Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which characteristic is unique to the autonomic nervous system (ANS) compared to the somatic nervous system?
Which characteristic is unique to the autonomic nervous system (ANS) compared to the somatic nervous system?
- ANS innervates smooth muscles, cardiac muscle, and glands. (correct)
- ANS controls skeletal muscle contraction.
- ANS responses are always stimulatory.
- ANS uses a single myelinated neuron to reach the effector.
How do the efferent pathways of the autonomic nervous system (ANS) differ from those of the somatic nervous system?
How do the efferent pathways of the autonomic nervous system (ANS) differ from those of the somatic nervous system?
- Both systems use a two-neuron chain, but the ANS neurons are more myelinated.
- The ANS uses a two-neuron chain; the somatic system uses a single neuron. (correct)
- The ANS uses a single neuron, while the somatic system uses a two-neuron chain.
- Both systems use a single neuron, but the somatic system's neuron is unmyelinated.
Which neurotransmitter is released by all somatic motor neurons, and what is its effect on the target organ?
Which neurotransmitter is released by all somatic motor neurons, and what is its effect on the target organ?
- Norepinephrine, stimulatory.
- Norepinephrine, inhibitory.
- Acetylcholine, stimulatory. (correct)
- Acetylcholine, inhibitory.
During a stressful situation, the autonomic nervous system (ANS) adjusts bodily functions. How do active muscles receive more oxygen, according to the text?
During a stressful situation, the autonomic nervous system (ANS) adjusts bodily functions. How do active muscles receive more oxygen, according to the text?
What is the primary function of the parasympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system (ANS)?
What is the primary function of the parasympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system (ANS)?
What physiological changes would you expect to observe in a person who is relaxing and reading a book after a meal, due to parasympathetic activity?
What physiological changes would you expect to observe in a person who is relaxing and reading a book after a meal, due to parasympathetic activity?
What are the characteristics of the sympathetic division?
What are the characteristics of the sympathetic division?
Where do parasympathetic fibers originate?
Where do parasympathetic fibers originate?
Which cranial nerve carries approximately 90% of all preganglionic parasympathetic fibers?
Which cranial nerve carries approximately 90% of all preganglionic parasympathetic fibers?
What is the location of ganglia in the sacral part of the parasympathetic division?
What is the location of ganglia in the sacral part of the parasympathetic division?
Which structures are innervated exclusively by the sympathetic nervous system?
Which structures are innervated exclusively by the sympathetic nervous system?
What is the first structure that preganglionic fibers pass through after leaving the spinal cord in the sympathetic nervous system?
What is the first structure that preganglionic fibers pass through after leaving the spinal cord in the sympathetic nervous system?
Where do sympathetic fibers synapsing in the head originate?
Where do sympathetic fibers synapsing in the head originate?
What is the outcome, if any, of preganglionic fibers traveling to the adrenal medulla?
What is the outcome, if any, of preganglionic fibers traveling to the adrenal medulla?
What is the role of visceral sensory neurons in the autonomic nervous system (ANS)?
What is the role of visceral sensory neurons in the autonomic nervous system (ANS)?
In a visceral reflex arc, how many neurons are in the motor pathway?
In a visceral reflex arc, how many neurons are in the motor pathway?
What type of neurons are contained in the walls of the gastrointestinal tract?
What type of neurons are contained in the walls of the gastrointestinal tract?
Which of the following neurotransmitters are considered major neurotransmitters of the autonomic nervous system (ANS)?
Which of the following neurotransmitters are considered major neurotransmitters of the autonomic nervous system (ANS)?
From where is acetylcholine (ACh) released?
From where is acetylcholine (ACh) released?
What outcome would you expect with stimulation of nicotinic receptors?
What outcome would you expect with stimulation of nicotinic receptors?
What determines whether the effect of acetylcholine (ACh) on muscarinic receptors will be inhibitory or excitatory?
What determines whether the effect of acetylcholine (ACh) on muscarinic receptors will be inhibitory or excitatory?
