Podcast
Questions and Answers
What type of organization provides goods and services without a profit motive?
What type of organization provides goods and services without a profit motive?
- Goods-producing business
- Service business
- For-profit organization
- Not-for-profit organization (correct)
Goods-producing businesses are primarily labor-intensive.
Goods-producing businesses are primarily labor-intensive.
False (B)
What is a 'barrier to entry' in a market?
What is a 'barrier to entry' in a market?
Any resource or capability a company must have before it can start competing in a given market.
Service businesses create value by performing activities that deliver some _________ to customers.
Service businesses create value by performing activities that deliver some _________ to customers.
Match the type of business with its primary characteristic:
Match the type of business with its primary characteristic:
Which of these types of businesses is more likely to be labor-intensive?
Which of these types of businesses is more likely to be labor-intensive?
The business mindset only focuses on profit generation.
The business mindset only focuses on profit generation.
What do we refer to when we consider the many decisions and problems a business must face before offering its products?
What do we refer to when we consider the many decisions and problems a business must face before offering its products?
What is one example of a disruptive technology?
What is one example of a disruptive technology?
The legal and regulatory environment has no effect on business operations.
The legal and regulatory environment has no effect on business operations.
What is the primary purpose of the research and development (R&D) functional area in a business?
What is the primary purpose of the research and development (R&D) functional area in a business?
The ________ environment consists of the conditions that affect the cost and availability of goods, services, and labor.
The ________ environment consists of the conditions that affect the cost and availability of goods, services, and labor.
Match the following environments of business with their descriptions:
Match the following environments of business with their descriptions:
Which of the following best defines 'competitive advantage'?
Which of the following best defines 'competitive advantage'?
All businesses are non-profit organizations.
All businesses are non-profit organizations.
List three steps to transition from a consumer to a business professional.
List three steps to transition from a consumer to a business professional.
A ________ is a concise description of how a business intends to generate revenue.
A ________ is a concise description of how a business intends to generate revenue.
Match the following types of businesses with their definitions:
Match the following types of businesses with their definitions:
Which of the following is NOT one of the major environments in which businesses operate?
Which of the following is NOT one of the major environments in which businesses operate?
Profit is defined as the total revenue generated by a business.
Profit is defined as the total revenue generated by a business.
What is the primary purpose of adding value in a business?
What is the primary purpose of adding value in a business?
The five major environments in which every business operates are economic, legal, ________, technological, and global.
The five major environments in which every business operates are economic, legal, ________, technological, and global.
What are the seven components of professionalism in business?
What are the seven components of professionalism in business?
What does adding value in a business primarily involve?
What does adding value in a business primarily involve?
A negative personality in the workplace can have a positive impact on the office atmosphere.
A negative personality in the workplace can have a positive impact on the office atmosphere.
The expected norms of behavior in any particular situation are referred to as ______.
The expected norms of behavior in any particular situation are referred to as ______.
Match the following business environments with their descriptions:
Match the following business environments with their descriptions:
Which of the following is NOT one of the major functional areas in a business enterprise?
Which of the following is NOT one of the major functional areas in a business enterprise?
Successful people often display a pessimistic outlook.
Successful people often display a pessimistic outlook.
What are seven components of professionalism?
What are seven components of professionalism?
The five major environments in which businesses operate include economic, legal, ______, social, and competitive.
The five major environments in which businesses operate include economic, legal, ______, social, and competitive.
What is a common risk associated with starting a new business?
What is a common risk associated with starting a new business?
Which functional area is primarily responsible for developing products to meet market opportunities?
Which functional area is primarily responsible for developing products to meet market opportunities?
Human resources is responsible for managing a company's finances.
Human resources is responsible for managing a company's finances.
What is one key responsibility of the finance and accounting department in a business?
What is one key responsibility of the finance and accounting department in a business?
Being a _____ player means showing loyalty to your organization and protecting your employer's reputation.
Being a _____ player means showing loyalty to your organization and protecting your employer's reputation.
Match the following functional areas with their primary focus:
Match the following functional areas with their primary focus:
Which of the following states a component of professionalism?
Which of the following states a component of professionalism?
