Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following is the MOST accurate definition of 'organising' in a business management context?
Which of the following is the MOST accurate definition of 'organising' in a business management context?
- Controlling and monitoring performance against set standards.
- Co-ordinating activities to achieve objectives. (correct)
- The process of setting objectives and creating strategies to achieve them.
- Motivating employees to perform at their best.
In what order should classifying activities, assigning authority, and gathering information occur?
In what order should classifying activities, assigning authority, and gathering information occur?
- Classifying activities, gathering information, assigning authority.
- Assigning authority, classifying activities, gathering information.
- Gathering information, assigning authority, classifying activities.
- Gathering information, classifying activities, assigning authority. (correct)
What is the primary purpose of the 'chain of command' principle in organising?
What is the primary purpose of the 'chain of command' principle in organising?
- To promote employee autonomy and independent work practices.
- To encourage informal communication and collaboration across departments.
- To establish a clear line of authority from top management to every employee. (correct)
- To ensure all employees have equal authority and decision-making power.
Why is the 'unity of command' principle important in the process of organising?
Why is the 'unity of command' principle important in the process of organising?
Which of the following factors does NOT typically influence a manager's span of control?
Which of the following factors does NOT typically influence a manager's span of control?
How does ethical consideration MOST appropriately relate to authority in a business?
How does ethical consideration MOST appropriately relate to authority in a business?
What differentiates 'line authority' from 'staff authority' in an organizational structure?
What differentiates 'line authority' from 'staff authority' in an organizational structure?
In which scenario would 'compulsory advice' from a staff specialist be MOST appropriate?
In which scenario would 'compulsory advice' from a staff specialist be MOST appropriate?
What BEST describes 'project authority' within an organisation?
What BEST describes 'project authority' within an organisation?
What is the fundamental difference between responsibility and accountability?
What is the fundamental difference between responsibility and accountability?
Why do managers delegate authority to subordinates?
Why do managers delegate authority to subordinates?
What BEST describes the core difference between centralization and decentralization?
What BEST describes the core difference between centralization and decentralization?
What BEST explains the primary reason for specialization in an organization?
What BEST explains the primary reason for specialization in an organization?
In which of the following scenarios would divisionalisation based on geographic location be MOST appropriate?
In which of the following scenarios would divisionalisation based on geographic location be MOST appropriate?
A company that organizes its structure around distinct projects is implementing what type of divisional structure?
A company that organizes its structure around distinct projects is implementing what type of divisional structure?
What advantage does a divisional structure based on consumer or client needs offer an organization?
What advantage does a divisional structure based on consumer or client needs offer an organization?
What is the primary function of an organizational structure?
What is the primary function of an organizational structure?
In a line organizational structure, how does authority flow?
In a line organizational structure, how does authority flow?
How does a line-and-staff organizational structure enhance the basic line structure?
How does a line-and-staff organizational structure enhance the basic line structure?
What is a defining characteristic of a matrix organizational structure?
What is a defining characteristic of a matrix organizational structure?
What is the primary advantage of a cross-functional team?
What is the primary advantage of a cross-functional team?
What is a key feature of a network organizational structure?
What is a key feature of a network organizational structure?
Why is adapting to change crucial for businesses in today's environment?
Why is adapting to change crucial for businesses in today's environment?
What role does knowledge management play in a changing organization?
What role does knowledge management play in a changing organization?
In order to effectively adjust to market needs, what action should a business MOST likely take?
In order to effectively adjust to market needs, what action should a business MOST likely take?
What is the relationship between a business's environment, strategy, and structure?
What is the relationship between a business's environment, strategy, and structure?
Why is effective integration and coordination essential for the swift expansion of organizational structures?
Why is effective integration and coordination essential for the swift expansion of organizational structures?
Why is it important for management to pay attention to feedback and ideas from their employees?
Why is it important for management to pay attention to feedback and ideas from their employees?
What can be achieved by businesses that organise based on geographic regions?
What can be achieved by businesses that organise based on geographic regions?
Flashcards
Organizing
Organizing
Co-ordinating activities so that objectives can be achieved.
Co-ordination
Co-ordination
Refers to the integration of the business parts to achieve the desired outcome.