How does norepinephrine (NE) affect cardiac and bronchial activity via adrenergic receptors?
How does norepinephrine (NE) affect cardiac and bronchial activity via adrenergic receptors?
Which of the following statements best describes the concept of dual innervation in the autonomic nervous system (ANS)?
Which of the following statements best describes the concept of dual innervation in the autonomic nervous system (ANS)?
What is meant by "antagonistic interaction" of the autonomic nervous system?
What is meant by "antagonistic interaction" of the autonomic nervous system?
How does sympathetic tone (vasomotor tone) contribute to blood pressure regulation?
How does sympathetic tone (vasomotor tone) contribute to blood pressure regulation?
When the sympathetic system shunts blood, what will happen?
When the sympathetic system shunts blood, what will happen?
In what situation would the sympathetic division override the parasympathetic division?
In what situation would the sympathetic division override the parasympathetic division?
Which activity is an example of the cooperative effect between the parasympathetic and sympathetic divisions?
Which activity is an example of the cooperative effect between the parasympathetic and sympathetic divisions?
What is the primary response of the sympathetic nervous system when body temperatures rise?
What is the primary response of the sympathetic nervous system when body temperatures rise?
What is the adrenal medulla considered?
What is the adrenal medulla considered?
How does the sympathetic division influence metabolic rate?
How does the sympathetic division influence metabolic rate?
Which best describes why the parasympathetic division has short-lived and highly localized control?
Which best describes why the parasympathetic division has short-lived and highly localized control?
What long term effect does the sympathetic division have?
What long term effect does the sympathetic division have?
How does the parasympathetic system effect the heart, and pupil size.
How does the parasympathetic system effect the heart, and pupil size.
An individual taking a drug that blocks parasympathetic responses may experience which of the following side effects?
An individual taking a drug that blocks parasympathetic responses may experience which of the following side effects?
In a scenario where an individual is experiencing increased stress, triggering the activation of the sympathetic nervous system, which of the following physiological responses is most likely to occur?
In a scenario where an individual is experiencing increased stress, triggering the activation of the sympathetic nervous system, which of the following physiological responses is most likely to occur?
Where does the main integrative center of ANS activity happen?
Where does the main integrative center of ANS activity happen?
Which part of the brain appears to exert the most direct influence over ANS?
Which part of the brain appears to exert the most direct influence over ANS?
The hypothalamus controls what function?
The hypothalamus controls what function?
What role does the cerebral cortex play in controlling ANS function?
What role does the cerebral cortex play in controlling ANS function?
What is Raynaud's disease categorized as?
What is Raynaud's disease categorized as?
Which condition is characterized by life-threatening, uncontrolled activation of autonomic neurons in quadriplegics and people with spinal cord injuries above T6?
Which condition is characterized by life-threatening, uncontrolled activation of autonomic neurons in quadriplegics and people with spinal cord injuries above T6?
How does the autonomic nervous system (ANS) ensure optimal support for the body's activities?
How does the autonomic nervous system (ANS) ensure optimal support for the body's activities?
What is the primary difference in the effectors innervated by the somatic and autonomic nervous systems?
What is the primary difference in the effectors innervated by the somatic and autonomic nervous systems?
Which of the following pathways accurately describes the efferent pathway of the autonomic nervous system (ANS)?
Which of the following pathways accurately describes the efferent pathway of the autonomic nervous system (ANS)?
How does the autonomic nervous system (ANS) exert either stimulatory or inhibitory effects on target organs?
How does the autonomic nervous system (ANS) exert either stimulatory or inhibitory effects on target organs?
During physical activity, the somatic and autonomic nervous systems work together. What is an example of such cooperation?
During physical activity, the somatic and autonomic nervous systems work together. What is an example of such cooperation?
What best describes 'dual innervation' in the autonomic nervous system (ANS)?
What best describes 'dual innervation' in the autonomic nervous system (ANS)?