Active listening is encouraged when communicating effectively in a professional environment.
Active listening is encouraged when communicating effectively in a professional environment.
What is an important skill for professionals to demonstrate when working in teams?
What is an important skill for professionals to demonstrate when working in teams?
The primary goal of the business services functional area is to help companies with specific needs in areas such as _____ and banking.
The primary goal of the business services functional area is to help companies with specific needs in areas such as _____ and banking.
Match the following terms with their definitions:
Match the following terms with their definitions:
Flashcards
Not-for-profit organizations
Not-for-profit organizations
Organizations that provide goods and services without aiming for profit.
Goods-producing businesses
Goods-producing businesses
Companies making tangible products.
Service businesses
Service businesses
Companies performing activities that benefit customers.
Capital-intensive businesses
Capital-intensive businesses
Signup and view all the flashcards
Labor-intensive businesses
Labor-intensive businesses
Signup and view all the flashcards
Barrier to entry
Barrier to entry
Signup and view all the flashcards
Business mindset
Business mindset
Signup and view all the flashcards
Positive and Negative Effects of Business
Positive and Negative Effects of Business
Signup and view all the flashcards
Business
Business
Signup and view all the flashcards
Adding Value
Adding Value
Signup and view all the flashcards
Revenue
Revenue
Signup and view all the flashcards
Business Model
Business Model
Signup and view all the flashcards
Profit
Profit
Signup and view all the flashcards
Competitive Advantage
Competitive Advantage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Consumer to Business Professional
Consumer to Business Professional
Signup and view all the flashcards
Major Business Environments
Major Business Environments
Signup and view all the flashcards
Functional Business Areas
Functional Business Areas
Signup and view all the flashcards
Business Professions
Business Professions
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are stakeholders?
What are stakeholders?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Disruptive Technology
Disruptive Technology
Signup and view all the flashcards
Economic Environment
Economic Environment
Signup and view all the flashcards
R&D
R&D
Signup and view all the flashcards
Operations
Operations
Signup and view all the flashcards
Etiquette
Etiquette
Signup and view all the flashcards
Positive Outlook
Positive Outlook
Signup and view all the flashcards
Business Value Addition
Business Value Addition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Consumer to Business Transition
Consumer to Business Transition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Business Environments
Business Environments
Signup and view all the flashcards
Business Functional Areas
Business Functional Areas
Signup and view all the flashcards
Professionalism
Professionalism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Optimism
Optimism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Adding value to a business
Adding value to a business
Signup and view all the flashcards
Marketing Function
Marketing Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Finance and Accounting
Finance and Accounting
Signup and view all the flashcards
Human Resources (HR)
Human Resources (HR)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Business Services
Business Services
Signup and view all the flashcards
Team Player
Team Player
Signup and view all the flashcards
Effective Communication
Effective Communication
Signup and view all the flashcards
Market Opportunities
Market Opportunities
Signup and view all the flashcards
Financial Reports
Financial Reports
Signup and view all the flashcards
Employee Development
Employee Development
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Chapter 1: Developing a Business Mindset
- This chapter prepares students for a whirlwind tour of the business world, starting with a brief overview of business operations and advice on transitioning from consumer to business professional.
- A business is any profit-seeking organization that delivers goods and services to meet customer needs.
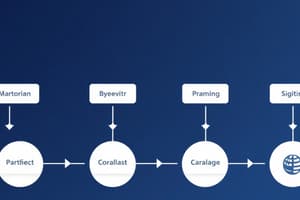
- Exhibit 1.1 demonstrates value addition in business: a farm turns raw materials into wheat, a mill converts wheat into flour, a bakery transforms flour into bread, and a grocery store makes the bread available to consumers.
Learning Objectives
- Explain the value added in businesses, and identify main types of businesses.
- List three steps to transition from consumer to business professional.
- Outline the five major environments in which businesses operate.
- Describe the six major functional areas in a business enterprise.
- Summarize seven critical business professions.
- Detail seven components of professionalism.
Understanding What Businesses Do
- A business is a profit-driven entity providing goods and services to meet customer demand.
Adding Value: The Business of Business
- Revenue: Funds generated by selling goods or services.
