Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following is a characteristic of rheumatoid arthritis (RA)?
Which of the following is a characteristic of rheumatoid arthritis (RA)?
- It is a chronic, multisystem, progressive autoimmune disorder (correct)
- Is a localized, non-systemic condition.
- Typically spares the joints.
- Primarily affects a single organ system.
Which of the following is a common site of involvement in rheumatoid arthritis, aside from the joints?
Which of the following is a common site of involvement in rheumatoid arthritis, aside from the joints?
- Liver
- Brain
- Salivary and lacrimal glands (correct)
- Pancreas
What is the approximate female to male ratio in terms of incidence for rheumatoid arthritis (RA)?
What is the approximate female to male ratio in terms of incidence for rheumatoid arthritis (RA)?
- 3:1 (correct)
- 1:3
- 1:5
- 1:1
What percentage of patients with rheumatoid arthritis are HLA-DR4 positive?
What percentage of patients with rheumatoid arthritis are HLA-DR4 positive?
The presence of which antibody is characteristically elevated in the serum of individuals with Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)?
The presence of which antibody is characteristically elevated in the serum of individuals with Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)?
The severity of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) tends to correlate with the levels of:
The severity of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) tends to correlate with the levels of:
Which of the following cell types is most directly responsible for tissue damage in Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)?
Which of the following cell types is most directly responsible for tissue damage in Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)?
Which cytokine activates macrophages and resident synovial cells?
Which cytokine activates macrophages and resident synovial cells?
Which cytokine recruits neutrophils and monocytes?
Which cytokine recruits neutrophils and monocytes?
Which cytokine stimulates bone resorption?
Which cytokine stimulates bone resorption?
Which set of cytokines stimulates resident synovial cells to secrete proteases that destroy hyaline cartilage?
Which set of cytokines stimulates resident synovial cells to secrete proteases that destroy hyaline cartilage?
During the pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA), what is the initiating cell?
During the pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA), what is the initiating cell?
What is the first stage of Rheumatoid Arthritis?
What is the first stage of Rheumatoid Arthritis?
What results in elevated ACPA production?
What results in elevated ACPA production?
In the targeting stage of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA), what describes the main events?
In the targeting stage of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA), what describes the main events?
During the fulminant stage of rheumatoid arthritis, which pathological process contributes to joint damage?
During the fulminant stage of rheumatoid arthritis, which pathological process contributes to joint damage?
What term describes fibrous fusion in the fulminant stage of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)?
What term describes fibrous fusion in the fulminant stage of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)?
Which of the following is a typical clinical presentation of rheumatoid arthritis?
Which of the following is a typical clinical presentation of rheumatoid arthritis?
In rheumatoid arthritis, what joints are typically affected in the hands and feet?
In rheumatoid arthritis, what joints are typically affected in the hands and feet?
The joints lead to radial deviation of the wrist, and which other deformities?
The joints lead to radial deviation of the wrist, and which other deformities?
Systemic symptoms of RA can include:
Systemic symptoms of RA can include:
What best describes the pathological findings in the joints of an individual with Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)?
What best describes the pathological findings in the joints of an individual with Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)?
What is the inflammatory exudate in the joints called?
What is the inflammatory exudate in the joints called?
What pathological changes does pannus formation lead to?
What pathological changes does pannus formation lead to?
Which of the following is a typical component observed in Rheumatoid nodules?
Which of the following is a typical component observed in Rheumatoid nodules?
What arteries are affected in Vasculitis?
What arteries are affected in Vasculitis?
Extra-articular manifestations of rheumatoid arthritis include:
Extra-articular manifestations of rheumatoid arthritis include:
What is a key difference between Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis?
What is a key difference between Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Which statement best describes the involvement of inflammation in Osteoarthritis versus Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Which statement best describes the involvement of inflammation in Osteoarthritis versus Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Pathology begins with small joints in ___ and begins with weight bearing joints in ___.
Pathology begins with small joints in ___ and begins with weight bearing joints in ___.
What is the primary pathogenic abnormality in osteoarthritis?
What is the primary pathogenic abnormality in osteoarthritis?
What is the primary cause of Gout?
What is the primary cause of Gout?
After how many years of hyperuricemia does gout usually present?
