Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the main organ of the respiratory system?
What is the main organ of the respiratory system?
- Windpipe
- Lungs (correct)
- Bronchi
- Nostrils
Which statement about the circulatory system is true?
Which statement about the circulatory system is true?
- It consists of the heart, blood, and blood vessels. (correct)
- It is responsible for breathing.
- It only transports oxygen.
- It absorbs carbon dioxide from the air.
What do veins do in the circulatory system?
What do veins do in the circulatory system?
- Distribute oxygenated blood.
- Collect deoxygenated blood to return it to the heart. (correct)
- Pump blood throughout the body.
- Carry blood away from the heart.
How many times does an adult's heart beat approximately in a year?
How many times does an adult's heart beat approximately in a year?
What happens when arteries are blocked?
What happens when arteries are blocked?
What is the correct order of air movement into the respiratory system?
What is the correct order of air movement into the respiratory system?
What part of the heart collects deoxygenated blood?
What part of the heart collects deoxygenated blood?
What is the primary function of blood in the circulatory system?
What is the primary function of blood in the circulatory system?
What is the primary function of red blood cells?
What is the primary function of red blood cells?
Which type of bone is known to be flat and thin, forming the ribcage?
Which type of bone is known to be flat and thin, forming the ribcage?
What is the name of the brain region responsible for balance and coordination?
What is the name of the brain region responsible for balance and coordination?
How many individual bones does an adult human typically have?
How many individual bones does an adult human typically have?
Which type of joint allows for movement?
Which type of joint allows for movement?
What type of nerves carry messages from the body to the brain?
What type of nerves carry messages from the body to the brain?
The sternum is referred to as what type of bone?
The sternum is referred to as what type of bone?
What function does plasma serve in the blood?
What function does plasma serve in the blood?
What connects the brain to the spinal cord?
What connects the brain to the spinal cord?
What type of actions are controlled by the spinal cord without brain involvement?
What type of actions are controlled by the spinal cord without brain involvement?
What is the primary function of the respiratory system?
What is the primary function of the respiratory system?
What distinguishes arteries from veins in the circulatory system?
What distinguishes arteries from veins in the circulatory system?
Which of the following statements about the heart is true?
Which of the following statements about the heart is true?
What component of blood is primarily responsible for transporting oxygen?
What component of blood is primarily responsible for transporting oxygen?
What happens to blood circulation when arteries are blocked?
What happens to blood circulation when arteries are blocked?
Which organ is primarily responsible for removing carbon dioxide from the body?
Which organ is primarily responsible for removing carbon dioxide from the body?
Which statement accurately describes blood vessels?
Which statement accurately describes blood vessels?
What is a significant fact about the adult human heart's blood pumping capability?
What is a significant fact about the adult human heart's blood pumping capability?
What are the two main functions of white blood cells?
What are the two main functions of white blood cells?
Which of the following describes the role of ligaments in the body?
Which of the following describes the role of ligaments in the body?
What is the main responsibility of the cerebellum?
What is the main responsibility of the cerebellum?
What physical characteristic differentiates the longest bone in the body?
What physical characteristic differentiates the longest bone in the body?
What is a defining feature of a reflex action?
What is a defining feature of a reflex action?
How does the plasma contribute to the functions of blood?
How does the plasma contribute to the functions of blood?
Which part of the brain is known as the control center for involuntary functions?
Which part of the brain is known as the control center for involuntary functions?
What type of joint is found in the skull?
What type of joint is found in the skull?
What transformation occurs to the number of bones from infancy to adulthood?
What transformation occurs to the number of bones from infancy to adulthood?
What are sensory nerves primarily responsible for?
What are sensory nerves primarily responsible for?
The main organs of the respiratory system are the ______, windpipe and bronchi.
The main organs of the respiratory system are the ______, windpipe and bronchi.
The ______ branches off into smaller tubes called bronchi or bronchial tubes.
The ______ branches off into smaller tubes called bronchi or bronchial tubes.
The right side of the heart collects impure (deoxygenated) blood from all parts of the ______.
The right side of the heart collects impure (deoxygenated) blood from all parts of the ______.
Veins carry blood ______ to the heart.
Veins carry blood ______ to the heart.
An adult's heart pumps nearly ______ litres of blood each day.
An adult's heart pumps nearly ______ litres of blood each day.
The heart contracts and relaxes 70-80 times a minute when we are at ______.
The heart contracts and relaxes 70-80 times a minute when we are at ______.
The circulatory system consists of the heart, blood, and ______.
The circulatory system consists of the heart, blood, and ______.
When arteries are blocked, the heart does not get sufficient ______ blood.
When arteries are blocked, the heart does not get sufficient ______ blood.
Red blood cells carry ______ to the cells of the body.
Red blood cells carry ______ to the cells of the body.
The ______ is responsible for protecting the body from diseases.
The ______ is responsible for protecting the body from diseases.
The skeletal system of an adult human has ______ individual bones.
The skeletal system of an adult human has ______ individual bones.
The ______ connects the brain to the spinal cord.
The ______ connects the brain to the spinal cord.
Bones give ______ and support to our body.
