Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which statement accurately distinguishes between non-infectious and infectious hoof diseases in bovine digits?
Which statement accurately distinguishes between non-infectious and infectious hoof diseases in bovine digits?
- Non-infectious hoof diseases include conditions like sole ulcers and white line disease, while infectious diseases are caused by pathogens like _Fusobacterium necrophorum_. (correct)
- Non-infectious hoof diseases always result from systemic conditions, while infectious diseases are localized.
- Infectious hoof diseases are characterized by rapid onset and resolution, unlike the chronic nature of non-infectious conditions.
- Infectious hoof diseases are primarily caused by environmental factors, whereas non-infectious diseases are always genetic.
What is the primary anatomical reason deep digital sepsis can rapidly affect multiple structures in the bovine digit?
What is the primary anatomical reason deep digital sepsis can rapidly affect multiple structures in the bovine digit?
- Extensive interosseous ligaments allow for direct pathogen transfer.
- The absence of synovial membranes facilitates bacterial spread.
- A highly vascularized digital cushion promotes systemic dissemination of infection.
- Close anatomical proximity of joints, tendons, and bursae allows infection to spread easily. (correct)
What is the MOST critical factor to consider when diagnosing deep digital sepsis (DDS) in cattle?
What is the MOST critical factor to consider when diagnosing deep digital sepsis (DDS) in cattle?
- Elevated white blood cell count on a complete blood count (CBC).
- Response to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
- History of recent calving or other metabolic stress.
- The presence of a draining tract near the coronary band along with severe lameness unresponsive to antibiotics. (correct)
For a dairy cow presenting with lameness, which sequence of events is MOST likely to lead to septic arthritis of the distal interphalangeal joint (DIPJ)?
For a dairy cow presenting with lameness, which sequence of events is MOST likely to lead to septic arthritis of the distal interphalangeal joint (DIPJ)?
Why is surgical intervention generally favored over conservative treatment for deep digital sepsis (DDS)?
Why is surgical intervention generally favored over conservative treatment for deep digital sepsis (DDS)?
What is the MOST important consideration regarding tourniquet use during regional intravenous perfusion (RIVP) in cattle?
What is the MOST important consideration regarding tourniquet use during regional intravenous perfusion (RIVP) in cattle?
At what angle should you insert the needle, relative to the coronary band, when performing a joint lavage/arthrocentesis?
At what angle should you insert the needle, relative to the coronary band, when performing a joint lavage/arthrocentesis?
Which surgical approach for digit removal results in increased lateral stability due to the preservation of more tissue?
Which surgical approach for digit removal results in increased lateral stability due to the preservation of more tissue?
During a P1 amputation in a bovine digit, at what angle should the Gigli wire be seated to ensure proper bone resection?
During a P1 amputation in a bovine digit, at what angle should the Gigli wire be seated to ensure proper bone resection?
In a comparative study of digit amputation versus facilitated ankylosis, what factor is considered LESS important in the prognosis of facilitated ankylosis compared to digit amputation?
In a comparative study of digit amputation versus facilitated ankylosis, what factor is considered LESS important in the prognosis of facilitated ankylosis compared to digit amputation?
A Hereford bull presents with an interdigital fibroma. Which factor is MOST likely associated with the development of this condition in the hind limbs?
A Hereford bull presents with an interdigital fibroma. Which factor is MOST likely associated with the development of this condition in the hind limbs?
Which statement BEST describes regional intravenous perfusion (RIVP) with antibiotics?
Which statement BEST describes regional intravenous perfusion (RIVP) with antibiotics?
Which of the following systemic diseases is LEAST likely to manifest with lameness?
Which of the following systemic diseases is LEAST likely to manifest with lameness?
The medial and lateral pouches of the fetlock joint communicate what percentage of the time?
The medial and lateral pouches of the fetlock joint communicate what percentage of the time?
What structure does the common digital flexor tendon sheath communicate with?
What structure does the common digital flexor tendon sheath communicate with?
What is the MAIN advantage of P1 amputation of the bovine digit?