In the context of autonomic nervous system function, what is the significance of 'dynamic antagonism' between the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions?
In the context of autonomic nervous system function, what is the significance of 'dynamic antagonism' between the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions?
How does the parasympathetic division contribute to homeostasis?
How does the parasympathetic division contribute to homeostasis?
The sympathetic division is often described as the "fight-or-flight" system. What physiological changes occur during the activation of this system?
The sympathetic division is often described as the "fight-or-flight" system. What physiological changes occur during the activation of this system?
What is the primary difference in the sites of origin between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems?
What is the primary difference in the sites of origin between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems?
How do the relative lengths of preganglionic and postganglionic fibers differ between the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the autonomic nervous system?
How do the relative lengths of preganglionic and postganglionic fibers differ between the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the autonomic nervous system?
Where are parasympathetic ganglia typically located?
Where are parasympathetic ganglia typically located?
Which cranial nerves contain preganglionic parasympathetic fibers?
Which cranial nerves contain preganglionic parasympathetic fibers?
Which nerve carries the majority of preganglionic parasympathetic fibers in the body?
Which nerve carries the majority of preganglionic parasympathetic fibers in the body?
Where do sacral preganglionic parasympathetic fibers primarily synapse?
Where do sacral preganglionic parasympathetic fibers primarily synapse?
Which structures receive sympathetic innervation exclusively?
Which structures receive sympathetic innervation exclusively?
Before synapsing in a sympathetic trunk ganglion, preganglionic fibers pass through which structure?
Before synapsing in a sympathetic trunk ganglion, preganglionic fibers pass through which structure?
Where do preganglionic fibers destined for the head region typically synapse?
Where do preganglionic fibers destined for the head region typically synapse?
How does the adrenal medulla integrate with the sympathetic nervous system to produce a response?
How does the adrenal medulla integrate with the sympathetic nervous system to produce a response?
What role do visceral sensory neurons play in the autonomic nervous system (ANS)?
What role do visceral sensory neurons play in the autonomic nervous system (ANS)?
How many consecutive neurons are in the motor pathway of a visceral reflex arc?
How many consecutive neurons are in the motor pathway of a visceral reflex arc?
Which nervous system is made up of sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons in the walls of the gastrointestinal tract?
Which nervous system is made up of sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons in the walls of the gastrointestinal tract?
Which type of fibers release acetylcholine (ACh)?
Which type of fibers release acetylcholine (ACh)?
Where are nicotinic receptors found?
Where are nicotinic receptors found?
What is the effect of acetylcholine (ACh) binding to nicotinic receptors?
What is the effect of acetylcholine (ACh) binding to nicotinic receptors?
On which of the following effector cells are muscarinic receptors found?
On which of the following effector cells are muscarinic receptors found?
What are the two major classes of adrenergic receptors that respond to norepinephrine (NE) or epinephrine?
What are the two major classes of adrenergic receptors that respond to norepinephrine (NE) or epinephrine?
The effect that norepinephrine has on a target organ is dependent on what?
The effect that norepinephrine has on a target organ is dependent on what?
What is the result of dynamic antagonism?
What is the result of dynamic antagonism?
What is sympathetic tone?
What is sympathetic tone?
What best describes the result if blood pressure were to suddenly drop?
What best describes the result if blood pressure were to suddenly drop?
In what way does the parasympathetic division demonstrate tone?
In what way does the parasympathetic division demonstrate tone?
What best describes the effect that sympathetic division can have during time of stress?
What best describes the effect that sympathetic division can have during time of stress?
What scenario requires cooperative effects from both the sympathetic and parasympathetic?
What scenario requires cooperative effects from both the sympathetic and parasympathetic?
When body temperatures rise, what is the sympathetic nervous system response?
When body temperatures rise, what is the sympathetic nervous system response?
What is the result of activation of the sympathetic nervous system on metabolic rate?
What is the result of activation of the sympathetic nervous system on metabolic rate?
Which best describes the effect of localized control on effectors?