After how many years of hyperuricemia does gout usually present?
A genetic condition associated with Gout is:
A genetic condition associated with Gout is:
What is the name of the crystal deposition disease where CPP crystals are rhomboid and positively birefringent?
What is the name of the crystal deposition disease where CPP crystals are rhomboid and positively birefringent?
A key difference between Gout and CPPD is that Gout's crystals are ___ and CPPD's crystals are ___.
A key difference between Gout and CPPD is that Gout's crystals are ___ and CPPD's crystals are ___.
What is a symptom of Reactive Arthritis?
What is a symptom of Reactive Arthritis?
Reactive arthritis often presents days to weeks after what?
Reactive arthritis often presents days to weeks after what?
Which of the following infections is least associated with Reactive Arthritis?
Which of the following infections is least associated with Reactive Arthritis?
Dystrophic calcification, commonly seen in the late stages of CPPD, differs mechanistically from metastatic calcification primarily by?
Dystrophic calcification, commonly seen in the late stages of CPPD, differs mechanistically from metastatic calcification primarily by?
Which of the following best describes the usual pattern of joint involvement in rheumatoid arthritis?
Which of the following best describes the usual pattern of joint involvement in rheumatoid arthritis?
In the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis, what is the role of TNF?
In the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis, what is the role of TNF?
Which of the following best describes the triggering stage in the pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)?
Which of the following best describes the triggering stage in the pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)?
What two factors lead to elevated ACPA production?
What two factors lead to elevated ACPA production?
Symmetrical joint involvement is a key feature of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA). What does symmetrical presentation mean in the context of RA?
Symmetrical joint involvement is a key feature of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA). What does symmetrical presentation mean in the context of RA?
Which joint deformities can result from Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)?
Which joint deformities can result from Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)?
Which of the following is the name for the fibrous fusion of a joint seen in the fulminant stage of rheumatoid arthritis?
Which of the following is the name for the fibrous fusion of a joint seen in the fulminant stage of rheumatoid arthritis?
What is the primary composition of the inflammatory exudate found in the joints of individuals with Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)?
What is the primary composition of the inflammatory exudate found in the joints of individuals with Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)?
Where are rheumatoid nodules typically found?
Where are rheumatoid nodules typically found?
Which of the following best characterizes the role of inflammatory mediators in osteoarthritis?
Which of the following best characterizes the role of inflammatory mediators in osteoarthritis?
What is the initiating cell in the pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)?
What is the initiating cell in the pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)?
In rheumatoid arthritis, the pathological changes in the joints include lymphocytosis. What key feature characterizes this process?
In rheumatoid arthritis, the pathological changes in the joints include lymphocytosis. What key feature characterizes this process?
During the fulminant stage of RA, synovial hyperplasia occurs. What is another term to describe this?
During the fulminant stage of RA, synovial hyperplasia occurs. What is another term to describe this?
Which of the following is associated with Gout?
Which of the following is associated with Gout?
What best describes the crystals found in Gout?
What best describes the crystals found in Gout?
Which of the following is part of the classic triad associated with Reactive Arthritis?
Which of the following is part of the classic triad associated with Reactive Arthritis?
Which characteristics describe CPP crystals?
Which characteristics describe CPP crystals?
The pathophysiology of gout involves several key steps. Which process directly leads to tissue damage and the formation of tophi?
The pathophysiology of gout involves several key steps. Which process directly leads to tissue damage and the formation of tophi?
A patient presents with joint pain, urethritis, and conjunctivitis following a recent gastrointestinal infection. Which condition is most likely the cause?
A patient presents with joint pain, urethritis, and conjunctivitis following a recent gastrointestinal infection. Which condition is most likely the cause?
In crystal arthropathies, what is the underlying process that leads to joint inflammation?
In crystal arthropathies, what is the underlying process that leads to joint inflammation?
What is pannus?
What is pannus?
Which interleukin recruits neutrophils and monocytes?
Which interleukin recruits neutrophils and monocytes?
Which of the following joints are commonly affected in rheumatoid arthritis in the hands and feet?
Which of the following joints are commonly affected in rheumatoid arthritis in the hands and feet?
Which systemic symptom is NOT associated with Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Which systemic symptom is NOT associated with Rheumatoid Arthritis?