What is the MAIN advantage of P1 amputation of the bovine digit?
What is the most commonly utilized local anesthetic used in cattle for regional intravenous perfusion?
What is the most commonly utilized local anesthetic used in cattle for regional intravenous perfusion?
What approach is considered the MOST common for DIP (distal interphalangeal) ankylosis?
What approach is considered the MOST common for DIP (distal interphalangeal) ankylosis?
What post-operative step is MOST important to monitor following digit amputation?
What post-operative step is MOST important to monitor following digit amputation?
Which postoperative management step is MOST critical following surgical removal of an interdigital fibroma to minimize recurrence?
Which postoperative management step is MOST critical following surgical removal of an interdigital fibroma to minimize recurrence?
In the context of digital dermatitis, which component of the infectious process is targeted by administering systemic antibiotics?
In the context of digital dermatitis, which component of the infectious process is targeted by administering systemic antibiotics?
Which of the following is the MOST significant disadvantage of digit amputation?
Which of the following is the MOST significant disadvantage of digit amputation?
Which approach to surgical intervention is indicated when a bull intended for natural service develops a severe, non-responsive infection in the digit?
Which approach to surgical intervention is indicated when a bull intended for natural service develops a severe, non-responsive infection in the digit?
For which of the following indications would regional intravenous perfusion (RIVP) be LEAST appropriate?
For which of the following indications would regional intravenous perfusion (RIVP) be LEAST appropriate?
During facilitated ankylosis, following drainage and necessary debridement of surrounding structures, how should the joint be prepared for fusion?
During facilitated ankylosis, following drainage and necessary debridement of surrounding structures, how should the joint be prepared for fusion?
For a deep digital sepsis case that is determined to be in the early stages, the veterinarian elects to perform a tenosynoviotomy. What is the PRIMARY goal of this therapy?
For a deep digital sepsis case that is determined to be in the early stages, the veterinarian elects to perform a tenosynoviotomy. What is the PRIMARY goal of this therapy?
Which of the following statements is MOST accurate regarding the prognosis of digit amputation in cattle?
Which of the following statements is MOST accurate regarding the prognosis of digit amputation in cattle?
When performing regional limb perfusions, which of the following is a potential complication?
When performing regional limb perfusions, which of the following is a potential complication?
What type of incision is performed during a P1 amputation?
What type of incision is performed during a P1 amputation?
What is the MOST likely post-surgical outcome if a 1700 lb beef cow undergoes digit amputation due to chronic deep digital sepsis?
What is the MOST likely post-surgical outcome if a 1700 lb beef cow undergoes digit amputation due to chronic deep digital sepsis?
Which of the following statements accurately describes the relationship between the navicular bursa and the distal interphalangeal joint?
Which of the following statements accurately describes the relationship between the navicular bursa and the distal interphalangeal joint?
What factor dictates the correct volume of lidocaine for proximal and distal torniquet placements?
What factor dictates the correct volume of lidocaine for proximal and distal torniquet placements?
If, after performing a surgical procedure, a veterinarian has to re-bandage the area, how often should this be performed?
If, after performing a surgical procedure, a veterinarian has to re-bandage the area, how often should this be performed?
What is the MAIN etiological factor behind interdigital fibromas?
What is the MAIN etiological factor behind interdigital fibromas?
What is the etiologic agent of foot rot?
What is the etiologic agent of foot rot?
What type of approach should be performed when addressing tenosynovitis nonsurgically?
What type of approach should be performed when addressing tenosynovitis nonsurgically?
Of the procedures discussed, which of the following results in the longest duration of healing?
Of the procedures discussed, which of the following results in the longest duration of healing?
Which statement accurately reflects the anatomical relationships within the bovine distal limb?
Which statement accurately reflects the anatomical relationships within the bovine distal limb?
A dairy cow presents with severe lameness localized to the distal limb, characterized by diffuse swelling extending to the mid-metacarpal region and unresponsiveness to initial antibiotic therapy. Which diagnostic step would be MOST beneficial to differentiate deep digital sepsis (DDS) from other causes of lameness?