Which best describes the effect of localized control on effectors?
What result does the sympathetic division display that makes it longer-lasting with body-wide effects?
What result does the sympathetic division display that makes it longer-lasting with body-wide effects?
According to the cerebral cortex, what area has a key influence over the ANS?
According to the cerebral cortex, what area has a key influence over the ANS?
What is the likely cause of autonomic neuropathy
What is the likely cause of autonomic neuropathy
How does the autonomic nervous system (ANS) coordinate with the somatic nervous system to support increased oxygen demand in active muscles?
How does the autonomic nervous system (ANS) coordinate with the somatic nervous system to support increased oxygen demand in active muscles?
Which of the following accurately describes the location and function of terminal ganglia within the parasympathetic nervous system?
Which of the following accurately describes the location and function of terminal ganglia within the parasympathetic nervous system?
A person is startled by a loud noise. What immediate effect would the sympathetic nervous system have on their pupils and why?
A person is startled by a loud noise. What immediate effect would the sympathetic nervous system have on their pupils and why?
How do white rami communicantes contribute to the function of the sympathetic nervous system?
How do white rami communicantes contribute to the function of the sympathetic nervous system?
The parasympathetic division influences specific organs. Which cranial nerve carries the most preganglionic parasympathetic fibers?
The parasympathetic division influences specific organs. Which cranial nerve carries the most preganglionic parasympathetic fibers?
What is the functional consequence of norepinephrine (NE) and epinephrine release from the adrenal medulla during sympathetic activation?
What is the functional consequence of norepinephrine (NE) and epinephrine release from the adrenal medulla during sympathetic activation?
What is the primary reason the parasympathetic division has more localized effects compared to the sympathetic division?
What is the primary reason the parasympathetic division has more localized effects compared to the sympathetic division?
How does biofeedback training assist in controlling ANS functions?
How does biofeedback training assist in controlling ANS functions?
In the context of visceral reflex arcs, what is the primary functional difference between somatic reflex arcs and visceral reflex arcs?
In the context of visceral reflex arcs, what is the primary functional difference between somatic reflex arcs and visceral reflex arcs?
Which best describes the impact of aging on the autonomic nervous system?
Which best describes the impact of aging on the autonomic nervous system?
Flashcards
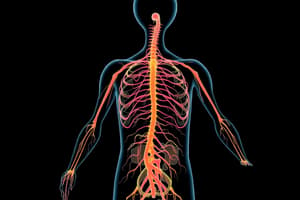
Automatic Nervous System (ANS)
Automatic Nervous System (ANS)
Motor neurons that innervate smooth muscles, cardiac muscle, and glands, operating via subconscious control.
Somatic Nervous System
Somatic Nervous System
Innervates skeletal muscles, using a single, thick myelinated axon directly to the muscle.
ANS Pathway
ANS Pathway
Uses a two-neuron chain: preganglionic neuron in CNS and postganglionic neuron outside CNS.