Chain of command
Chain of command
The line of authority that flows from the top of the business down to any employee.
Unity of command
Unity of command
Signup and view all the flashcards
Span of control
Span of control
Signup and view all the flashcards
Authority
Authority
Signup and view all the flashcards
Line authority
Line authority
Signup and view all the flashcards
Staff authority
Staff authority
Signup and view all the flashcards
Advisory authority
Advisory authority
Signup and view all the flashcards
Compulsory advice
Compulsory advice
Signup and view all the flashcards
Co-operative authority
Co-operative authority
Signup and view all the flashcards
Line-and-staff authority
Line-and-staff authority
Signup and view all the flashcards
Functional authority
Functional authority
Signup and view all the flashcards
Project authority
Project authority
Signup and view all the flashcards
Responsibility
Responsibility
Signup and view all the flashcards
Accountability
Accountability
Signup and view all the flashcards
Delegation
Delegation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Centralization and decentralization
Centralization and decentralization
Signup and view all the flashcards
Centralisation
Centralisation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Decentralisation
Decentralisation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Specialisation
Specialisation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Divisionalisation
Divisionalisation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Line organisational structure
Line organisational structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Line-and-staff organisational structure
Line-and-staff organisational structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Divisional organisational structure
Divisional organisational structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Matrix organisational structure
Matrix organisational structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cross-functional team
Cross-functional team
Signup and view all the flashcards
Permanent team
Permanent team
Signup and view all the flashcards
Network organisational structure
Network organisational structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Introduction
- Once planning is complete, plans must be put into action which involves organizing
- Organizing means coordinating activities so that objectives can be achieved
- Organizing as a management task is concerned with classifying/ allocating activities to divisions
- It also creates posts within those divisions and determines employees duties, responsibilities, and authority
- Organization is interdependent within the management process and must go hand in hand with planning, leading, motivating, and controlling
- It should consider the business environment which determines the business strategy
- This strategy determines structure; how a business is organized must change with the environment
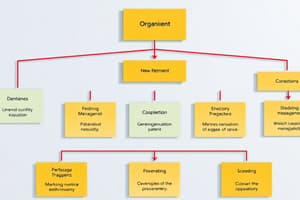
Steps in the organizing process
- Gathering information
- Identifying and analyzing activities
- Classifying activities
- Allocating staff
- Assigning authority and responsibility
- Facilitating work
Principles of organizing
- Principles include co-ordination, chain of command, unity of command, span of control
Co-ordination
- Integration of business parts to achieve desired outcome
- Three elements:
- Clear objectives
- Well defined policies/procedures
- Effective communication
Chain of command
- Line of authority that flows from the top of the business down to any employee
- Clarifies the order of reporting, avoids confusion, makes decision-making and communication better
Unity of command
- States that each employee should answer to, and take instructions from only their immediate superior
Span of control
- Refers to the number of direct subordinates reporting to any manager
- A manager's span of control is influenced by:
- The manager's/ subordinates' training, qualifications and competence
- The physical distances between employees
- The degree of non-supervisory tasks in a manager's job description
- The interaction required with the subordinates
- The similarity of subordinates' tasks
- The level of standardization of subordinates' tasks
- The frequency of new problems
- The strictness of control required
Authority
- Authority is the right to make decisions, issue orders, and utilize resources
- The types of authority a business uses will depend on structure
- Even when management possesses authority, their point of view may not always be what is best for the business ethically
- Management needs to be conscious of paying attention to their employee's feedback/ideas, so decisions are appropriate based on a complete picture of the daily activities
Types of Authority
- Include line authority, staff authority (advisory, compulsory, and co-operative authority), line-and-staff authority, functional authority, and project authority
Line authority
- Direct authority a manager has over an employee that is under their line of command
Staff authority
- Largely advisory usually on middle management level
- Three types of staff authority:
- Advisory authority - Specialist knowledge is used, but the inputs of the specialist are not enforceable and only advice
- Compulsory advice - A manager is compelled to listen to the specialist, but isn't compelled to carry out recommendations
- Co-operative authority - Specialist has equal authority regarding a certain matter, and consensus between them/the manager must be reached before decisions are made
Line-and-staff authority
- Line managers and staff managers form a collaborative partnership
- Line departments will not be successful without the support of staff departments as they can be seen as internal