A dairy cow presents with severe lameness localized to the distal limb, characterized by diffuse swelling extending to the mid-metacarpal region and unresponsiveness to initial antibiotic therapy. Which diagnostic step would be MOST beneficial to differentiate deep digital sepsis (DDS) from other causes of lameness?
What is the MOST crucial reason to perform surgical intervention, such as digital amputation or facilitated ankylosis, in cases of deep digital sepsis, rather than relying solely on systemic antibiotics?
What is the MOST crucial reason to perform surgical intervention, such as digital amputation or facilitated ankylosis, in cases of deep digital sepsis, rather than relying solely on systemic antibiotics?
What systemic effect is MOST likely to be observed following regional intravenous perfusion (RIVP) with a high dose of local anesthetic, if the tourniquet is prematurely released?
What systemic effect is MOST likely to be observed following regional intravenous perfusion (RIVP) with a high dose of local anesthetic, if the tourniquet is prematurely released?
Which modification to the standard joint lavage/arthrocentesis technique is MOST important when treating a chronic septic joint with extensive fibrosis?
Which modification to the standard joint lavage/arthrocentesis technique is MOST important when treating a chronic septic joint with extensive fibrosis?
Which approach to digit removal is LEAST advisable if the goal is to preserve the animal's weight-bearing capacity and stability?
Which approach to digit removal is LEAST advisable if the goal is to preserve the animal's weight-bearing capacity and stability?
What step during P1 amputation of the bovine digit is MOST crucial for minimizing post-operative complications associated with bone infection and promoting effective wound healing?
What step during P1 amputation of the bovine digit is MOST crucial for minimizing post-operative complications associated with bone infection and promoting effective wound healing?
When comparing digit amputation and facilitated ankylosis for treating deep digital sepsis (DDS) in cattle, which factor is MOST likely to influence the choice of facilitated ankylosis.
When comparing digit amputation and facilitated ankylosis for treating deep digital sepsis (DDS) in cattle, which factor is MOST likely to influence the choice of facilitated ankylosis.
Which aspect of interdigital fibroma etiology is MOST important to consider when implementing preventative measures in a closed herd of mixed-breed beef cattle where the condition has become increasingly prevalent?
Which aspect of interdigital fibroma etiology is MOST important to consider when implementing preventative measures in a closed herd of mixed-breed beef cattle where the condition has become increasingly prevalent?
What is the intended outcome of utilizing a high concentration of antibiotics during regional intravenous perfusion (RIVP)?
What is the intended outcome of utilizing a high concentration of antibiotics during regional intravenous perfusion (RIVP)?
A veterinary clinic is located in an area where Bluetongue virus is endemic. Which statement BEST reflects the risk this disease presents to surgical interventions of the bovine digit?
A veterinary clinic is located in an area where Bluetongue virus is endemic. Which statement BEST reflects the risk this disease presents to surgical interventions of the bovine digit?
Why is the medial and lateral pouch not connecting in the fetlock joint significant when addressing septic arthritis?
Why is the medial and lateral pouch not connecting in the fetlock joint significant when addressing septic arthritis?
What structure of the bovine digit is of MOST concern when performing needle lavage within the common digital flexor tendon sheath?
What structure of the bovine digit is of MOST concern when performing needle lavage within the common digital flexor tendon sheath?
What is the MOST important advantage of P1 amputation?
What is the MOST important advantage of P1 amputation?
What is the volume of lidocaine MOST appropriate to infuse, for a distal torniquet?
What is the volume of lidocaine MOST appropriate to infuse, for a distal torniquet?
Which of the following is the MOST common approach utilized for DIP (distal interphalangeal) ankylosis?
Which of the following is the MOST common approach utilized for DIP (distal interphalangeal) ankylosis?
If a veterinarian performs a digit amputation, how often should they tell the owners to re-bandage?
If a veterinarian performs a digit amputation, how often should they tell the owners to re-bandage?
When addressing digital dermatitis, what is the reason for NOT using systemic antibiotics?
