Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of the Krebs cycle?
What is the primary function of the Krebs cycle?
- Catabolism and anabolism of various molecules (correct)
- Synthesis of amino acids exclusively
- Production of glucose from fatty acids
- Conversion of lactic acid to pyruvate
Which coenzyme is NOT required by the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex?
Which coenzyme is NOT required by the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex?
- Thiamin pyrophosphate (TPP)
- Biotin (correct)
- FAD
- Lipoic acid
What is produced during the oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate?
What is produced during the oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate?
- Acetyl CoA (correct)
- Oxaloacetate
- Succinyl CoA
- Glucose
How many ATP are produced from each acetyl CoA during the Krebs cycle?
How many ATP are produced from each acetyl CoA during the Krebs cycle?
Where does the Krebs cycle primarily occur?
Where does the Krebs cycle primarily occur?
What enzyme begins the digestion of carbohydrates in the mouth?
What enzyme begins the digestion of carbohydrates in the mouth?
During carbohydrate metabolism, where does the Krebs cycle occur?
During carbohydrate metabolism, where does the Krebs cycle occur?
Which type of carbohydrate cannot be digested due to the absence of the cellulase enzyme?
Which type of carbohydrate cannot be digested due to the absence of the cellulase enzyme?
What is the primary pathway for the oxidation of glucose?
What is the primary pathway for the oxidation of glucose?
What is produced during the anaerobic phase of glucose oxidation?
What is produced during the anaerobic phase of glucose oxidation?
Which process allows galactose and fructose to be converted into glucose?
Which process allows galactose and fructose to be converted into glucose?
What effect does 2,3 bisphosphoglycerate (BPG) have on hemoglobin?
What effect does 2,3 bisphosphoglycerate (BPG) have on hemoglobin?
What is one of the products of glycolysis that is important for lipogenesis?
What is one of the products of glycolysis that is important for lipogenesis?
What is the anabolic role of succinyl CoA in the Krebs cycle?
What is the anabolic role of succinyl CoA in the Krebs cycle?
Which of the following is a product of gluconeogenesis?
Which of the following is a product of gluconeogenesis?
Which substance is produced by the Hexose Monophosphate Shunt (HMP shunt)?
Which substance is produced by the Hexose Monophosphate Shunt (HMP shunt)?
What is the impact of glucose-6-P dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency?
What is the impact of glucose-6-P dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency?
What happens to blood glucose levels one hour after a meal?
What happens to blood glucose levels one hour after a meal?
Which hormone is mainly responsible for decreasing blood glucose levels?
Which hormone is mainly responsible for decreasing blood glucose levels?
What is an important role of NADPH produced from the HMP shunt?
What is an important role of NADPH produced from the HMP shunt?
In the context of fatty acid synthesis, what is the initial molecule produced in mitochondria?
In the context of fatty acid synthesis, what is the initial molecule produced in mitochondria?
What effect does glucagon have on blood glucose levels?
What effect does glucagon have on blood glucose levels?
Which hormone inhibits glucose uptake by the liver?
Which hormone inhibits glucose uptake by the liver?
What is the renal threshold for blood glucose above which glucose appears in urine?
What is the renal threshold for blood glucose above which glucose appears in urine?
What condition occurs when blood glucose levels drop below 40 mg/dl?
What condition occurs when blood glucose levels drop below 40 mg/dl?
Which hormone is known to stimulate gluconeogenesis?
Which hormone is known to stimulate gluconeogenesis?
What can excessive insulin during diabetes treatment lead to?
What can excessive insulin during diabetes treatment lead to?
What condition is characterized by glucose appearing in urine despite normal insulin levels?
What condition is characterized by glucose appearing in urine despite normal insulin levels?
Which condition is NOT a cause of hypoglycemia?
Which condition is NOT a cause of hypoglycemia?
What is the primary characteristic of Type I Diabetes Mellitus?
What is the primary characteristic of Type I Diabetes Mellitus?
Which of the following is a symptom of diabetes mellitus?
Which of the following is a symptom of diabetes mellitus?
What is the effect of low insulin levels on carbohydrate metabolism?
What is the effect of low insulin levels on carbohydrate metabolism?
What distinguishes hyperglycemic coma from hypoglycemic coma?
What distinguishes hyperglycemic coma from hypoglycemic coma?
Which statement is true regarding the hereditary state of Type II Diabetes Mellitus?
Which statement is true regarding the hereditary state of Type II Diabetes Mellitus?
Which complication is more commonly associated with Type I Diabetes Mellitus?
Which complication is more commonly associated with Type I Diabetes Mellitus?
What is the effect of low insulin on lipid metabolism?
What is the effect of low insulin on lipid metabolism?
At what fasting blood glucose level is diabetes mellitus diagnosed?
At what fasting blood glucose level is diabetes mellitus diagnosed?
Flashcards
Carbohydrate Digestion
Carbohydrate Digestion
The process of breaking down carbohydrates into simpler sugars for absorption.
Glucose Uptake
Glucose Uptake
Absorbed sugars are transported to the liver and converted to glucose for use.