Preganglionic Neuron
Preganglionic Neuron
Signup and view all the flashcards
Postganglionic Neuron
Postganglionic Neuron
Signup and view all the flashcards
Neurotransmitter: Acetylcholine (ACh) in SNS
Neurotransmitter: Acetylcholine (ACh) in SNS
Signup and view all the flashcards
Neurotransmitters in ANS
Neurotransmitters in ANS
Signup and view all the flashcards
Parasympathetic Division
Parasympathetic Division
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sympathetic Division
Sympathetic Division
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dual Innervation
Dual Innervation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Craniosacral Division
Craniosacral Division
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thoracolumbar Division
Thoracolumbar Division
Signup and view all the flashcards
Parasympathetic Fiber Length
Parasympathetic Fiber Length
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sympathetic Fiber Length
Sympathetic Fiber Length
Signup and view all the flashcards
Parasympathetic Ganglia
Parasympathetic Ganglia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sympathetic Ganglia
Sympathetic Ganglia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Craniosacral Division Details
Craniosacral Division Details
Signup and view all the flashcards
Parasympathetic: Oculomotor Nerves (III)
Parasympathetic: Oculomotor Nerves (III)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Parasympathetic: Facial Nerves (VII)
Parasympathetic: Facial Nerves (VII)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Parasympathetic: Glossopharyngeal Nerves (IX)
Parasympathetic: Glossopharyngeal Nerves (IX)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Parasympathetic: Vagus Nerves (X)
Parasympathetic: Vagus Nerves (X)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sacral Part of Parasympathetic
Sacral Part of Parasympathetic
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sympathetic location
Sympathetic location
Signup and view all the flashcards
Preganglionic route in Sympathetic
Preganglionic route in Sympathetic
Signup and view all the flashcards
Action routes of trunk ganglion
Action routes of trunk ganglion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Location of Terminal ganglia
Location of Terminal ganglia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Location of sympathetic Trunk Ganglia
Location of sympathetic Trunk Ganglia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Location of Collateral Ganglia
Location of Collateral Ganglia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gray rami communicantes
Gray rami communicantes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pathways to the head
Pathways to the head
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pathways to the thorax
Pathways to the thorax
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pathways with Synapses in Collateral Ganglia
Pathways with Synapses in Collateral Ganglia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pathways to the abdomen
Pathways to the abdomen
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pathways to the pelvis
Pathways to the pelvis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Adrenal Medulla Synapses
Adrenal Medulla Synapses
Signup and view all the flashcards
Visceral sensory neurons
Visceral sensory neurons
Signup and view all the flashcards
Visceral Reflex arcs
Visceral Reflex arcs
Signup and view all the flashcards
Major neurotransmitters
Major neurotransmitters
Signup and view all the flashcards
The ACh is release
The ACh is release
Signup and view all the flashcards
NE is released
NE is released
Signup and view all the flashcards
division changes
division changes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Autonomic neuropathy
Autonomic neuropathy
Signup and view all the flashcards
ANS is under control
ANS is under control
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hypothalamic controls
Hypothalamic controls
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cortical controls
Cortical controls
Signup and view all the flashcards
ANS control deficiency
ANS control deficiency
Signup and view all the flashcards
neurons are derived
neurons are derived
Signup and view all the flashcards
N S structures in PNS come From
N S structures in PNS come From
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
- Key to anticipating the effects and side effects of drugs on patients.
- Consists of motor neurons that innervate smooth muscles, cardiac muscle, and glands.
- Adjusts body activities by shunting blood, and regulating heart rate, blood pressure, etc.
- Operates via subconscious control.
- Also called the involuntary nervous system or general visceral motor system.
ANS vs Somatic Nervous System
- Both contain motor fibers, but differ in effectors, efferent pathways/ganglia, and target responses
Effectors
- Somatic nervous system: innervates skeletal muscles.
- ANS: innervates cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, and glands.
Efferent Pathways and Ganglia
- SNS: cell body is in the CNS, and a single, thick myelinated Group A axon extends directly to skeletal muscle via spinal or cranial nerves.
- ANS: uses a two-neuron chain.
- Preganglionic neuron: cell body is in the CNS, features a thin, lightly myelinated preganglionic axon extending to the ganglion.
- Postganglionic (ganglionic) neuron: Located outside the CNS; a cell body synapses with the preganglionic axon in an autonomic ganglion, featuring a nonmyelinated postganglionic axon to the effector organ.
Neurotransmitter Effects
- Somatic nervous system: all somatic motor neurons release acetylcholine (ACh), always with a stimulatory effect.
- ANS: preganglionic fibers release ACh, while postganglionic fibers release norepinephrine or ACh at effectors. The effect can be stimulatory or inhibitory based on receptor types.
Overlap Between Somatic and Autonomic Function
- Higher brain centers coordinate both systems.
- Spinal/cranial nerves contain somatic/autonomic fibers.
- Adaptations involve skeletal muscles and visceral organs.