Bones give ______ and support to our body.
The longest bone in the human body is the ______.
The longest bone in the human body is the ______.
Joints are connected by ______, which are strong elastic bands of tissue.
Joints are connected by ______, which are strong elastic bands of tissue.
The cerebellum helps maintain ______ and coordination.
The cerebellum helps maintain ______ and coordination.
Nerves are made up of ______ or neurons.
Nerves are made up of ______ or neurons.
Plasma carries nutrients and ______ for the body.
Plasma carries nutrients and ______ for the body.
Oxygen is absorbed from the inhaled air and carbon dioxide is removed from the lungs as ______ air.
Oxygen is absorbed from the inhaled air and carbon dioxide is removed from the lungs as ______ air.
Blood is a part of the ______ system that transports oxygen to all parts of our body.
Blood is a part of the ______ system that transports oxygen to all parts of our body.
The ______ carries blood away from the heart.
The ______ carries blood away from the heart.
The left side of the heart distributes ______ blood to the different parts of the body.
The left side of the heart distributes ______ blood to the different parts of the body.
The ______ collects impure (deoxygenated) blood from all parts of the body.
The ______ collects impure (deoxygenated) blood from all parts of the body.
The air we breathe in has more ______, while the air that we breathe out has more carbon dioxide.
The air we breathe in has more ______, while the air that we breathe out has more carbon dioxide.
The circulatory system transports digested food materials and other substances to all parts of the ______.
The circulatory system transports digested food materials and other substances to all parts of the ______.
The ______ is a muscular organ, divided into four chambers, that pumps blood throughout the body.
The ______ is a muscular organ, divided into four chambers, that pumps blood throughout the body.
Blood is classified into four groups: A, B, AB, and ______.
Blood is classified into four groups: A, B, AB, and ______.
The ______ part of the brain is responsible for reasoning, learning, and memory.
The ______ part of the brain is responsible for reasoning, learning, and memory.
______ are responsible for blood clotting in the body.
______ are responsible for blood clotting in the body.
The ______ is a cage of 24 ribs that protects the heart and lungs.
The ______ is a cage of 24 ribs that protects the heart and lungs.
Ligaments are strong elastic bands of tissue that join ______ together.
Ligaments are strong elastic bands of tissue that join ______ together.
The ______ is the control center of the nervous system.
The ______ is the control center of the nervous system.
A human baby is born with around ______ bones.
A human baby is born with around ______ bones.
The two halves of the cerebrum are known as the right brain and the ______ brain.
The two halves of the cerebrum are known as the right brain and the ______ brain.
Motor nerves carry messages from the brain to different parts of the ______.
Motor nerves carry messages from the brain to different parts of the ______.
Joints where movement is possible are called ______ joints.
Joints where movement is possible are called ______ joints.
The lungs are the main organ of the circulatory system.
The lungs are the main organ of the circulatory system.
Arteries carry deoxygenated blood away from the heart.
Arteries carry deoxygenated blood away from the heart.
The right side of the heart collects deoxygenated blood.
The right side of the heart collects deoxygenated blood.
Blood vessels in an adult human body can be measured at over 96,000 km if laid end to end.
Blood vessels in an adult human body can be measured at over 96,000 km if laid end to end.
The heart pumps blood approximately 72 times a minute when at rest.
The heart pumps blood approximately 72 times a minute when at rest.
Veins are responsible for circulating oxygenated blood throughout the body.
Veins are responsible for circulating oxygenated blood throughout the body.
When we breathe in, the oxygen is absorbed from exhaled air.
When we breathe in, the oxygen is absorbed from exhaled air.
The windpipe is also known as the trachea.
The windpipe is also known as the trachea.
Blood transports oxygen and nutrients to our cells and collects carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide from them.
Blood transports oxygen and nutrients to our cells and collects carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide from them.
White blood cells protect our body from diseases and defend against viruses and bacteria.
White blood cells protect our body from diseases and defend against viruses and bacteria.
The number of bones in an adult human is typically 308.
The number of bones in an adult human is typically 308.
The cerebellum is responsible for creativity and logical reasoning.
The cerebellum is responsible for creativity and logical reasoning.
Ligaments are strong elastic bands that attach muscles to bones.
Ligaments are strong elastic bands that attach muscles to bones.
Reflex actions are controlled by the brain.
Reflex actions are controlled by the brain.
The ribcage is made up of 24 ribs.
The ribcage is made up of 24 ribs.
Motor nerves carry messages from the brain to different body parts.
Motor nerves carry messages from the brain to different body parts.
The longest bone in the human body is the femur.
The longest bone in the human body is the femur.
Plasma is responsible for repairing blood cells.
Plasma is responsible for repairing blood cells.
The lungs are the main organ of the circulatory system.
The lungs are the main organ of the circulatory system.
Veins circulate pure oxygenated blood to different parts of the body.
Veins circulate pure oxygenated blood to different parts of the body.
An adult's heart pumps approximately 7500 litres of blood each day.
An adult's heart pumps approximately 7500 litres of blood each day.
The right side of the heart distributes pure blood to all parts of the body.