During the synovitis and joint swelling stage of RA pathogenesis, what type of cytokines are elevated?
During the synovitis and joint swelling stage of RA pathogenesis, what type of cytokines are elevated?
Which of the following is the most important cytokine for treatment in RA?
Which of the following is the most important cytokine for treatment in RA?
What is the long term consequence of immunosuppression?
What is the long term consequence of immunosuppression?
Which crystal shape is associated with CPPD?
Which crystal shape is associated with CPPD?
What would cause an increase in urate secretion?
What would cause an increase in urate secretion?
What is the primary abnormality in osteoarthritis?
What is the primary abnormality in osteoarthritis?
What type of pattern is seen in vasculitis?
What type of pattern is seen in vasculitis?
Which factor is least related to development of gout?
Which factor is least related to development of gout?
Which is a symptom of crystal arthropathies?
Which is a symptom of crystal arthropathies?
Other than arthritis, what other symptoms occur in Reactive Arthritis?
Other than arthritis, what other symptoms occur in Reactive Arthritis?
During the maturation stage of rheumatoid arthritis, which of the following processes occurs?
During the maturation stage of rheumatoid arthritis, which of the following processes occurs?
A researcher is investigating potential genetic factors predisposing individuals to rheumatoid arthritis. Based on current understanding, which gene would be most relevant to investigate?
A researcher is investigating potential genetic factors predisposing individuals to rheumatoid arthritis. Based on current understanding, which gene would be most relevant to investigate?
Which of the following is the correct order of stages in RA?
Which of the following is the correct order of stages in RA?
Given that cellular and humoral immune responses are both adaptive immunity, what would be the best treatment option?
Given that cellular and humoral immune responses are both adaptive immunity, what would be the best treatment option?
A 60 year old patient presents in your clinic with the following symptoms. They include arthritis, urethritis, conjunctivitis, mono and oligoarticular. Which of the following is the likely cause.
A 60 year old patient presents in your clinic with the following symptoms. They include arthritis, urethritis, conjunctivitis, mono and oligoarticular. Which of the following is the likely cause.
What is the likelihood of developing gout if an individual has hyperuricemia?
What is the likelihood of developing gout if an individual has hyperuricemia?
What is the difference between reactive and septic arthritis? Select all that apply.
What is the difference between reactive and septic arthritis? Select all that apply.
Which metabolic bone disease is also known as 'osteitis deformans'?
Which metabolic bone disease is also known as 'osteitis deformans'?
Which of the following best describes the impact of osteoporosis on bone strength?
Which of the following best describes the impact of osteoporosis on bone strength?
Which factor is directly associated with mortality in individuals who have osteoporosis?
Which factor is directly associated with mortality in individuals who have osteoporosis?
In the context of bone remodeling, what characterizes bone-wasting diseases like osteoporosis?
In the context of bone remodeling, what characterizes bone-wasting diseases like osteoporosis?
Which of the following is a significant attributing factor to osteoporosis related to age?
Which of the following is a significant attributing factor to osteoporosis related to age?
Trabecular, forearm, and spinal fractures characterize which type of osteoporosis?
Trabecular, forearm, and spinal fractures characterize which type of osteoporosis?
What best describes the use of X-rays in diagnosing osteoporosis?
What best describes the use of X-rays in diagnosing osteoporosis?
In metabolic bone diseases, what does the term 'osteopenia' refer to?
In metabolic bone diseases, what does the term 'osteopenia' refer to?
What is the underlying cause of osteomalacia and rickets?
What is the underlying cause of osteomalacia and rickets?
Which of the following clinical features is commonly observed in individuals with osteomalacia?
Which of the following clinical features is commonly observed in individuals with osteomalacia?
What alterations are typically observed in serum concentrations in individuals with osteomalacia?
What alterations are typically observed in serum concentrations in individuals with osteomalacia?
What laboratory findings are characteristically observed in osteomalacia?
What laboratory findings are characteristically observed in osteomalacia?
What is the primary cause of secondary hyperparathyroidism?
What is the primary cause of secondary hyperparathyroidism?
What is the effects of excessive parathyroid hormone (PTH) on bone?
What is the effects of excessive parathyroid hormone (PTH) on bone?