- Active muscles require more oxygen and glucose; thus, ANS nerves increase heart rate and open airways.
Divisions of the Autonomic Nervous System
- Two arms of ANS: parasympathetic and sympathetic.
- The Parasympathetic division promotes maintenance and conserves energy.
- The Sympathetic division mobilizes during activity.
- Dual innervation: all visceral organs are served by both divisions, causing opposite effects.
- Dynamic antagonism between divisions maintains homeostasis.
Role of the Parasympathetic Division
- Keeps body energy use low during maintenance activities; directs digestion, diuresis, and defecation.
- Referred to as the "rest-and-digest" system.
- Relaxing example: blood pressure, heart rate, and respiratory rates are low, gastrointestinal activity is high, and pupils are constricted with lenses accommodated for close vision
Role of the Sympathetic Division
- Mobilizes the body during activity.
- Referred to as the "fight-or-flight" system.
- Exercise, excitement, emergency, and embarrassment activate the sympathetic system, increasing heart rate, causing dry mouth and cold, sweaty skin, and dilating pupils.
- During physical activity, blood is shunted to skeletal muscles/the heart, bronchioles dilate, and the liver releases glucose.
Key Anatomical Differences between the Parasympathetic and Sympathetic Divisions
- Three main differences including sites of origin, relative lengths of fibers, and location of ganglia.
Sites of Origin
- Parasympathetic fibers are craniosacral, originating in the brain and sacral spinal cord.
- Sympathetic fibers are thoracolumbar, originating in the thoracic and lumbar regions of the spinal cord.
Relative Lengths of Fibers
- Parasympathetic has long preganglionic and short postganglionic fibers.
- Sympathetic has short preganglionic and long postganglionic fibers.
Location of Ganglia
- Parasympathetic ganglia are located in or near their visceral effector organ.
- Sympathetic ganglia lie close to the spinal cord.
Parasympathetic Division
- Also called the craniosacral division because fibers originate in the brain stem and sacral regions/cord.
- Long preganglionic fibers extend from the CNS almost to target organs. These synapse with postganglionic neurons in terminal ganglia, which are close to or inside the target organs.
- Short postganglionic fibers synapse with effectors.
Cranial Part of Parasympathetic Division
- Cell bodies are located in the brain stem
- Preganglionic Fibers
- Oculomotor nerves (III): Control smooth muscle of eye, cause pupils to constrict and lenses to bulge for focusing.
- Postganglion cell bodies located in ciliary ganglia within eye orbitals.
Cranial Part of Parasympathetic Division
- Facial nerves (VII): stimulate large glands in the head.
- Fibers that activate nasal and lacrimal glands have synapse in pterygopalatine ganglia.
- Fibers that activate submandibular and sublingual salivary glands synapse in submandibular ganglia.
- Glossopharyngeal nerves (IX): stimulate parotid salivary glands; fibers synapse in otic ganglia.
Cranial Part of Parasympathetic Division
- Vagus nerves (X): account for ~90% of all preganglionic parasympathetic fibers in the body; serve all thoracic and abdominal viscera.
- Preganglionic fibers arise from the medulla and synapse in terminal ganglia (intramural ganglia) in the walls of target organs.
- Cardiac plexus: slows heart rate.
- Pulmonary plexus: serves lungs and bronchi.
Sacral Part of Parasympathetic Division
- Originates from neurons in $S_2-S_4$, serves pelvic organs and the distal half of the large intestine.
- Axons travel in the ventral root of spinal nerves and then branch off, forming the pelvic splanchnic nerves.
- Synapses with: -Ganglia in pelvic floor (inferior hypogastric [pelvic] plexus). -Intramural ganglia in walls of the distal half of the large intestine, urinary bladder, ureters, and reproductive organs.
Sympathetic Division
- It is more complex and innervates more organs than the parasympathetic.
- Some structures, including sweat glands, arrector pili muscles of hair follicles, and smooth muscles of all blood vessels.