The right side of the heart distributes pure blood to all parts of the body.
When we breathe in, air moves down the trachea before entering the lungs.
When we breathe in, air moves down the trachea before entering the lungs.
The heart beats more than 30 million times a year.
The heart beats more than 30 million times a year.
Arteries carry blood towards the heart.
Arteries carry blood towards the heart.
Carbon dioxide is absorbed from the inhaled air in the lungs.
Carbon dioxide is absorbed from the inhaled air in the lungs.
The longest bone in a human body is the femur.
The longest bone in a human body is the femur.
There are five types of bones in the adult human body.
There are five types of bones in the adult human body.
The cerebellum is responsible for thinking and creativity.
The cerebellum is responsible for thinking and creativity.
Ligaments are responsible for connecting muscles to bones.
Ligaments are responsible for connecting muscles to bones.
White blood cells help transport oxygen and nutrients in the body.
White blood cells help transport oxygen and nutrients in the body.
The ribcage consists of 26 ribs.
The ribcage consists of 26 ribs.
There are fewer bones in an adult than in a human baby.
There are fewer bones in an adult than in a human baby.
Nerves are made up of muscle cells.
Nerves are made up of muscle cells.
The brain stem controls voluntary muscle movements.
The brain stem controls voluntary muscle movements.
The reflex action does not involve the brain.
The reflex action does not involve the brain.
Explain the role of the lungs in the respiratory system.
Explain the role of the lungs in the respiratory system.
What is the function of arteries in the circulatory system?
What is the function of arteries in the circulatory system?
Describe the significance of the heart's four chambers.
Describe the significance of the heart's four chambers.
What happens to the heart rate at rest?
What happens to the heart rate at rest?
How does the respiratory system aid in gas exchange?
How does the respiratory system aid in gas exchange?
What is the main purpose of the circulatory system?
What is the main purpose of the circulatory system?
Why is it important to have a separation of deoxygenated and oxygenated blood in the heart?
Why is it important to have a separation of deoxygenated and oxygenated blood in the heart?
What impact do blocked arteries have on the heart?
What impact do blocked arteries have on the heart?
What is the term for the fluid that circulates nutrients and oxygen in the human body?
What is the term for the fluid that circulates nutrients and oxygen in the human body?
What type of blood cell is primarily responsible for carrying oxygen?
What type of blood cell is primarily responsible for carrying oxygen?
Name the three main types of bones in the human body.
Name the three main types of bones in the human body.
What is the role of the cerebrum in the brain?
What is the role of the cerebrum in the brain?
What connects two or more bones at a joint?
What connects two or more bones at a joint?
What type of joint allows for movement in the body?
What type of joint allows for movement in the body?
What basic function do white blood cells serve in the body?
What basic function do white blood cells serve in the body?
How many individual bones does an adult human typically have?
How many individual bones does an adult human typically have?
What structure connects the brain and spinal cord?
What structure connects the brain and spinal cord?
What is a reflex action?
What is a reflex action?
What role do the lungs play in the respiratory system?
What role do the lungs play in the respiratory system?
Why is the heart considered a muscular organ?
Why is the heart considered a muscular organ?
Explain the difference between arteries and veins in the circulatory system.
Explain the difference between arteries and veins in the circulatory system.
What happens during a heart attack?
What happens during a heart attack?
How does blood contribute to the body's transport system?
How does blood contribute to the body's transport system?
What is the function of the bronchi in the respiratory system?
What is the function of the bronchi in the respiratory system?
Describe the purpose of blood vessels in the circulatory system.
Describe the purpose of blood vessels in the circulatory system.
Why is it important for the heart to beat 70-80 times a minute at rest?
Why is it important for the heart to beat 70-80 times a minute at rest?
Explain the role of white blood cells in the human body.
Explain the role of white blood cells in the human body.
What are the main components of blood and their primary functions?
What are the main components of blood and their primary functions?
What are the five types of bones in the human body?
What are the five types of bones in the human body?
Describe the role of ligaments in the skeletal system.
Describe the role of ligaments in the skeletal system.
What is the primary function of the cerebrum?
What is the primary function of the cerebrum?
How does blood circulation change as a person grows from infancy to adulthood?
How does blood circulation change as a person grows from infancy to adulthood?
What separates the left and right sides of the cerebrum and what are their roles?
What separates the left and right sides of the cerebrum and what are their roles?
What are the two types of joints in the human body and how do they differ?
What are the two types of joints in the human body and how do they differ?
What neurotransmitters transmit messages between nerves and the brain?
What neurotransmitters transmit messages between nerves and the brain?
What is a reflex action and how is it initiated?
What is a reflex action and how is it initiated?
Study Notes
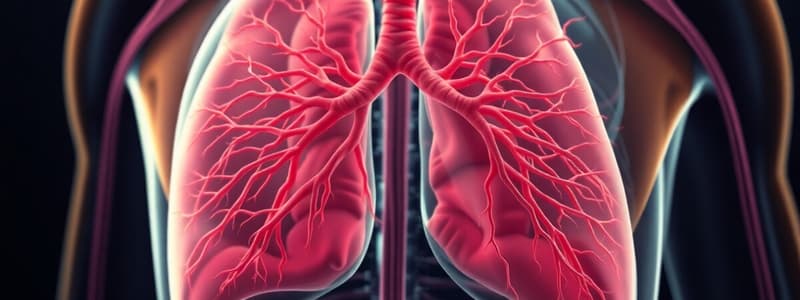
Respiratory System
- The respiratory system is responsible for breathing and gas exchange.