Increased osteoclast number and activity with a characteristic tunnelling or dissecting pattern is associated with?
Increased osteoclast number and activity with a characteristic tunnelling or dissecting pattern is associated with?
What is the usual course of Paget's disease of bone?
What is the usual course of Paget's disease of bone?
Which term describes the loss of distinction between cortex and medulla, seen in the late stages of Paget's disease?
Which term describes the loss of distinction between cortex and medulla, seen in the late stages of Paget's disease?
What is the role of the p62/sequestosome 1 (SQSTM1) gene in Paget's disease?
What is the role of the p62/sequestosome 1 (SQSTM1) gene in Paget's disease?
What is a key histological feature observed in the acute phase of Paget's disease?
What is a key histological feature observed in the acute phase of Paget's disease?
What is the goal of bisphosphonate treatment in Paget's disease?
What is the goal of bisphosphonate treatment in Paget's disease?
What is the primary reason that osteoporotic fractures lead to mortality?
What is the primary reason that osteoporotic fractures lead to mortality?
A 70-year-old woman presents with a hip fracture after a fall from standing height. Her bone mineral density T-score is -3.0. Which management is most appropriate?
A 70-year-old woman presents with a hip fracture after a fall from standing height. Her bone mineral density T-score is -3.0. Which management is most appropriate?
A researcher is studying the effects of different interventions on osteoporosis. Which outcome measure would be MOST sensitive for detecting a change in bone density over a 1-year period?
A researcher is studying the effects of different interventions on osteoporosis. Which outcome measure would be MOST sensitive for detecting a change in bone density over a 1-year period?
In osteomalacia, what is the specific relationship between serum calcium and phosphate levels?
In osteomalacia, what is the specific relationship between serum calcium and phosphate levels?
A patient presents with advanced secondary hyperparathyroidism due to chronic kidney disease. Which skeletal manifestation are they LEAST likely to exhibit?
A patient presents with advanced secondary hyperparathyroidism due to chronic kidney disease. Which skeletal manifestation are they LEAST likely to exhibit?
Following diagnosis of Paget’s disease, a patient is found to have an elevated serum alkaline phosphatase level but no demonstrable bony abnormalities on X-ray. What is the most appropriate next step?
Following diagnosis of Paget’s disease, a patient is found to have an elevated serum alkaline phosphatase level but no demonstrable bony abnormalities on X-ray. What is the most appropriate next step?
What is bone quality?
What is bone quality?
Which fracture site is NOT associated with Osteoporosis?
Which fracture site is NOT associated with Osteoporosis?
What happens to the progenitor osteoblast cells as we age?
What happens to the progenitor osteoblast cells as we age?
What does osteomalacia radiology show?
What does osteomalacia radiology show?
A patient has osteomalacia due to cancer that is phosphate wasting. What Vitamin D resistance best describes this?
A patient has osteomalacia due to cancer that is phosphate wasting. What Vitamin D resistance best describes this?
In primary hyperparathyroidism, what percentage of people that have this condition have a parathyroid adenoma?
In primary hyperparathyroidism, what percentage of people that have this condition have a parathyroid adenoma?
What is the outcome of NET that results from bone resulting in increased activity?
What is the outcome of NET that results from bone resulting in increased activity?
A late sign of Paget's disease is:
A late sign of Paget's disease is:
What histological result is apparent with diagnostic features?
What histological result is apparent with diagnostic features?
What can happen with primary hyperparathyroidism?
What can happen with primary hyperparathyroidism?
A long term intravenous treatment to help increase bone density carries potential risks to the patient. What is a key risk?
A long term intravenous treatment to help increase bone density carries potential risks to the patient. What is a key risk?
What bone cells go unchecked in sclerosing bone diseases?
What bone cells go unchecked in sclerosing bone diseases?
What features distinguish osteolysis in Paget disease from other lytic bone lesions?
What features distinguish osteolysis in Paget disease from other lytic bone lesions?
In the management of Paget's disease, what differentiates the use of bisphosphonates from surgical intervention?
In the management of Paget's disease, what differentiates the use of bisphosphonates from surgical intervention?
Which of the following is a potential outcome of bone fractures associated with osteoporosis?