When addressing digital dermatitis, what is the reason for NOT using systemic antibiotics?
What is one of the MOST significant disadvantages of digit amputation?
What is one of the MOST significant disadvantages of digit amputation?
When is a tenosynoviotomy indicated to address tenosynovitis?
When is a tenosynoviotomy indicated to address tenosynovitis?
Of the procedures discussed, which results in the longest duration of healing?
Of the procedures discussed, which results in the longest duration of healing?
If a bull has a planned breeding soundness exam in one month, which procedure would be MOST appropriate for an interdigital fibroma?
If a bull has a planned breeding soundness exam in one month, which procedure would be MOST appropriate for an interdigital fibroma?
A farmer in your area calls you to say that his herd seems to be experiencing a large amount of hoof related issues. The primary complaint is the spreading of claws. Which of the following is MOST likely to be the issue?
A farmer in your area calls you to say that his herd seems to be experiencing a large amount of hoof related issues. The primary complaint is the spreading of claws. Which of the following is MOST likely to be the issue?
Which of the following correctly puts in order the steps of a digit amputation?
Which of the following correctly puts in order the steps of a digit amputation?
Comparing digit amputation versus facilitated ankylosis, which statement is MOST accurate?
Comparing digit amputation versus facilitated ankylosis, which statement is MOST accurate?
Flashcards
Primary weight bearing digits in cattle?
Primary weight bearing digits in cattle?
Primary weight bearing digits are 3 and 4 in both front and hind limbs.
Navicular bursa communication?
Navicular bursa communication?
It does not communicate with the distal interphalangeal joint
Fetlock pouches communication?
Fetlock pouches communication?
Medial and lateral pouches of fetlock communicate 98% of the time.
Common digital flexor tendon sheath communication?
Common digital flexor tendon sheath communication?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sole ulcer definition?
Sole ulcer definition?
Signup and view all the flashcards
White line disease?
White line disease?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Corkscrew claw definition?
Corkscrew claw definition?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Interdigital fibroma definition?
Interdigital fibroma definition?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Interdigital necrobacillosis definition?
Interdigital necrobacillosis definition?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Digital dermatitis definition?
Digital dermatitis definition?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Deep digital sepsis (DDS) definition?
Deep digital sepsis (DDS) definition?
Signup and view all the flashcards
DDS indicator around coronary band?
DDS indicator around coronary band?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Structures affected in DDS?
Structures affected in DDS?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Presumptive diagnosis for DDS?
Presumptive diagnosis for DDS?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Definitive diagnosis for DDS?
Definitive diagnosis for DDS?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Septic DIPJ causes in dairy cattle?
Septic DIPJ causes in dairy cattle?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Septic DIPJ causes in beef cattle?
Septic DIPJ causes in beef cattle?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Surgical intervention for bovine digit?
Surgical intervention for bovine digit?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Regional intravenous perfusion?
Regional intravenous perfusion?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Regional intravenous perfusion indication?
Regional intravenous perfusion indication?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Complications associated with RIVP?
Complications associated with RIVP?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Joint lavage/arthrocentesis indication?
Joint lavage/arthrocentesis indication?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Joint lavage/arthrocentesis consideration?
Joint lavage/arthrocentesis consideration?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Claw preserving procedures of the digit?
Claw preserving procedures of the digit?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Claw removing procedures of the digit?
Claw removing procedures of the digit?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Approaches involving digit removal?
Approaches involving digit removal?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Digit amputation Advantages?
Digit amputation Advantages?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Digit amputation disadvantages?
Digit amputation disadvantages?
Signup and view all the flashcards
P1 amputation advantages?
P1 amputation advantages?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Exarticulation advantages?
Exarticulation advantages?
Signup and view all the flashcards
P1 amputation pre-op steps?
P1 amputation pre-op steps?
Signup and view all the flashcards
P1 amputation intra-op steps?
P1 amputation intra-op steps?
Signup and view all the flashcards
P1 amputation post-op steps?
P1 amputation post-op steps?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Likelihood of good recovery after amputation?