- The organs involved are the lungs, windpipe (trachea), and bronchi.
- Air enters through the nose, is cleaned by nasal hairs, and travels down the trachea.
- The trachea branches into bronchi, which lead to air sacs in the lungs.
- Oxygen is absorbed into the bloodstream from inhaled air, and carbon dioxide is released from the blood into exhaled air.
Circulatory System
- The circulatory system transports blood, oxygen, nutrients, and waste products throughout the body.
- The heart, blood, and blood vessels (arteries and veins) are the key components.
- The heart is a muscular organ with four chambers that pumps blood to different parts of the body.
- Arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart.
- Veins carry deoxygenated blood back to the heart.
- An adult heart pumps about 7,500 liters of blood daily.
- The human body contains over 96,000 kilometers of blood vessels.
- A blocked artery can lead to a heart attack due to insufficient oxygen reaching heart cells.
Blood
- Blood is a fluid that carries oxygen and nutrients to cells and removes waste products.
- Red blood cells (RBCs) carry oxygen and carbon dioxide.
- White blood cells (WBCs) fight infections and defend against foreign bodies.
- Platelets help with blood clotting and repair blood cells.
- Plasma carries nutrients.
- Blood is classified into four groups: A, B, AB, and O.
Skeletal System
- The skeletal system provides structure and support to the body.
- It also protects internal organs.
- An adult skeleton contains 206 bones, while newborns have around 300 bones.
- Some bones fuse together as we grow.
- The femur (thighbone) is the longest bone in the human body.
Ribcage
- The ribcage is a protective structure composed of 24 ribs.
- These ribs protect the lungs, heart, stomach, and kidneys.
- The sternum (breastbone) connects the ribs in the middle of the chest.
- The last two ribs are called floating ribs because they are not attached to the sternum.
Joints and Ligaments
- Joints are points where bones connect.
- Ligaments are strong elastic tissues that hold bones together at the joints.
- Movable joints allow for movement (e.g., arms, legs, fingers).
- Non-movable joints do not allow for movement (e.g., joints in the ribcage and skull).
Nervous System
- The nervous system controls all body functions.
- The brain, spinal cord, and nerves make up the nervous system.
Brain
- The brain is the control center of the nervous system.
- It has three main parts: cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem.
- The cerebrum is responsible for thought, learning, memory, and voluntary muscle control.
- The cerebellum controls balance, posture, and coordination of voluntary muscles.
- The brainstem connects the brain to the spinal cord and controls involuntary functions (e.g., breathing, digestion, blood circulation).
Spinal Cord
- The spinal cord acts as a bridge between the brain and the rest of the body.
- It carries messages between the brain and body through nerves.
- It also controls reflex actions, which are quick, automatic responses to stimuli that do not involve the brain.
Nerves
- Nerves are made up of nerve cells (neurons).
- They form a network throughout the body that carries messages.
- Sensory nerves carry messages from the body to the brain or spinal cord.
- Motor nerves carry messages from the brain or spinal cord to the body.
- Mixed nerves carry messages in both directions.
Reflex Action
- A reflex action is an automatic, involuntary response to a stimulus.
- It is controlled by the spinal cord, not the brain.
- An example is quickly removing your hand from a hot object.
Respiratory System
- The lungs, windpipe, and bronchi are key organs in the respiratory system.
- Air enters through the nose, where hair cleans it.
- The windpipe (trachea) leads to smaller tubes called bronchi.
- Bronchi end in air sacs where oxygen is absorbed and carbon dioxide is removed.
- Inhaled air is rich in oxygen, while exhaled air contains more carbon dioxide.
Circulatory System
- Transports digested food, oxygen, and other substances throughout the body.
- Composed of the heart, blood, and blood vessels (arteries and veins).
- The heart is a muscular organ with four chambers that pumps blood.
- It beats 70-80 times per minute at rest.
- The right side collects deoxygenated blood, the left side distributes oxygenated blood.
- Arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart.
- Veins carry deoxygenated blood back to the heart.
- An adult's heart pumps around 7,500 liters of blood daily.
- The circulatory system has over 96,000 km of blood vessels.
- Blockage in arteries can lead to heart attacks due to insufficient oxygenated blood reaching the heart.
Blood
- Carries oxygen and nutrients to cells and collects carbon dioxide and waste products.
- Composed of:
- Red Blood Cells (RBCs): Transport oxygen and carbon dioxide.
- White Blood Cells (WBCs): Protect the body from disease and foreign bodies.
- Platelets: Repair blood cells and help with blood clotting.
- Plasma: Carries nutrients.
- Human blood is classified into four groups: A, B, AB, and O.
Skeletal System
- Provides shape, support, and protection for internal organs.