- Also called the thoracolumbar division. Contains preganglionic neurons in spinal cord segments T₁-L₂ forming the lateral horns of the spinal cord.
Key Anatomical Differences Between the ANS
- Preganglionic fibers pass through white rami communicates and enter the sympathetic trunk (chain or paravertebral) ganglia.
- Paravertebral ganglia vary in size, position, and number.
- 23 paravertebral ganglia exist in the sympathetic trunk (chain).
- 3 Cervical.
- 11 Thoracic.
- 4 Lumbar.
- 4 Sacral.
- 1 Coccygeal.
Location of the Sympathetic Trunk
- Short preganglionic fibers can follow one of three pathways after entering the sympathetic trunk ganglion.
Synapse in Trunk Ganglia
- Synapse with ganglionic neuron in the same trunk ganglion.
- Ascend or descend the sympathetic trunk to synapse in another trunk ganglion.
Synapse in Collateral Ganglia
- Pass through the trunk ganglion and emerge without synapsing in the trunk (only in the abdomen and pelvis). Synapse outside of the trunk in collateral ganglia.
Summary of Autonomic Ganglia
- Terminal ganglia are in the parasympathetic nervous system and are located within the wall of the organ served (intramural ganglia), or close to the organ.
- Sympathetic trunk ganglia are in the sympathetic nervous system and are paired, beside the spinal cord.
- Collateral (prevertebral) ganglia are in the sympathetic nervous system and are unpaired, anterior to the spinal cord.
Sympathetic Pathways
- Postganglionic axons enter ventral rami via gray rami communicantes (nonmyelinated postganglionic fibers.)
- White rami communicantes: myelinated preganglionic
- Contain sympathetic system neurons.
- These fibers innervate sweat glands, arrector pili muscles, and vascular smooth muscle via.
Pathways to the Head
- Fibers emerge from T₁ to T₄ and synapse in the superior cervical ganglion. -Innervate the skin and blood vessels of the head. -Stimulate dilator muscles of the iris. -Inhibit nasal and salivary glands. Innervate smooth muscle of the upper eyelid. -Branch to the heart.
Pathways to the Thorax
- Preganglionic fibers emerge from T₁ to T₆ and synapse in cervical trunk ganglia.
- Postganglionic fibers emerge from middle and inferior cervical ganglia and enter nerves C₄ to C₈. -Innervate the heart via the cardiac plexus. -Thyroid gland and the skin. -Lungs and esophagus.
Pathways with Synapses in Collateral Ganglia
- Most fibers from T₅ to L₂ synapse in collateral ganglia outside of the trunk, forming splanchnic nerves.
Pathways to the Abdomen
Preganglionic fibers from T₅ to L₂ travel through thoracic splanchnic nerves, synapse in celiac and superior mesenteric ganglia. Postganglionic fibers serve the stomach, intestines, liver, spleen, and kidneys.
Pathways to the Pelvis
Preganglionic fibers originate from T₁₀ to L₂ and travel through the trunk of lumbar and sacral ganglia. some synapse with postganglionic fibers run in lumbar and sacral splanchnic nerves.
Pathways with Synapses in the Adrenal Medulla
- Some preganglionic fibers pass directly to the adrenal medulla without synapsing.
- Upon stimulation, medullary cells secrete norepinephrine and epinephrine into the blood.
- Sympathetic ganglia and the adrenal medulla arise from the same tissue, with the adrenal medulla considered a "misplaced" sympathetic ganglion
Visceral Reflexes.
- They send sensory signals regarding chemical changes stretch, temperature, and irritation of viscera.
- Receptors for visceral senses are free nerve endings widely scattered throughout viscera.
- Cell bodies are located in dorsal root ganglia and in sensory ganglia of cranial nerves.
- Axons travel in the same nerves as autonomic motor fibers (ex: parasympathetic fibers of the vagus nerve) as they monitor conditions or organs serviced by ANS nerves.