Likelihood of good recovery after amputation?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Facilitate ankylosis steps?
Facilitate ankylosis steps?
Signup and view all the flashcards
DIP ankylosis approach?
DIP ankylosis approach?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tenosynovitis Non-Surgical treatment plan?
Tenosynovitis Non-Surgical treatment plan?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tenosynovitis surgical treatment plan?
Tenosynovitis surgical treatment plan?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Digit amputation statistics?
Digit amputation statistics?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Facilitated ankylosis statistics?
Facilitated ankylosis statistics?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Interdigital fibroma Etiology?
Interdigital fibroma Etiology?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Interdigital fibroma diagnoses?
Interdigital fibroma diagnoses?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Interdigital fibroma treatment?
Interdigital fibroma treatment?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
- This lecture outlines lameness evaluations in bovine digits, diseases, and surgical procedures.
Normal Bovine Distal Limb Anatomy
- The main weight-bearing digits in the front and hind limbs should be assessed.
Relevant Articular Anatomy
- The navicular bursa does not communicate with the distal interphalangeal joint.
- Medial and lateral pouches of the fetlock communicate around 98% of the time.
- The common digital flexor tendon sheath communicates proximal to the bifurcation.
Diseases of Bovine Digit
- Non-infectious hoof diseases include subsolar abscesses, sole ulcers, white line disease, vertical wall cracks, interdigital fibromas, penetrating foreign bodies, and P3 fractures.
- Infectious hoof diseases include digital dermatitis ("hairy heel warts"), interdigital necrobacillosis ("foot rot"), and systemic ailments with lameness.
- Systemic ailments with lameness include vesicular stomatitis, BVDV (mucosal disease), malignant catarrhal fever, blue tongue virus, and foot and mouth disease.
- Solar lesions due to penetrating foreign bodies are problematic due to pedal osteitis or infection of P3.
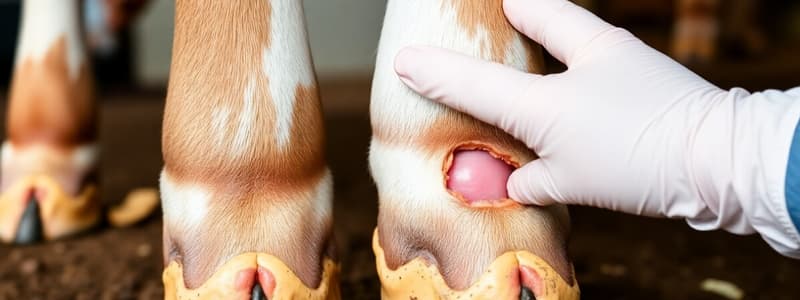
Deep Digital Sepsis (DDS)
- Indicators include focal, warm, asymmetric swelling around the coronary band as well as diffuse, warm, symmetric swelling extending to the mid-metacarpal/metatarsal region, and severe lameness unresponsive to antibiotic treatment.
- Closely associated anatomic proximity and uncontrolled foot infection directly lead to infection of: distal interphalangeal joint, distal sesamoid bone and bursa, deep digital flexor tendon (DDF), DDF tendon sheath, and superficial digital flexor tendon (SDF).
- Presumptive diagnoses of DDS include swelling, distribution, temperature, and lameness severity.
- Definitive diagnoses include radiographs, arthrocentesis, and surgical investigation.
- Structures commonly affected: distal interphalangeal joint and the tendon sheath.
- Sole ulceration, white line disease, and extension of interdigital necrobacillosis are most common cause of septic arthritis of DIPJ in dairy cattle
- Subsolar abscess, penetrating wounds, and extension of interdigital necrobacillosis are the most common cause of septic arthritis of DIPJ in beef cattle.
- Deep digital sepsis should be treated surgically, as conservative treatment is often ineffective.
Surgical Interventions
- Surgical interventions include local debridement, drainage, lavage of affected structures, digit amputation, and facilitated ankylosis.
- Local anesthetics with 2% lidocaine are common in cattle for regional intravenous perfusion and provide complete anesthesia of the limb distal to the tourniquet.
