Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of carrier proteins in active transport?
What is the primary function of carrier proteins in active transport?
- To bind and transfer specific particles against their concentration gradient (correct)
- To form ion channels in the cell membrane
- To produce energy for cellular respiration
- To facilitate passive diffusion across the membrane
Which of the following statements about active transport is true?
Which of the following statements about active transport is true?
- It requires energy released during respiration for the movement against a gradient (correct)
- It can take place without the involvement of carrier proteins
- It moves particles from higher to lower concentration without energy
- It only occurs in plant cells
What factor is crucial for the process of active uptake in cells?
What factor is crucial for the process of active uptake in cells?
- The presence of a sodium gradient
- The temperature of the surrounding environment
- The permeability of the cell membrane
- The number of mitochondria within the cell (correct)
How does the binding of solute molecules occur in the active transport process?
How does the binding of solute molecules occur in the active transport process?
What is a defining characteristic of carrier proteins used in active transport?
What is a defining characteristic of carrier proteins used in active transport?
What is the direction of movement in diffusion?
What is the direction of movement in diffusion?
Which factor is NOT mentioned as affecting the rate of diffusion?
Which factor is NOT mentioned as affecting the rate of diffusion?
How does an increase in temperature affect diffusion?
How does an increase in temperature affect diffusion?
How does stirring influence diffusion?
How does stirring influence diffusion?
What effect does size of molecules have on diffusion?
What effect does size of molecules have on diffusion?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Diffusion
- Movement of particles occurs from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration, following a concentration gradient.
- Random motion of molecules facilitates diffusion by allowing substances to spread out.
Factors Affecting Rate of Diffusion (TADS)
- Temperature: Higher temperatures increase kinetic energy, leading to a faster diffusion rate (e.g., ammonia diffuses quicker when heated).
- Distance: Greater distances result in longer diffusion times.
- Air Current: If air currents align with the diffusion direction, the rate of diffusion increases.
- Stirring: Enhances diffusion by increasing the kinetic energy of molecules.
- Size of Molecules: Smaller molecules generally diffuse faster.
- Surface Area to Volume Ratio: Higher ratios facilitate increased diffusion rates.
- Concentration Gradient: Larger differences in concentration accelerate diffusion.
Importance of Diffusion
- Essential for gas exchange in all living organisms.
- Plays a critical role in photosynthesis by obtaining carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen.
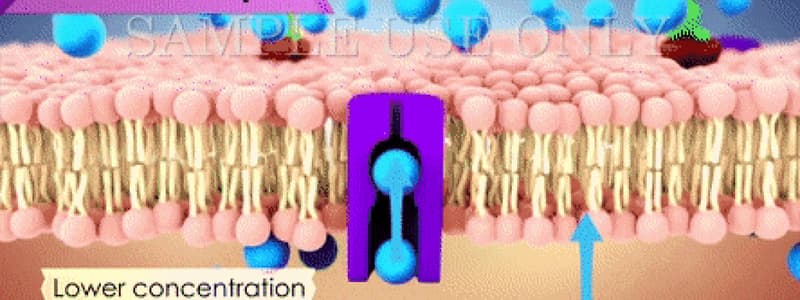
Active Transport
- Defined as the movement of particles against their concentration gradient—from lower to higher concentration—using energy from respiration.
- Utilizes Carrier Proteins found in cell membranes that transport particles by binding specifically to them.
Mechanism of Carrier Proteins
- A solute molecule binds to the carrier’s specific site.
- Energy is employed to rotate the carrier protein, moving the solute to a region of higher concentration.
Factors Affecting Active Uptake
- Number of mitochondria in the cell is crucial, as they generate the energy required for active transport through aerobic respiration.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.