- An adult has 206 bones, while a baby is born with around 300.
- The number of bones decreases as some fuse together during growth.
- The longest bone is the femur (thighbone).
Ribcage
- A cage of 24 flat, thin bones.
- Protects the lungs, heart, stomach, and kidneys.
- The sternum (breastbone) lies in the middle of the chest.
- The last two ribs are not attached to the sternum and are called floating ribs.
Joints and Ligaments
- Joints connect two or more bones.
- Ligaments are strong elastic tissues that hold bones together.
- Movable joints: Allow movement (e.g., arms, legs, fingers).
- Non-movable joints: Do not allow movement (e.g., ribcage, skull).
Nervous System
- The brain is the control center of the nervous system.
- It manages all body functions, even during sleep.
Brain
- Divided into three parts:
- Cerebrum: The largest part, responsible for thinking, voluntary muscle control, intelligence, creativity, learning, memory, and logical reasoning.
- Cerebellum: Controls and coordinates voluntary muscles, balance, and posture.
- Brain Stem (Medulla): Connects the brain to the spinal cord, controls involuntary muscles (e.g., stomach, heart) and functions like breathing and digestion.
Spinal Cord
- A thick bundle of nerves protected by the vertebral column.
- Acts as a bridge between the brain and the rest of the body, transmitting signals.
- Also controls reflex actions, which are immediate responses to stimuli that do not involve the brain.
Nerves
- Made up of nerve cells (neurons).
- Form a network throughout the body, carrying messages to and from the brain, spinal cord, and other parts.
- Sensory nerves: Carry messages from the body to the brain or spinal cord.
- Motor nerves: Carry messages from the brain or spinal cord to the body.
- Mixed nerves: Carry messages in both directions.
Reflex Action
- An automatic response to a stimulus, controlled by the spinal cord and not the brain.
- An example is quickly withdrawing a hand from a hot object.
The Human Body: Organ Systems
- The human body is made up of organ systems, which work together to perform vital functions.
The Respiratory System
- The respiratory system's main organs are the lungs, windpipe (trachea), and bronchi.
- Air enters through the nose, where hair filters it.
- The air then travels down the trachea, branching into smaller tubes called bronchi.
- Bronchi end in balloon-like air sacs where oxygen is absorbed from inhaled air and carbon dioxide is removed to be exhaled.
The Circulatory System
- The circulatory system transports digested food and other substances throughout the body.
- It comprises the heart, blood, and blood vessels (arteries and veins).
The Heart
- The heart is a muscular organ with four chambers.
- It pumps blood to all parts of the body, contracting and relaxing 70-80 times per minute at rest.
- The right side of the heart collects deoxygenated blood, while the left side distributes oxygenated blood.
Arteries
- Arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart.
Veins
- Veins carry deoxygenated blood towards the heart.
Blood
- Blood is a fluid that carries oxygen and nutrients to cells, and collects carbon dioxide and waste products.
Red Blood Cells (RBCs)
- Carry oxygen and carbon dioxide.
White Blood Cells (WBCs)
- Protect from diseases by fighting foreign bodies like viruses and bacteria.
Platelets
- Repair blood cells and are responsible for blood clotting.
Plasma
- Carries nutrients.
Blood Types
- Human blood is classified into four groups: A, B, AB, and O.
The Skeletal System
- Bones provide shape, support, and protection for the body.
- The skeletal system of an adult has 206 bones, while a baby is born with around 300.
- Some smaller bones fuse together as we grow.
Types of Bones
- The thighbone (femur) is the longest bone in the body.
- The ribcage, consisting of 24 flat, thin bones, protects the lungs, heart, stomach, and kidneys.
- The sternum (breastbone) connects the ribs.
Joints
- Joints are points where bones connect, facilitated by ligaments.
Types of Joints
- Movable joints allow for movement (e.g., arms, legs, fingers).
- Non-movable joints do not allow for movement (e.g., ribcage, skull).
The Nervous System
- The nervous system is controlled by the brain.
- The brain is active even during sleep.
The Brain
- The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain, responsible for thought, voluntary muscle control, intelligence, creativity, learning, memory, and reasoning.
- The cerebellum controls voluntary muscle coordination, balance, and posture.
- The brain stem connects the brain to the spinal cord, controlling involuntary muscles like the stomach and heart.
The Spinal Cord
- The spinal cord is a bundle of nerves within the vertebral column that acts as a bridge between the brain and the rest of the body.
- It controls reflex actions that do not involve the brain.
Nerves
- Nerves are made of nerve cells (neurons).
- They form a network that carries messages to and from the brain, spinal cord, and other parts of the body.
Types of Nerves
- Sensory nerves carry messages from the body to the brain/spinal cord.
- Motor nerves carry messages from the brain/spinal cord to the body.
- Mixed nerves carry messages both ways.
Reflex Actions
- Reflex actions are automatic responses to stimuli, bypassing the brain and controlled by the spinal cord.
Respiratory System
- The respiratory system is responsible for breathing.
- The main organs are lungs, windpipe (trachea), and bronchi.
- The windpipe branches into bronchi, which end with balloon-like air sacs.