- Regional intravenous perfusion has a rapid onset (5-10 min) and should not last more than 30 minutes.
- Regional intravenous perfusion is indicated for arthrocentesis, digit amputation, facilitated ankylosis, interdigital fibroma removal and debridement of lesions like subsolar abscess, pedal osteitis, retroarticular abscess.
- Proximal tourniquet placement involved 30mL of lidocaine.
- Distal tourniquet placement involves 15-20 mL of lidocaine.
Regional Intravenous Perfusion (RIVP)
- RIVP with antibiotics allows for a high concentration of drug at the infection site.
- RIVP with antibiotics minimizes systemic exposure.
- Limitations concern food animals and the availability of few drugs.
- 2.2 mg/kg of florfenicol (300 mg/mL) can be used
- 1.5 g ampicillin sulbactam reconstituted in 3.2 mL sterile H2O or 0.9% NaCl can be used.
- Complications associated with RIVP reported in cattle include compartment syndrome, phlebitis, venous thrombosis distal to the tourniquet, and local bacteremia.
Joint Lavage/Arthrocentesis
- Indications include acute lesions.
- A Bier Block is the procedure.
- Use an 18g (1.5 in) needle with a 60° angle dorso-proximal to the coronary band.
- Placement of the needle should be axial or abaxial to the extensor tendon.
Procedures of the Digit
- Claw preserving procedures are joint lavage, arthrotomy, and facilitate ankylosis (DIP resection).
- Claw removing procedures are claw amputation and claw disarticulation.
- The types of surgical approaches for digit removal include P1 amputation, P2 exarticulation, and P3 exarticulation.
Digit Amputation
- The pros include a quick and relatively inexpensive procedure with rapid return to production, as well as complete removal of affected tissues.
- The cons include poor cosmetic appearance and a potential decrease in productive life, along with consideration of the claw, weight, and the environment.
- P1 amputation has the advantages of complete removal of infected structures and decreased pain.
- Exarticulation at the proximal and distal interphalangeal joint allows for lateral stability increased by leaving more tissue.
Digit Amputation: Pre-Op, Intra-Op, Post-Op
- Pre-Op steps are systemic antibiotics, Bier block and sterile preparation.
- Intra-Op steps are U-shaped skin incision, use of Gigli wire seated at 45°, wound lavage, vessel ligation, and hemostatic bandage.
- Post-Op procedure includes 1st bandage change within 24-36 hours, blood clot removal, and re-bandaging every 4–5 days.
Digit Amputation Prognosis
- A study determined the likelihood of good recovery in cattle weighing less than 705 lb was 71.4%.
- A study determined the likelihood of good recovery in cattle weighing more than 1500 lb was 27.3%.
- Bulls intended for natural service should have claw-saving procedures when possible.
DIP Ankylosis
- Ankylosis procedures involve draining the infection, debriding the joint, removing articular cartilage, and stabilizing the joint.
- Approaches can be dorsal, abaxial, axial, or caudal (most common).
Tenosynovitis Treatment
- Non-surgical options are needle lavage of the common digital flexor tendon sheath in acute cases.
- Surgical options are tenosynoviotomy (opening of the tendon sheath for more aggressive lavage) and tenectomy.
Procedure Comparison: Digit Amputation vs. Facilitated Ankylosis
- Digit amputation has a duration of healing of 4-6 weeks, while facilitated ankylosis has a duration of healing lasting 7-12 months.
- Prognostic factors for digit amputation include the digit and weight.
- Prognostic factors for facilitated ankylosis are weight/size and most importantly, the digit.
- Better herd longevity is seen with facilitated ankylosis at 18-22 months, compared to digit amputation at 15-17 months.
Interdigital Fibroma
- Etiology can stem from abnormal spreading of claws, genetics (Hereford, Holstein), males being more prone than females, and affecting hind limbs more than forelimbs.
- Diagnoses is non-painful proliferative tissue within the interdigital space that can become painful.
- Treatment is surgical en bloc removal.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.