Which of the following is a potential outcome of bone fractures associated with osteoporosis?
What term describes the reduced bone mineral density that is not severe enough to be classified as osteoporosis?
What term describes the reduced bone mineral density that is not severe enough to be classified as osteoporosis?
What best defines osteomalacia?
What best defines osteomalacia?
Which of the following best describes the role of Vitamin D in osteomalacia?
Which of the following best describes the role of Vitamin D in osteomalacia?
In osteomalacia, what contributes to alterations in the serum concentrations?
In osteomalacia, what contributes to alterations in the serum concentrations?
Which of the following is a typical laboratory finding in individuals with osteomalacia?
Which of the following is a typical laboratory finding in individuals with osteomalacia?
What is the most common cause of primary hyperparathyroidism?
What is the most common cause of primary hyperparathyroidism?
What is a direct effect of excessive parathyroid hormone (PTH) on bone?
What is a direct effect of excessive parathyroid hormone (PTH) on bone?
Which of the following describes the bone resorption process seen in hyperparathyroidism?
Which of the following describes the bone resorption process seen in hyperparathyroidism?
What is an accurate description of the usual course of Paget's disease of bone?
What is an accurate description of the usual course of Paget's disease of bone?
In the late stages of Paget's disease, what change occurs in the bone that is observable radiologically?
In the late stages of Paget's disease, what change occurs in the bone that is observable radiologically?
What is a key function of the p62/sequestosome 1 (SQSTM1) gene in the context of Paget's disease?
What is a key function of the p62/sequestosome 1 (SQSTM1) gene in the context of Paget's disease?
What is the primary intended action of bisphosphonate medications in the treatment of Paget's disease?
What is the primary intended action of bisphosphonate medications in the treatment of Paget's disease?
Which genetic mutation is most closely associated with Paget's disease of bone?
Which genetic mutation is most closely associated with Paget's disease of bone?
In the acute phase of Paget's disease of bone, which histological feature is most characteristic?
In the acute phase of Paget's disease of bone, which histological feature is most characteristic?
What best describes bone quality?
What best describes bone quality?
Why might long-term intravenous bisphosphonate treatment carry potential risks?
Why might long-term intravenous bisphosphonate treatment carry potential risks?
In sclerosing bone diseases, which of the following cellular activities goes unchecked, leading to increased bone density?
In sclerosing bone diseases, which of the following cellular activities goes unchecked, leading to increased bone density?
What feature distinguishes osteolysis in Paget's disease from other lytic bone lesions?
What feature distinguishes osteolysis in Paget's disease from other lytic bone lesions?
A researcher is examining potential genetic factors that could lead to rheumatoid arthritis. Which gene would be the most relevant to examine?
A researcher is examining potential genetic factors that could lead to rheumatoid arthritis. Which gene would be the most relevant to examine?
What causes the NET result and increased activity from bone?
What causes the NET result and increased activity from bone?
What serum level concentrations can indicate that you are developing osteomalacia?
What serum level concentrations can indicate that you are developing osteomalacia?
What alteration is present on radiology results of osteomalacia?
What alteration is present on radiology results of osteomalacia?
Which situation can lead to Vitamin D resistance when a patient also has waste phosphate that requires Vitamin D?
Which situation can lead to Vitamin D resistance when a patient also has waste phosphate that requires Vitamin D?
As we age, progenitor osteoblast cells are morphing into what other cells?
As we age, progenitor osteoblast cells are morphing into what other cells?
Which fracture is an unlikely indicator of Osteoporosis?
Which fracture is an unlikely indicator of Osteoporosis?
A 70-year-old with a hip fracture after falling. The bone mineral density T-score is -3.0. What is the most appropriate treatment?
A 70-year-old with a hip fracture after falling. The bone mineral density T-score is -3.0. What is the most appropriate treatment?
In osteomalacia, there is a relationship that reflects calcium and phosphate levels. Which selection reflects this?
In osteomalacia, there is a relationship that reflects calcium and phosphate levels. Which selection reflects this?
A patient has advanced secondary hyperparathyroidism due to chronic kidney disease. Which location is least likely to exhibit?
A patient has advanced secondary hyperparathyroidism due to chronic kidney disease. Which location is least likely to exhibit?