- Oxygen is absorbed during inhalation, and carbon dioxide is released during exhalation.
Circulatory System
- Transports digested food, nutrients, and oxygen to all parts of the body.
- Removes waste products like carbon dioxide.
- Composed of the heart, blood, and blood vessels (arteries and veins).
- The heart is a muscular organ with four chambers.
- It pumps blood through the chambers about 70-80 times per minute at rest.
- The right side carries deoxygenated blood from the body to the lungs.
- The left side carries oxygenated blood to the body.
- Arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart.
- Veins carry deoxygenated blood to the heart.
Blood
- A fluid that transports oxygen, nutrients, and removes waste products.
- Components:
- Red blood cells (RBCs): Carry oxygen and carbon dioxide.
- White blood cells (WBCs): Fight infections.
- Platelets: Repair blood cells and aid in clotting.
- Plasma: Carries nutrients.
- Blood is classified into four groups: A, B, AB, and O.
Skeletal System
- Provides shape, support, and protection for the body.
- An adult has 206 bones; a baby is born with around 300, which fuse as they grow.
- The longest bone is the thighbone (femur).
- The ribcage is a protective structure made of 24 ribs, protecting internal organs like lungs, heart, stomach, and kidneys.
- The sternum (breastbone) lies in the middle of the chest.
- The last two ribs are "floating" as they are not attached to the sternum.
Joints and Ligaments
- Joints are connections between two or more bones.
- Ligaments are strong, elastic bands of tissue that hold bones together.
- Types of joints:
- Movable joints: Allow movement (e.g., arms, legs, fingers).
- Non-movable joints: Do not allow movement (e.g., skull, ribcage).
Nervous System
- The brain is the control center of the body.
- It controls all body functions, even during sleep.
- The brain has three parts: Cerebrum, Cerebellum, and Brain Stem.
- The cerebrum is the largest part and controls voluntary movements, intelligence, creativity, thought, learning, memory, and logic.
- The cerebellum controls balance, posture, and coordination of voluntary muscles.
- The brain stem connects the brain to the spinal cord and controls involuntary functions like breathing, digestion, and blood circulation.
Spinal Cord
- A thick bundle of nerves protected by the vertebral column.
- Acts as a bridge between the brain and the rest of the body for communication.
- Controls reflexes, which are automatic responses to a stimulus.
Nerves
- Made up of nerve cells (neurons).
- Act as a network that carries messages to and from the brain, the spinal cord, and other parts of the body.
- Types:
- Sensory nerves: Carry messages from the body to the brain or spinal cord.
- Motor nerves: Carry messages from the brain or spinal cord to the body.
- Mixed nerves: Carry messages both ways.
Reflex Action
- An automatic response to a stimulus, controlled by the spinal cord, without brain involvement.
- Example: Quickly removing your hand from a hot object.
Respiratory System
- The respiratory system is responsible for breathing, and its main organs are the lungs, windpipe (trachea), and bronchi.
- When we breathe in, air enters through the nose and is cleaned by the hair in the nostrils.
- Air then travels down the windpipe (trachea) and branches into smaller tubes called bronchi.
- The bronchi end in balloon-like air sacs where oxygen is absorbed and carbon dioxide is released.
- The air we breathe in has more oxygen, while the air we breathe out has more carbon dioxide.
Circulatory System
- The circulatory system transports digested food, oxygen, and other substances to all parts of the body.
- It is responsible for the flow of blood throughout the body, and consists of the heart, blood, and blood vessels (veins and arteries).
Heart
- The heart is a muscular organ divided into four chambers and pumps blood to all parts of the body.
- It contracts and relaxes 70-80 times per minute when at rest (usually 72 times).
- The right side of the heart collects deoxygenated blood from the body, while the left side distributes oxygenated blood.
- Arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart to the body.
- Veins carry deoxygenated blood back to the heart.
Blood
- Blood is a fluid that transports oxygen and nutrients to cells and collects carbon dioxide and waste products.
- Red blood cells (RBCs) carry oxygen to cells and carbon dioxide away.
- White blood cells (WBCs) protect against diseases and defend the body from foreign bodies like viruses and bacteria.
- Platelets repair blood cells and are responsible for blood clotting.
- Plasma carries nutrients.
Skeletal System
- Bones provide shape, support, and protection for the body.
- An adult skeleton has 206 bones, while a baby is born with around 300 bones.
- The number of bones reduces as we grow because some small bones fuse together.
Types of Bones
- The longest bone in the body is the femur (thighbone), averaging 19 inches in length.
- Ribs are flat, thin bones that protect the lungs, heart, stomach, and kidneys.
- The ribcage is made of 24 ribs, with the sternum (breastbone) in the middle.
- The last two ribs are not attached to the sternum and are called floating ribs.
Joints and Ligaments
- Joints are points where two or more bones attach.
- Ligaments are strong, elastic bands of tissue that connect bones.
- Movable joints allow for movement, like in arms, legs, and fingers.
- Non-movable joints do not allow for movement, like those in the ribcage and skull.
Nervous System
- The nervous system is controlled by the brain, and its main components are the brain, spinal cord, and nerves.
