Podcast
Questions and Answers
The interior region of a phospholipid bilayer is characterized as:
The interior region of a phospholipid bilayer is characterized as:
- Hydrophobic (correct)
- Polar
- Hydrophilic
- Hydrophilic and polar
In water, phospholipids can spontaneously form lipid bilayer structures. What bonds/forces/interactions are most influential in the formation of the lipid bilayer?
In water, phospholipids can spontaneously form lipid bilayer structures. What bonds/forces/interactions are most influential in the formation of the lipid bilayer?
- Hydrophobic exclusion of nonpolar fatty acid tails (correct)
- Van der Waals attractions among water molecules and fatty acid tails
- Covalent bonds among phospholipids
- Hydrogen bond interactions among water molecules and polar phospholipid heads (correct)
- Ionic interactions among Cl- ions and phosphates in the phospholipid heads
What type of molecule is sometimes found spanning a cell's plasma membrane with part of the molecule on one side of the membrane, part embedded in the membrane, and part on the other side?
What type of molecule is sometimes found spanning a cell's plasma membrane with part of the molecule on one side of the membrane, part embedded in the membrane, and part on the other side?
- Phospholipid
- Protein (correct)
- Carbohydrate
- RNA
An amphipathic molecule is one that:
An amphipathic molecule is one that:
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
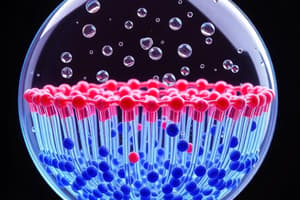
Phospholipid Bilayer
- The interior of a phospholipid bilayer is hydrophobic, meaning it repels water and does not dissolve in it.
Formation of Lipid Bilayer
- Lipid bilayers form in water due to critical interactions:
- Hydrogen bonds among water molecules and polar phospholipid heads facilitate stability.
- Hydrophobic exclusion effects prevent nonpolar fatty acid tails from interacting with water.
- Van der Waals attractions among fatty acid tails help maintain structure.
- Covalent bonds do not play a major role in the formation of the lipid bilayer.
Membrane-Spanning Molecules
- Proteins can span the plasma membrane, with distinct regions located on both sides of the membrane and embedded within it, allowing for functional diversity.
Amphipathic Molecules
- Amphipathic molecules possess both polar (hydrophilic) and nonpolar (hydrophobic) regions.
- These molecules can interact with both hydrophobic and hydrophilic environments, which is essential for membrane structure and function.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.