Functional authority
- The right that staff specialists have to give orders to line employees in an established area
Project authority
- Horizontal (sideways) authority of a project manager that can extend over many different departments
Responsibility
- The duty to do certain work
- Upon accepting a job, the employee takes responsibility for their actions
- The nature, scope (range), and details of job responsibilities should always be clear to the employee whether they are at a managerial level or not
Accountability
- Any means of ensuring that the employee who is supposed to perform an activity in fact performs it
Delegation
- The process by which managers allocate to subordinates the responsibility and authority to execute and make decisions for accomplishing objectives in certain situations
Centralization vs decentralization
- Centralization and decentralization of authority are management philosophies of delegation
- Centralization is the degree to which the decision-making power is concentrated at a single point in the organization
- Decentralization is the degree to which lower-level management provides input regarding the decision-making process or actually makes the decisions
Specialization
- Refers to the division of work to improve how goals are achieved
- Few employees have the skills, knowledge and expertise to perform every task, so they're appointed to work in divisions where special skills/ interests /knowledge can be applied
Divisionalization
- Means creating self-managing units within a business, and each division has its own:
- General manager
- Operations manager
- Financial manager
- Human resources manager
- Marketing manager
Value Chain
- A functional structure can be organized around a business's value chain.
- Value chain - A series of activities from sourcing raw materials to delivering a product
Types of divisional structure
- Divisional structure can be based on products or geographic location
- Also on projects or consumer/client needs
Organizational structures
- Help the business to achieve goals by providing a framework for managers to divide responsibilities, allocate authority, coordinate activities, control performance, and hold employees accountable
- The environment influences the structural design of organizations
- Include the line, line-and-staff, functional, and divisional organizational structure, matrix, team, and network organizational structure
Line organizational structure
- Is a simple hierarchy where the lines of authority run vertically from the top to the bottom of the business
Line-and-staff organizational structure
- Has vertical lines of authority for its basic functions, but staff specialists are added to perform more complicated functions
Functional organizational structure
- Structure of line organization reflects basic functions of a business
Divisional organizational structure
- Aims to support self-contained divisions
Matrix organizational structure
- Uses both vertical and horizontal lines of authority
- The vertical functional line of authority provides control within functional departments
- The horizontal divisional line provides coordination across these functional departments
- Unity of command isn't always possible
Team organizational structure
- Cross-functional team - selected group of employees from different functional departments who meet as a team to solve shared problems
- Permanent team - group of employees from several functions with a permanent job of solving general problems
Network organizational structure
- Has its functions operated by separate businesses which are run by a small headquarters
- Instead of business functions under one roof, these services are provided by other businesses under contract
- These businesses are connected electronically (computers, internet, email) to the central office
The changing organization
- Today's businesses function in an 'economy of ideas' where change is introduced quickly
- Uncertainty occurs when the external environment is rapidly changing/complex
- An uncertain environment causes increased differences among divisions/departments, and an increased need for coordination between divisions
- It also causes a need for the business to adapt to change
Management for a changing organization
- In a changing organization, important energy comes from good, new ideas.
- Knowledge management - Using the intellect of the people who work for the business finding, unlocking, and sharing their expertise, skills, wisdom and relationships
- Communication among different divisions departments or other sub-units of the business must be of a high level
- Management changes have become a function critical to management
- For a business to adjust to market needs it may be needed to change organizational structure
- Businesses should realize they need to have an organizational structure that can respond quickly to the needs of the market
- Structure determines business strategy, so structure needs to change with the environment
Summary
- Today's organizations revolve around resources with people as the most important
- The process is all actions converting efforts into customer's value of productivity
- Organizing involves using certain principles for identifying and arranging a business's activities and resources
- This is done by structuring the business at horizontal and vertical levels by allocating duties, responsibilities and authority to workforce members/divisions
- An effective business structure contributed to achieving business objectives/encouraging cooperation
- A person can understand expansion of organizational structures by recognizing the organization's need to design systems which will enable workforce integration/ coordination
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.