- The brain is the control center and is responsible for all body functions, even during sleep.
Brain
- The brain has three main parts: the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brain stem.
- The cerebrum is the largest part, responsible for thought, intelligence, learning, memory, and voluntary muscle control.
- The cerebellum controls voluntary muscle coordination, balance, and posture.
- The brain stem (medulla) connects the brain to the spinal cord and controls involuntary functions like breathing, digestion, and blood circulation.
Spinal Cord
- The spinal cord is a thick bundle of nerves within the vertebral column.
- It acts as a bridge between the brain and the rest of the body.
- It controls reflex actions, which are rapid involuntary responses to stimuli.
Nerves
- Nerves are made up of nerve cells (neurons).
- They form a network throughout the body and carry messages to and from the brain, spinal cord, and other body parts.
- Sensory nerves carry messages from the body to the brain or spinal cord.
- Motor nerves carry messages from the brain or spinal cord to the body.
- Mixed nerves carry messages both ways.
Reflex Actions
- A reflex action is an automatic, involuntary response to a stimulus.
- It occurs rapidly and doesn't involve the brain, being controlled by the spinal cord.
- For example, removing your hand quickly from a hot object.
Respiratory System
- The respiratory system is responsible for taking in oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide.
- The main organs are the lungs, windpipe (trachea), and bronchi.
- Air enters the nose, is cleaned by nostril hair, and moves down the trachea.
- The trachea branches into smaller tubes called bronchi.
- Bronchi end in balloon-like air sacs where oxygen is absorbed and carbon dioxide is released.
Circulatory System
- The circulatory system transports digested food, oxygen, and other substances throughout the body.
- It is made of the heart, blood, and blood vessels (arteries and veins).
- The heart is a muscular organ with four chambers that pumps blood to all parts of the body.
- It beats 70-80 times per minute at rest.
- The right side of the heart receives deoxygenated blood and the left side distributes oxygenated blood.
- Arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart.
- Veins carry deoxygenated blood back to the heart.
- An adult heart pumps around 7500 liters of blood daily.
Blood
- Blood is a fluid that carries oxygen and nutrients to cells and removes waste products.
- Red blood cells (RBCs) carry oxygen and remove carbon dioxide.
- White blood cells (WBCs) protect against diseases by fighting foreign bodies.
- Platelets help repair blood vessels and are responsible for clotting.
- Plasma carries nutrients.
Skeletal System
- The skeletal system provides shape, support, and protection for the body.
- An adult has 206 bones, while a baby is born with around 300.
- The longest bone is the femur (thighbone).
- The ribcage is a protective cage of 24 ribs that shields the lungs, heart, stomach, and kidneys.
Joints and Ligaments
- Joints are points where bones connect.
- Ligaments are strong, elastic tissues that join bones together.
- Movable joints allow movement (e.g., arms, legs, fingers).
- Non-movable joints do not allow movement (e.g., ribcage, skull).
Nervous System
- The nervous system controls all body functions.
- The brain is the control center of the nervous system.
- The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain, responsible for thinking, learning, memory, and voluntary muscle control.
- The cerebellum coordinates movement, balance, and posture.
- The brainstem connects the brain to the spinal cord and controls involuntary functions.
- The spinal cord is a bundle of nerves protected by the vertebral column that relays messages between the brain and the body.
- Nerves are made of nerve cells (neurons) that carry messages throughout the body.
- Sensory nerves carry messages from the body to the brain or spinal cord.
- Motor nerves carry messages from the brain or spinal cord to the body.
- Mixed nerves carry messages both ways.
Reflex Actions
- Reflex actions are automatic responses to stimuli that do not involve the brain.
- The spinal cord controls reflex actions.
- Reflexes are fast and help protect the body.
Respiratory System
- The respiratory system allows us to breathe and exchange gases.
- It includes the lungs, windpipe (trachea), and bronchi.
- Air enters through the nose, is cleaned by nostril hair, travels down the trachea, and branches into bronchi.
- Bronchi lead to balloon-like air sacs where oxygen is absorbed into the bloodstream and carbon dioxide is released.
- Exhaled air has more carbon dioxide than inhaled air.
Circulatory System
- The circulatory system is responsible for blood circulation throughout the body.
- It includes the heart, blood, and blood vessels (arteries and veins).
- The heart is a four-chambered muscular organ that pumps blood.
- It beats 70-80 times per minute at rest.
- The right side receives deoxygenated blood and the left side pumps oxygenated blood.
- Arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart.
- Veins carry deoxygenated blood to the heart.
Blood
- Blood is a critical fluid that transports oxygen and nutrients to cells and removes waste products.
- It is composed of red blood cells (RBCs), white blood cells (WBCs), platelets, and plasma.
- RBCs carry oxygen and carbon dioxide.
- WBCs defend against diseases and foreign bodies.
- Platelets aid blood clotting and cell repair.
- Plasma carries nutrients.
Skeletal System
- The skeletal system provides shape, support, and protection for the body.
- It is made up of 206 bones in adults.
- Babies are born with around 300 bones that fuse together as they grow.