- Business model: A plan to generate revenue.
- Profit: The remainder after deducting business costs from revenue.
Competing to Attract and Satisfy Customers
- Competitive advantage: A product or company feature enhancing customer appeal.
Identifying Major Types of Businesses
- Not-for-profit organizations: Deliver goods and services without profit motives.
- Goods-producing businesses: Create value by producing tangible things.
- Service businesses: Create value through activities benefiting customers.
Risk and Reward
- Healthy relationship: Companies gain from positive outcomes and learn from negative ones.
- Moral hazard: When the rewards or repercussions of a decision belong to someone other than the decision-maker.
Risk and Reward (cont.)
- Goods-producing businesses are often capital-intensive.
- Service businesses tend to be labor-intensive.
Risk and Reward (cont.)
- Barrier to entry: Resource or capability needed before entering a market.
Seeing Business from the Inside Out
- Business mindset: Understanding the various decisions and challenges impacting businesses before product delivery.
The Business Mindset
- This exhibit showcases a comparison between the consumer and manager's perspectives on functions like product, marketing, image, price, availability, and service.
Positive and Negative Effects of Business
- Businesses contribute by offering goods/services, providing employment, and paying taxes, but can also create pollution, create health risks, and disrupt communities.
The Multiple Environments of Business
- Market environment: Target customers, buying influences, and competitors.
- Economic environment: Conditions and forces affecting goods, services, and labor.
- Technological environment: Forces resulting from practical applications of science to innovations, products, and processes.
- Legal and regulatory environment: Laws and regulations at various levels influencing businesses.
- Social environment: Population trends, social values, and societal relationships with businesses.
Recognizing the Multiple Environments of Business
- Social environment: Trends and forces in society.
- Stakeholders: Internal and external groups impacted by business decisions.
- Disruptive technologies: Those that fundamentally change an industry.
Recognizing the Multiple Environments of Business (cont.)
- Economic Environment: Conditions affecting cost/availability of goods/services/labor, influencing buyer/seller behaviour.
- Legal and Regulatory Environment: Laws and regulations from local to international levels.
- Market Environment: Target customers, influencing behaviours, and competitors.
Identifying the Major Functional Areas in a Business Enterprise
- Research and development (R&D): Designs new products.
- Information technology (IT): Supports communication within the company.
- Manufacturing, production, or operations: Creates goods or services for the company.
- Marketing: Identifies market opportunities and crafts branding/advertising/pricing strategies.
- Finance and accounting: Responsible for every aspect of a company's finances.
- Human resources (HR): Recruits and develops staff.
- Business services: Addresses specific company needs (e.g., banking, real estate, law).
Exploring Careers in Business
- List diverse job roles (e.g., Operations Management, HR Specialist, Information Technology Manager, Marketing Specialist, Sales Professional, Accountant, Financial Manager)
Achieving Professionalism
- Professionalism: Performing at a high level and exhibiting purpose and pride.
Major Functional Areas in a Business Enterprise
- A diagram displaying the interrelationship of major business functions: Finance, Production/Operations, R&D, Accounting, Marketing Strategy, Sales, Customer Support, Marketing Research, Product Planning, Human Resources, and Business Services.
Elements of Professionalism
- Be the best: Strive for excellence in all endeavors.
- Be dependable: Keep promises and commitments.
- Be ethical: Make ethically sound decisions.
- Be a team player: Contribute to the team's success.
- Be clear: Communicate effectively with others.
- Be respectful: Act respectfully towards all.
Being a Team Player
- Professionals are contributors to a wider cause.
- To be effective, team members support other team members.
- Professionals show loyalty and uphold a positive corporate image.
Communicating Effectively
- Active listening is crucial.
- Provide clear and practical information.
- Offer facts instead of opinions.
- Conciseness and efficiency are essential in communication.
- Clarify responsibilities and expectations.
- Make arguments that are compelling and persuasive.
Demonstrating Etiquette
- Etiquette includes accepted norms of behavior in various situations.
Maintaining a Confident, Positive Outlook
- Successful people are optimistic and persistent.
- Positive energy is infectious.
Applying What You've Learned
- Topics for review and application in businesses and their operations.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.