Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the function of a cell membrane?
What is the function of a cell membrane?
It separates the cell from its surroundings, exhibits selective permeability, and forms additional compartments in eukaryotic cells.
What is the cell membrane mostly made up of?
What is the cell membrane mostly made up of?
Lipids and proteins, although some carbohydrates.
What is the fluid mosaic model?
What is the fluid mosaic model?
It describes the cell membrane as a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins that can move laterally.
What is the purpose of cholesterol in the membrane?
What is the purpose of cholesterol in the membrane?
Do proteins move within the cell membrane?
Do proteins move within the cell membrane?
What are the two integral transmembrane protein types?
What are the two integral transmembrane protein types?
What are integral proteins?
What are integral proteins?
What are peripheral proteins?
What are peripheral proteins?
What are the six major functions of membrane proteins?
What are the six major functions of membrane proteins?
What is signal transduction?
What is signal transduction?
What is recognition in cell membranes?
What is recognition in cell membranes?
What is the membrane naturally permeable to?
What is the membrane naturally permeable to?
Is the membrane permeable to water?
Is the membrane permeable to water?
Is the membrane permeable to polar molecules?
Is the membrane permeable to polar molecules?
Is the membrane permeable to ions or charged particles?
Is the membrane permeable to ions or charged particles?
Which two protein types help transport across the lipid bilayer?
Which two protein types help transport across the lipid bilayer?
What are channel proteins?
What are channel proteins?
What are carrier proteins?
What are carrier proteins?
What is passive transport?
What is passive transport?
What is diffusion?
What is diffusion?
What does diffusion do?
What does diffusion do?
What is osmosis?
What is osmosis?
What is tonicity?
What is tonicity?
What is isotonic?
What is isotonic?
What is hypotonic?
What is hypotonic?
What is hypertonic?
What is hypertonic?
A solution that has relatively high solute and low free water is?
A solution that has relatively high solute and low free water is?
A solution that has relatively low solute and high free water is?
A solution that has relatively low solute and high free water is?
A solution that has equal solute and equal free water is?
A solution that has equal solute and equal free water is?
What happens to water in a U tube with hypotonic solution on one side?
What happens to water in a U tube with hypotonic solution on one side?
Water moves by osmosis from the ___ solution into the ___ solution.
Water moves by osmosis from the ___ solution into the ___ solution.
What is osmoregulation?
What is osmoregulation?
What is facilitated diffusion?
What is facilitated diffusion?
What is diffusion in channels?
What is diffusion in channels?
What is diffusion in carriers?
What is diffusion in carriers?
What is active transport?
What is active transport?
What allows cells to maintain internal solute concentrations different from their environment?
What allows cells to maintain internal solute concentrations different from their environment?
What is an example of active transport?
What is an example of active transport?
How does the sodium potassium pump work?
How does the sodium potassium pump work?
When open to ECM, what can go into sodium potassium pump?
When open to ECM, what can go into sodium potassium pump?
When open to cytoplasm, what can go into Na+/K+ pump?
When open to cytoplasm, what can go into Na+/K+ pump?
How large is the voltage across the membrane?
How large is the voltage across the membrane?
How do ions react to the potential of the membrane?
How do ions react to the potential of the membrane?
What are the two types of bulk transport mechanisms?
What are the two types of bulk transport mechanisms?
What is exocytosis?
What is exocytosis?
What is endocytosis?
What is endocytosis?
What is phagocytosis?
What is phagocytosis?
What is pinocytosis?
What is pinocytosis?
What is receptor-mediated endocytosis?
What is receptor-mediated endocytosis?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
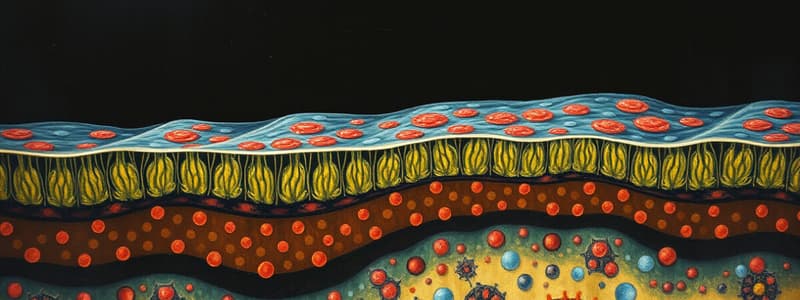
Cell Membrane and Structure
- The cell membrane separates the cell from its environment, allowing for selective permeability and compartmentalization in eukaryotic cells.
- Composed predominantly of lipids (phospholipids) and proteins, it forms a bilayer structure.
- The fluid mosaic model describes the dynamic nature of the membrane, where proteins can move laterally while flip-flopping occurs infrequently.
Role of Cholesterol
- Cholesterol serves as a temperature buffer for the membrane, preventing freezing at low temperatures and reducing fluidity at high temperatures due to its rigid structure.
Protein Types and Functions
- Integral Proteins: Penetrate the lipid bilayer, often spanning the entire membrane; they typically have hydrophobic regions in the center and hydrophilic regions at the ends.
- Peripheral Proteins: Located on the inner or outer membrane surfaces, they are attached to integral proteins and play roles in cell structure and signaling.
- Membrane proteins perform diverse functions including transport, catalyzing reactions, signal transduction, recognition, intercellular connections, and linking to the cytoskeleton.
Transport Mechanisms
- Passive transport requires no energy and includes simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion.
- Diffusion: Movement from high to low concentration, equalizing solute concentrations across membranes.
- Osmosis: A specific type of diffusion involving water moving across a semipermeable membrane towards a hypertonic solution.
- Tonicity describes a solution's ability to affect cell water levels: isotonic (equal solute), hypotonic (lower outside), and hypertonic (higher outside).
Water Movement and Regulation
- Water flows from hypotonic solutions into hypertonic solutions, dictated by the concentration gradient.
- Osmoregulation: Essential for animal cells without cell walls, involving structures like contractile vacuoles to manage internal water levels.
Active Transport
- Active transport utilizes ATP to move solutes against their concentration gradient via carrier proteins.
- The Sodium/Potassium pump is a key example, exchanging sodium and potassium ions across the membrane.
Membrane Potential and Ions
- The voltage across the membrane ranges from -50 to -200 mV, generating a negative interior and positive exterior.
- Ions respond to this electrochemical gradient, with negative ions attracted to the positive outside and vice versa for positive ions.
Bulk Transport Mechanisms
- Exocytosis: The process of expelling substances from the cell using vesicles.
- Endocytosis: The intake of substances through the membrane, encompassing phagocytosis (cell eating), pinocytosis (cell drinking), and receptor-mediated endocytosis (specific internalization using receptors).
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.