- The longest bone is the femur (thigh bone).
Ribcage
- The ribcage is a protective cage of 24 ribs.
- It safeguards the lungs, heart, stomach, and kidneys.
- The sternum (breastbone) forms the front of the ribcage.
- The last two ribs are "floating ribs" and are not attached to the sternum.
Joints and Ligaments
- Joints are points where two or more bones connect.
- Ligaments are strong, elastic bands that hold bones together.
- Movable joints allow for movement (e.g., arms, legs, fingers).
- Non-movable joints do not allow for movement (e.g., ribcage, skull).
Nervous System
- The nervous system is responsible for controlling body functions.
- It includes the brain, spinal cord, and nerves.
Brain
- The brain is the control center of the nervous system.
- It has three main parts: the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem.
- The cerebrum is the largest part, responsible for thinking, voluntary muscle control, intelligence, creativity, memory, and logical reasoning.
- The cerebellum controls coordination, balance, and posture.
- The brainstem connects the brain to the spinal cord and controls involuntary actions like breathing, digestion, and blood circulation.
Spinal Cord
- The spinal cord is a thick nerve bundle protected by the vertebral column.
- It acts as a bridge between the brain and the rest of the body, transmitting signals.
- It also controls reflexes, automatic responses that don't involve the brain.
Nerves
- Nerves are made up of nerve cells (neurons) that form a network throughout the body.
- They carry messages to and from the brain, spinal cord, and other parts of the body.
- Sensory nerves carry messages from the body to the brain or spinal cord.
- Motor nerves carry messages from the brain or spinal cord to the body.
- Mixed nerves carry messages in both directions.
Reflex Action
- A reflex action is an automatic and immediate response to a stimulus without involving the brain (controlled by the spinal cord).
- A simple example is quickly withdrawing your hand from a hot object.
Respiratory System
- The respiratory system is responsible for breathing.
- It's comprised of the lungs, windpipe (trachea), and bronchi.
- Air enters through the nose and is cleaned by the hair in the nostrils.
- The windpipe branches into smaller tubes called bronchi.
- Bronchi end with balloon-like air sacs.
- Oxygen is absorbed from inhaled air, and carbon dioxide is removed from the lungs as exhaled air.
Circulatory System
- The circulatory system is responsible for transporting digested food, oxygen, and other substances throughout the body.
- It consists of the heart, blood, and blood vessels (arteries and veins).
- The heart is a muscular organ, divided into four chambers.
- The right side of the heart collects deoxygenated blood, and the left side distributes oxygenated blood.
- Arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart.
- Veins carry deoxygenated blood to the heart.
Blood Composition
- Blood transports oxygen and nutrients to cells and collects waste products.
- It is made up of:
- Red blood cells (RBCs): Carry oxygen and carbon dioxide.
- White blood cells (WBCs): Protect the body from diseases.
- Platelets: Repair blood cells and are responsible for clotting.
- Plasma: Carries nutrients.
Skeletal System
- The skeletal system provides shape, support, and protects internal organs.
- An adult has 206 bones.
- A baby is born with around 300 bones, which fuse together as they grow.
- The longest bone is the femur (thighbone).
Ribcage
- The ribcage consists of 24 ribs.
- It protects the lungs, heart, stomach, and kidneys.
- The sternum (breastbone) is located in the middle of the chest.
- The last two ribs are not attached to the sternum and are called floating ribs.
Joints and Ligaments
- Joints are points where two or more bones connect.
- They are held together by ligaments, strong elastic bands of tissue.
- There are two types of joints:
- Movable joints: Allow for movement, like those in the arms, legs, and fingers.
- Non-movable joints: Do not allow for movement, like those in the ribcage and skull.
Nervous System
- The brain is the control center of the nervous system.
- It controls all body functions, even during sleep.
- The brain has three parts:
- Cerebrum: The largest part, responsible for thinking, voluntary muscle control, intelligence, creativity, learning, memory, and logical reasoning.
- Cerebellum: Controls coordination, balance, and posture.
- Brain stem (medulla): Connects the brain to the spinal cord, and controls involuntary muscles like the stomach and heart.
Spinal Cord
- The spinal cord is a bundle of nerves protected by the vertebral column.
- It serves as a bridge between the brain and the rest of the body.
- It controls reflex actions, which occur without the involvement of the brain.
Nerves
- Nerves are made of nerve cells (neurons).
- They form a network throughout the body and carry messages to and from the brain, spinal cord, and other parts of the body.
- There are three types:
- Sensory nerves: Carry messages from the body to the brain or spinal cord.
- Motor nerves: Carry messages from the brain or spinal cord to the body.
- Mixed nerves: Carry messages both ways.
Reflex Action
- A reflex action is an automatic response to a stimulus.
- It occurs quickly and does not involve the brain.
- It is controlled by the spinal cord.
- An example is removing your hand from a hot object.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Description
Explore the essential functions of the respiratory and circulatory systems in this quiz. Learn about how the body exchanges gases and circulates blood to deliver vital nutrients. Test your knowledge of key organs, their roles, and the physiological processes involved in breathing and blood circulation.