Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the difference between integral and peripheral membrane proteins?
What is the difference between integral and peripheral membrane proteins?
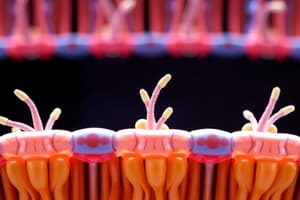
Integral proteins are embedded in the whole bilayer, whereas peripheral proteins are located on the inner or outer surface of the phospholipid bilayer.
How do transmembrane proteins become embedded in the plasma membrane?
How do transmembrane proteins become embedded in the plasma membrane?
Transmembrane proteins are anchored into the membrane by translocation and are stopped by a membrane anchor sequence.
What are 6 functions of the cell membrane?
What are 6 functions of the cell membrane?
Cell compartmentalization, anchoring cytoskeleton, protein sorting, adhesion of cells, cell signaling, selective uptake and export of ions and molecules.
What 3 types of macromolecules compose the plasma membrane?
What 3 types of macromolecules compose the plasma membrane?
What is glycosylation and what does it produce?
What is glycosylation and what does it produce?
What are phospholipids and how does their structure affect their role?
What are phospholipids and how does their structure affect their role?
Why is the phospholipid bilayer termed a semifluid?
Why is the phospholipid bilayer termed a semifluid?
What does it mean to be semi-permeable?
What does it mean to be semi-permeable?
What is selective permeability?
What is selective permeability?
What is the difference between active and passive transport?
What is the difference between active and passive transport?
What is the difference between osmosis and diffusion?
What is the difference between osmosis and diffusion?
How can you tell whether a solution is hypertonic, hypotonic, or isotonic to a cell placed within it?
How can you tell whether a solution is hypertonic, hypotonic, or isotonic to a cell placed within it?
What happens to plant/animal cells when placed in either a hypotonic, hypertonic, or isotonic solution?
What happens to plant/animal cells when placed in either a hypotonic, hypertonic, or isotonic solution?
What is the difference between exocytosis and endocytosis?
What is the difference between exocytosis and endocytosis?
What are the differences between an antiporter, a symporter, and a uniporter?
What are the differences between an antiporter, a symporter, and a uniporter?
What is the difference between a channel protein and a transport protein?
What is the difference between a channel protein and a transport protein?
Describe 3 ways a cell can communicate with cells immediately around it.
Describe 3 ways a cell can communicate with cells immediately around it.
Describe how a cell communicates with cells very far removed from it.
Describe how a cell communicates with cells very far removed from it.
Describe the stages of cell signaling.
Describe the stages of cell signaling.
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Membrane Proteins
- Integral proteins are fully embedded in the phospholipid bilayer, while peripheral proteins associate with the membrane's surface.
- Transmembrane proteins act as receptors and traverse the membrane multiple times, anchored by translocation and a membrane anchor sequence.
Functions of the Cell Membrane
- Provides compartmentalization for cellular processes.
- Facilitates cytoskeleton anchoring for structural integrity.
- Assists in protein sorting for cell function.
- Promotes cellular adhesion.
- Engages in cell signaling for communication.
- Supports selective uptake and export of ions and molecules.
Composition of Plasma Membrane
- Composed of three primary macromolecules: lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates.
Glycosylation
- A biochemical process where carbohydrates are added to lipids or proteins, producing glycolipids and glycoproteins.
Phospholipid Structure
- Consists of a hydrophilic phosphate head and hydrophobic lipid tails; structural elements influence membrane fluidity through length, kinks, and cholesterol content.
Membrane Properties
- The phospholipid bilayer is termed semifluid due to the mobility of some proteins and the anchoring of others.
- Semi-permeable membranes allow small molecules like water to pass freely, while large molecules face barriers.
Transport Mechanisms
- Selective permeability allows certain molecules to enter or exit while restricting others.
- Active transport requires energy (ATP), contrasting with passive transport, which occurs without energy (e.g., diffusion, osmosis).
- Osmosis refers to water movement, while diffusion pertains to solute movement.
Tonicity and Cell Response
- Isotonic solutions have equal solute concentrations; they are ideal for animal cells but not for plant cells, which may become flaccid.
- Hypertonic solutions cause plasmolysis in plants and crenation in animal cells.
- Hypotonic solutions lead to turgidity in plant cells due to water influx and lysis in animal cells.
Vesicular Transport
- Exocytosis involves packaging materials to be expelled from the cell.
- Endocytosis entails engulfs external materials into vesicles for intracellular processing.
Transport Proteins
- Uniporters transport a single type of molecule across the membrane.
- Symporters move two or more different molecules in the same direction; antiporters move them in opposite directions.
Protein Types
- Channel proteins form open structures that allow selective molecule passage through the membrane.
- Transport proteins facilitate ion and molecular movement via passive diffusion or secondary active transport.
Cellular Communication
- Local communication occurs through gap junctions, tight junctions, and desmosomes.
- Distant communication utilizes endocrine signaling, where hormones travel through the circulatory system to target cells.
Cell Signaling Process
- Involves three sequential stages: reception (signal detection), transduction (signal processing), and response (cellular action).
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.