Visceral reflexes
- Visceral reflex arcs share components with somatic reflex arcs (receptor, sensory neuron, integration center, motor neuron, and effector) but have three distinct differences. -Visceral reflex arcs have two consecutive neurons in the motor pathway. -Afferent fibers are visceral sensory neurons. -Effectors are smooth muscle cardiac muscle, and glands rather than skeletal muscles.
Neurotransmitters
- Major neurotransmitters of the ANS are acetylcholine (ACh) and norepinephrine (NE).
- ACh (same as ACh used by somatic motor neurons) is released by cholinergic fibers at all ANS preganglionic axons and all parasympathetic postganglionic axons.
- NE is released by adrenergic fibers at almost all sympathetic postganglionic axons.
Cholinergic Receptors
- There are two types that bind to ACh: Nicotinic and Muscarinic receptors.
- They are named after drugs that bind to them and mimic ACh effects: nicotine and muscarine (Mushroom poison)
Nicotinic Receptors
- Found on all postganglionic neurons (sympathetic and parasympathetic), hormone-producing cells of the adrenal medulla, sarcolemma of skeletal muscle cells at the neuromuscular junction.
- The Effect of ACh at nicotinic receptors is always stimulatory; opens ion channels, depolarizing the postynaptic cell.
Muscarinic Receptors
- Located on all effector cells stimulated by postganglionic cholinergic fibers.
- The effect of ACh at muscarinic receptors can be either inhibitory or excitatory.
Adrenergic Receptors
- Two major classes that respond to NE or epinephrine: alpha (α) and beta (β) receptors.
- Divided into subclasses: α₁, α₂ and B1, B2, B3.
Effects Depend on Receptors on Target Organ
- Binding of NE to cardiac muscle B₁ receptors increases, whereas epinephrine causes bronchial relaxation when bound to B₂ receptors.
Parasympathetic and Sympathetic Interactions
- Most visceral organs have dual innervation.
- Action potentials fire down axons of both divisions, producing antagonism that precisely controls the visceral activity.
- Both ANS divisions are partially active, establishing basal sympathetic and parasympathetic control.
Sympathetic Tone
- Sympathetic tone: almost all blood vessel smooth muscle are innervated by only sympathetic fibers, meaning this division controls blood pressure, even at rest.
- vasomotor tone: a continual state of partial constriction of blood vessels increases constriction raises the the pressure drop means dilating them decreases blood pressure.
Parasympathetic Tone
- Division normally dominates the heart and smooth muscle of digestive and urinary tract organs, and it activates most glands(except adrenal and sweat glands.
- Slows the heart and dictates normal activity levels of digestive and urinary tracts.
Cooperative Effects
- Cooperation between divisions: the control of external genitalia. -Parasympathetic fibers cause vasodilation for erection of the penis/clitoris.
- Sympathetic fibers cause ejaculation of semen in males, along with reflex contraction of the female's vagina.
Unique Roles of the Sympathetic Division
- Adrenal medulla, sweat glands, arrector pili muscles, kidneys, and almost all blood vessels receive only sympathetic fibers.
Other Unique Functions of Sympathetic Division
- Thermoregulatory responses to heat body temps rise, sympathetic nerves dilate skin blood vessels, allowing heat to escape, and activate sweat glands body temps in drop blood vessels constrict.
Release of Renin
- Sympathetic system causes it to activate a system that increases blood pressure.
Metabolic Effects
- Increases the rates of cells raises blood glucose levels mobilise fats for fuells.
Localized Versus Diffuse Effects
- Parasympathetic division elicits short-lived and localized control over effectors; ACh is quickly destroyed by acetylcholinesterase.
- Sympathetic division provides longer-lasting, body-wide effects; NE is inactivated more slowly than ACh, and NE/epinephrine hormones from adrenal medulla have prolonged effects after sympathetic signals stop.
Control of Autonomic Nervous System
- Cerebral structures hypothalamus, spinal cord.
- Cerebral input may modify input.
- Cerebral.
- Cerebral input may modify input.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.