Glucose Oxidation
Glucose Oxidation
The breakdown of glucose to produce energy, primarily through glycolysis and the Krebs cycle.
Glycolysis
Glycolysis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glycolysis Energy Production
Glycolysis Energy Production
Signup and view all the flashcards
Anaerobic Glycolysis
Anaerobic Glycolysis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Carbohydrate Storage
Carbohydrate Storage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Maltose Breakdown
Maltose Breakdown
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pyruvate Oxidation
Pyruvate Oxidation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex (PDC)
Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex (PDC)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle)
Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Coenzymes of PDC
Coenzymes of PDC
Signup and view all the flashcards
Krebs Cycle Function
Krebs Cycle Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glucagon Function
Glucagon Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Catecholamines Effect on Glucose
Catecholamines Effect on Glucose
Signup and view all the flashcards
Corticosteroids' Glucose Regulation
Corticosteroids' Glucose Regulation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Growth Hormone's Role
Growth Hormone's Role
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hepatic Regulation During Fasting
Hepatic Regulation During Fasting
Signup and view all the flashcards
Renal Threshold for Glucose
Renal Threshold for Glucose
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hyperglycemia Symptoms
Hyperglycemia Symptoms
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hypoglycemia Cause
Hypoglycemia Cause
Signup and view all the flashcards
Krebs Cycle Role
Krebs Cycle Role
Signup and view all the flashcards
Heme Synthesis
Heme Synthesis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Amino Acid Synthesis
Amino Acid Synthesis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fatty Acid Synthesis Location
Fatty Acid Synthesis Location
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gluconeogenesis in Krebs cycle
Gluconeogenesis in Krebs cycle
Signup and view all the flashcards
HMP Shunt Location
HMP Shunt Location
Signup and view all the flashcards
NADPH+H Function
NADPH+H Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Favism Definition
Favism Definition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diabetes Mellitus Type I
Diabetes Mellitus Type I
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diabetes Mellitus Type II
Diabetes Mellitus Type II
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hyperglycemia
Hyperglycemia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Polyphagia
Polyphagia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ketoacidosis (in relation to diabetes)
Ketoacidosis (in relation to diabetes)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hypoglycemic Coma
Hypoglycemic Coma
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diagnosis of Diabetes
Diagnosis of Diabetes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hyperglycemic Coma
Hyperglycemic Coma
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
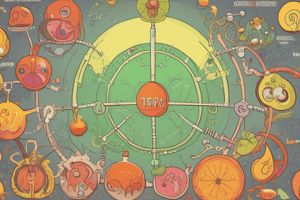
Carbohydrate Metabolism
- Carbohydrates are digested in the mouth, with salivary amylase acting on cooked starch and glycogen, converting them into dextrin, maltose, and isomaltose. Some starch remains undigested.
- Pancreatic amylase acts on both cooked and uncooked starches at a pH of 7.1, converting them into maltose and isomaltose.
- Final digestion involves intestinal enzymes. Lactose is broken down by lactase into glucose and galactose. Maltose is broken down by maltase into two glucose molecules. Sucrose is broken down by sucrase into glucose and fructose. Isomaltose is broken down by dextrinase into two glucose molecules (bond between carbon 1 and 6).
- Cellulose is not digested due to the lack of the enzyme cellulase, which breaks the β-linkages. It is used in treating constipation.
- Absorbed sugars are taken up by the liver, where galactose and fructose are converted into glucose.
- Sugar utilization follows three pathways: oxidation, storage, and conversion.
- Oxidation: Glycolysis and the Krebs cycle produce energy. The pentose phosphate pathway (HMP shunt) produces ribose, NADPH, and glucuronic acid.
- Storage: Glycogenesis stores glucose as glycogen.
- Conversion: Conversion occurs to fatty acids, or into ribose and deoxyribose for DNA and RNA synthesis. Ribose and deoxyribose also help convert lactose into milk.
- Glucose oxidation occurs in the cytoplasm, except the Krebs cycle which occurs in mitochondria.
- Complete oxidation involves glycolysis (cytoplasm) and the Krebs cycle (mitochondria) to produce CO2 and H2O.
- Glycolysis: Is the anaerobic phase of glucose oxidation, the Embden-Meyerhof pathway, which means the oxidation of glucose into pyruvate. It's most important in muscle during exercise because of O2 lack, and in red blood cells (RBCs) due to the absence of mitochondria.
- Glycolysis produces 8 or 6 ATP in the presence of O2, decreasing Hb's affinity for O2, making O2 easier to reach tissues.
- Glycolysis produces pyruvic acid that initiates the Krebs cycle. DHAP (dihydroxyacetone phosphate) converts to glycerol-3-phosphate, which is important for lipogenesis. Glycolysis also produces 2 amino acids: serine (from 3-phosphoglycerate) and alanine (from pyruvate).
- Mitochondrial Pathway: The Krebs cycle fully oxidizes glucose to CO2 and H2O. The first stage is the oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA. The second stage is the Krebs cycle.
- Oxidative Decarboxylation: This process is catalyzed by the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDC or PDH) and requires 5 coenzymes (TPP, lipoic acid, CoASH, FAD, and NAD).
