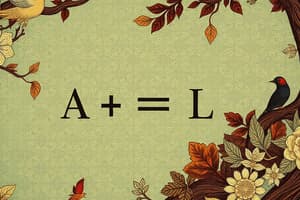Podcast
Questions and Answers
What does the basic accounting equation express?
What does the basic accounting equation express?
- The relationship between a company's equity and its cash flow.
- The relationship between a company's resources and the sources of those resources. (correct)
- The relationship between a company's revenue and its liabilities.
- The relationship between a company's assets and its expenses.
If a company takes out a loan, how is the accounting equation affected?
If a company takes out a loan, how is the accounting equation affected?
- Assets decrease and equity increases.
- Assets increase and liabilities increase. (correct)
- Assets remain constant while liabilities decrease.
- Assets increase and liabilities decrease.
What is included in the equity section of the accounting equation?
What is included in the equity section of the accounting equation?
- Owner's claim on assets after liabilities are paid. (correct)
- Retained earnings and liabilities.
- Total revenue and accounts payable.
- Owner's capital and expenses.
Which of the following transactions increases both assets and equity?
Which of the following transactions increases both assets and equity?
What is the expanded accounting equation?
What is the expanded accounting equation?
What ensures that the accounting equation remains in balance?
What ensures that the accounting equation remains in balance?
Which component of the accounting equation includes obligations the company owes?
Which component of the accounting equation includes obligations the company owes?
In a double-entry bookkeeping system, what must happen with each transaction?
In a double-entry bookkeeping system, what must happen with each transaction?
What occurs when a company incurs an expense?
What occurs when a company incurs an expense?
Why is the accounting equation considered essential for financial analysis?
Why is the accounting equation considered essential for financial analysis?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Basic Accounting Equation
- The fundamental equation of accounting:
- Assets = Liabilities + Equity
- Represents the relationship between a company's resources (assets) and the sources of those resources (liabilities and equity).
Components
-
Assets
- Resources owned by the company (e.g., cash, inventory, property).
- Future economic benefits.
-
Liabilities
- Obligations the company owes to external parties (e.g., loans, accounts payable).
- Represents claims against the company's assets.
-
Equity
- The owner's claim on the assets after liabilities are paid off.
- Includes capital contributions and retained earnings.
Expanded Accounting Equation
- Provides more detail:
- Assets = Liabilities + Owner's Capital + Revenues - Expenses
Relationship and Balance
- The accounting equation must always be in balance.
- Each transaction affects at least two accounts, maintaining the balance.
Examples of Transactions
-
Acquiring Assets
- Purchase equipment for cash:
- Assets increase (equipment), and assets decrease (cash).
- Purchase equipment for cash:
-
Borrowing Money
- Taking out a loan increases assets (cash) and liabilities (loan payable).
-
Owner Investment
- Owner contributes cash to the business:
- Assets increase (cash) and equity increases (owner's capital).
- Owner contributes cash to the business:
-
Generating Revenue
- Sales increase assets (cash or accounts receivable) and increase equity (revenue).
-
Incur Expenses
- Paying for utilities decreases assets (cash) and decreases equity (expenses).
Double-Entry System
- Each transaction is recorded in at least two accounts to ensure the accounting equation remains balanced.
Importance
- The accounting equation forms the backbone of the double-entry bookkeeping system.
- Essential for financial analysis, understanding a company's financial health, and facilitating reporting.
Basic Accounting Equation
- Central concept in accounting, demonstrating that assets are financed through liabilities and equity.
- Formula: Assets = Liabilities + Equity
Components
- Assets: Resources owned by the company, providing future economic benefits.
- Examples: Cash, inventory, property, plant, and equipment.
- Liabilities: Obligations the company owes to external parties.
- Examples: Loans, accounts payable, salaries payable.
- Represent claims against the company's assets.
- Equity: The owner's claim on the assets after liabilities are paid off.
- Includes initial capital contributions and retained earnings (profits accumulated over time).
Expanded Accounting Equation
- Provides a more detailed breakdown of equity:
- Assets = Liabilities + Owner's Capital + Revenues - Expenses
Relationship and Balance
- The accounting equation must always remain in balance.
- Every transaction affects at least two accounts, maintaining the balance.
- Example: Buying equipment with cash increases assets (equipment) but decreases assets (cash), maintaining the balance.
Examples of Transactions
- Acquiring Assets:
- When a company purchases equipment for cash, assets increase (equipment) and decrease (cash).
- Borrowing Money:
- Taking out a loan increases assets (cash) and liabilities (loan payable).
- Owner Investment:
- When the owner contributes cash to the business, assets increase (cash) and equity increases (owner's capital).
- Generating Revenue:
- Sales increase assets (cash or accounts receivable) and increase equity (revenue).
- Incurring Expenses:
- Paying for utilities decreases assets (cash) and decreases equity (expenses).
Double-Entry System
- Each accounting transaction is recorded in at least two accounts to ensure the accounting equation stays balanced.
Importance
- The accounting equation forms the foundation of the double-entry bookkeeping system.
- It is crucial for financial analysis, understanding a company's financial health, and generating accurate financial reports.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.