 1} \frac{x - 1}{x - 1}$?
What is the result of the limit $\lim_{x \to 1} \frac{x - 1}{x - 1}$?
At what point does the function $f(x)$ become discontinuous at $a$ if $f(a)$ is not defined?
At what point does the function $f(x)$ become discontinuous at $a$ if $f(a)$ is not defined?
How do you determine the instantaneous velocity of a function $y = x^2 - 3x + 2$?
How do you determine the instantaneous velocity of a function $y = x^2 - 3x + 2$?
What is the area under the curve for $y = 3x^5 - 4x^2$ between $x = 1$ and $x = 2$?
What is the area under the curve for $y = 3x^5 - 4x^2$ between $x = 1$ and $x = 2$?
Which of the following expressions represents a Riemann sum for the function $y = 2x - 3 + \frac{1}{x}$ on the interval [1, 3]?
Which of the following expressions represents a Riemann sum for the function $y = 2x - 3 + \frac{1}{x}$ on the interval [1, 3]?
For the limit $\lim_{\theta \to 0} \frac{\sin(2\theta)}{\theta}$, what is the expected value?
For the limit $\lim_{\theta \to 0} \frac{\sin(2\theta)}{\theta}$, what is the expected value?
What is the integral of the function $f(x) = 2x - \frac{3}{x}$ over the interval [1, 2]?
What is the integral of the function $f(x) = 2x - \frac{3}{x}$ over the interval [1, 2]?
What are the dimensions of the open box made from an 8 ″ by 15 ″ piece of cardboard that yields maximum volume?
What are the dimensions of the open box made from an 8 ″ by 15 ″ piece of cardboard that yields maximum volume?
For the function f(x) = 2x^3 - 15x^2 + 36x + 10, in which intervals is the function increasing?
For the function f(x) = 2x^3 - 15x^2 + 36x + 10, in which intervals is the function increasing?
Which of the following is true about the inflection points of the function f(x) = x^2 e^x?
Which of the following is true about the inflection points of the function f(x) = x^2 e^x?
What is the maximum velocity attained by a ball projected vertically if the expression for its height is given by s(t) = -16t^2 + 50t + 36?
What is the maximum velocity attained by a ball projected vertically if the expression for its height is given by s(t) = -16t^2 + 50t + 36?
Which expression represents a Riemann sum for the function y = 3x over the interval [1, 3] using 4 subintervals?
Which expression represents a Riemann sum for the function y = 3x over the interval [1, 3] using 4 subintervals?
Flashcards
Limit of a function as x approaches b from the right
Limit of a function as x approaches b from the right
The value that the function f(x) approaches as x gets closer and closer to b, but only from x values greater than b.
Definite Integral
Definite Integral
The definite integral of a function from a to b represents the area under the curve of the function over the interval from a to b.
Instantaneous Velocity
Instantaneous Velocity
The rate at which an object's position is changing with respect to time at a specific moment.
Maximum Height
Maximum Height
Signup and view all the flashcards
Area enclosed by a curve and axis
Area enclosed by a curve and axis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Average Value of a function
Average Value of a function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Riemann Sum
Riemann Sum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tangent Line
Tangent Line
Signup and view all the flashcards
Limit of a function at a point
Limit of a function at a point
Signup and view all the flashcards
Limit at infinity
Limit at infinity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Continuity at a point
Continuity at a point
Signup and view all the flashcards
Derivative
Derivative
Signup and view all the flashcards
Product Rule
Product Rule
Signup and view all the flashcards
Trigonometric Limits
Trigonometric Limits
Signup and view all the flashcards
Indeterminate form
Indeterminate form
Signup and view all the flashcards
Integration
Integration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tangent line equation
Tangent line equation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Local Maxima
Local Maxima
Signup and view all the flashcards
Local Minima
Local Minima
Signup and view all the flashcards
Inflection Point
Inflection Point
Signup and view all the flashcards
Maximize Volume
Maximize Volume
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Limits
- Evaluate limits from #1 to #6
- Limit problems involve finding the value a function approaches as the input approaches a certain value.
- Specific limit problems are given to practice calculation.
Derivatives
- Find dy/dx for #12 to #20
- These problems involve finding the instantaneous rate of change of a function.
- Various functions are included, from polynomials to trigonometric and logarithmic functions.
Applications of Derivatives
- Problems #10 and #11 investigate continuity and the first and second derivatives at a specific point.
- Continuity involves examining if the function is defined at that input value and if the limit of the function as the input approaches that value is equal to the value at that input value.
- Sign analysis of the first and second derivatives gives information about the function's behavior.
Integrals
- Evaluate integrals from #21 to #30
- Integrals are used for finding areas under curves and accumulating quantities over an interval.
- These types of problems are given to practice finding the area between a curve and the x-axis or between two curves.
Applications of Integrals
- Evaluate definite integrals #26 to #30
- Application problems involve finding areas, volumes, and related rates of change.
Modeling with Calculus
- Problems #31 to #41 explore various calculus applications, including finding equations of tangents, local maxima and minima, and applying optimization concepts.
- Specific problems involving problems involving finding the equation of a line tangent to a curve at a specific point.
- Optimization problems finding maximum or minimum values.
- Related rates finding the rate of change of one quantity in terms of the rate of change of another quantity.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.