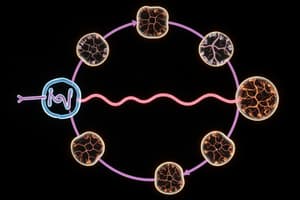
- Citric Acid Cycle (CAC) / Krebs' cycle / TCA: Occurs in the mitochondria.
- Catabolic Role: Produces 12 ATP for each acetyl CoA. Used in the complete oxidation of carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins.
- Anabolic Role: Synthesizes heme (succinyl CoA + glycine), and certain amino acids (transamination).
- Fatty Acid Synthesis: Acetyl CoA and oxaloacetate form citrate, which then enters the cytoplasm to form fatty acids.
- Gluconeogenesis: The synthesis of glucose from non-carbohydrate sources, uses the Krebs cycle.
- Importance of CO2: Important in several processes including the synthesis of fatty acids (from acetyl CoA and CO2 to malonyl CoA), oxaloacetate formation (from pyruvate and CO2), and urea synthesis (from NH3 and CO2).
- Pentose Phosphate Shunt (HMP Shunt): Occurs in the cytoplasm of the liver. Produces pentoses for DNA and RNA synthesis and NADPH+H for fatty acid, cholesterol, sphingosine, galactolipid, glucuronic acid, and non-essential amino acid synthesis. It also reduces glutathione.
- Favism: A deficiency in glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) leads to red blood cell (RBC) hemolysis, especially after eating fava beans. The deficiency affects the production of NADPH, thus affecting the reduction of glutathione, leading to hemolysis.
- Blood Glucose: Fasting blood glucose level is 70-110 mg/dl. One-hour after meal it reaches 120-150 mg/dl. Insulin decreases blood glucose by transferring glucose to cells, stimulating glycolysis and glycogenesis, inhibiting glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis, stimulating lipogenesis, and stimulating protein synthesis.
- Anti-insulin Hormones: Glucagon, catecholamines, corticosteroids (glucocorticoid), growth hormone, and thyroid hormones all increase blood glucose by stimulating or inhibiting processes.
- Hepatic Regulation: During fasting, glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis increase blood glucose. After a meal, glycogenesis and lipogenesis increase.
- Renal Regulation: Renal threshold is the blood glucose level above which glucose appears in urine (180 mg/dl). Abnormal low renal threshold (100 mg/dl) is called diabetes innocense.
- Variation in Blood Glucose (Hyperglycemia): Blood glucose above normal. Fasting levels >126 mg/dl, postprandial levels >200 mg/dl Causes include: ↓ insulin (diabetes mellitus, pancreas removal); ↑ anti-insulin hormones (adrenaline, cortisone, growth hormone, and thyroid problems).
- Hypoglycemia: Blood glucose below 40 mg/dl. It's dangerous as the brain depends on glucose. Symptoms include confusion, dizziness, tremors, weakness, tachycardia, and ultimately coma.
- Causes of hypoglycemia: Excessive insulin dose, missed meals during insulin therapy, insulinoma (tumor secreting excess insulin), ↓ anti-insulin hormones (Addison's disease, hypothyroidism, etc.), glycogen storage diseases (Von Gierke's disease), fructosemia/galactosemia.
- Diabetes Mellitus (DM): Symptoms include polyphagia (excessive eating), polydipsia (excessive drinking), polyuria (excessive urination), glucosuria (glucose in urine), and excessive loss of water-soluble vitamins. Type I DM is insulin-dependent, typically occurring during childhood, and is autoimmune. Type II DM is non-insulin-dependent, usually occurring after 35, and is often linked to obesity.
- Protein Metabolism in DM: Insulin ↓ protein catabolism → ↓ levels of glucose → Muscle wasting happens; Antibody formation → Resistance & ↑ Infection; Poor wound healing.
- Lipid Metabolism in DM: ↓ insulin → ↑ lipolysis → Loss of weight, Fatty liver, ↑ Free Fatty acid→ Hypercholesterolemia, atherosclerosis.
- Microangiopathy: Damage to small blood vessels. Retinopathy affects the retina → blindness; Nephropathy affects the kidneys → renal failure.
- Diagnosis of DM: Oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) measures glucose tolerance (body utilizing glucose without appearing in urine).
- Glycosylated Hemoglobin (HbA1c): A measure of average blood glucose over 2-3 months. Normal is 4-8%; >8% indicates diabetes.
- Difference between DM and Renal Glucosuria: In DM, high glucose and diseased pancreas, treating with insulin. Renal glucosuria is due to a ↓ renal threshold, normal glucose, a diseased kidney, treating with glucose.
- Diabetic Coma: A severe complication of diabetes. Hyperglycemic (ketotic) coma is due to high ketone bodies and lactic acidosis. Hyperglycemic hyperosmolar coma is a non-ketotic coma due to severe dehydration. Hypoglycemic coma is due to insulin overdose.
- Glucosuria: Glucose in urine. Hyperglycemic glucosuria is due to high blood glucose. Normoglycemic glucosuria is due to a lower than normal renal threshold, or an experimental condition (after phlorizin injection, which inhibits glucose absoption).
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.