Following a Pagets disease diagnosis, there is an elevated serum alkaline phosphatase level. However, there is no demonstrable bony abnormalities on the x-ray. What is the next appropriate step?
Following a Pagets disease diagnosis, there is an elevated serum alkaline phosphatase level. However, there is no demonstrable bony abnormalities on the x-ray. What is the next appropriate step?
What are the late signs of Paget's disease?
What are the late signs of Paget's disease?
During the early stages of Paget's disease, what histological result can identify it when providing diagnostic features?
During the early stages of Paget's disease, what histological result can identify it when providing diagnostic features?
When handling Paget's disease, what can be done to support the patient?
When handling Paget's disease, what can be done to support the patient?
What is the key distinction between surgical action and bisphosphonates for Paget's disease?
What is the key distinction between surgical action and bisphosphonates for Paget's disease?
What can happen as a result from primary hyperparathyroidism?
What can happen as a result from primary hyperparathyroidism?
What occurs when there is reduced Vitamin D during osteomalacia?
What occurs when there is reduced Vitamin D during osteomalacia?
Which of the following best describes the use of x-rays in diagnosing osteoporosis?
Which of the following best describes the use of x-rays in diagnosing osteoporosis?
Which best describes the use and effectiveness of a bone biopsy?
Which best describes the use and effectiveness of a bone biopsy?
Which of the following bone remodeling processes is characteristic of bone-wasting diseases like osteoporosis?
Which of the following bone remodeling processes is characteristic of bone-wasting diseases like osteoporosis?
What causes endogenous reductions when pertaining to Vitamin D?
What causes endogenous reductions when pertaining to Vitamin D?
In sclerosing bone diseases, which type of bone cellular process goes unchecked?
In sclerosing bone diseases, which type of bone cellular process goes unchecked?
If the diagnosis is unclear for a Bone Scan, what is the next best step?
If the diagnosis is unclear for a Bone Scan, what is the next best step?
What is the term for the late-stage progression of imaging results where there is not a clear imaging outcome?
What is the term for the late-stage progression of imaging results where there is not a clear imaging outcome?
In cases of hypophosphaternica and neoplasticism, what form of osteomalacia is present?
In cases of hypophosphaternica and neoplasticism, what form of osteomalacia is present?
Which of the following is the most common metabolic bone disease?
Which of the following is the most common metabolic bone disease?
In osteoporosis, compromised bone strength leads to an increased risk of:
In osteoporosis, compromised bone strength leads to an increased risk of:
What two factors determine bone strength?
What two factors determine bone strength?
Which of the following is a typical fracture site associated with osteoporosis?
Which of the following is a typical fracture site associated with osteoporosis?
What is a key characteristic of osteoporotic fragility fractures?
What is a key characteristic of osteoporotic fragility fractures?
What is the main concern regarding osteoporosis?
What is the main concern regarding osteoporosis?
In bone-wasting diseases like osteoporosis, what process is exaggerated?
In bone-wasting diseases like osteoporosis, what process is exaggerated?
What is the term for the amount of mineral per volume in bone?
What is the term for the amount of mineral per volume in bone?
What leads to accelerated bone loss following menopause?
What leads to accelerated bone loss following menopause?
What is the role of osteoprotegerin in the bone remodeling process?
What is the role of osteoprotegerin in the bone remodeling process?
Histologically, what cellular change is seen in osteoporosis?
Histologically, what cellular change is seen in osteoporosis?
Which biochemical marker, measured in serum, is specifically indicative of bone formation?
Which biochemical marker, measured in serum, is specifically indicative of bone formation?
Which tool has become the 'gold standard' for osteoporosis diagnosis?
Which tool has become the 'gold standard' for osteoporosis diagnosis?
What is the T-score range in densitometry that defines osteopenia?
What is the T-score range in densitometry that defines osteopenia?
What characterizes osteomalacia?
What characterizes osteomalacia?
What is the most common cause of osteomalacia?
What is the most common cause of osteomalacia?
What vitamin deficiency states are specifically associated with osteomalacia or Rickets?
What vitamin deficiency states are specifically associated with osteomalacia or Rickets?
Which of the following is most linked to Rickets and/or Osteomalacia?
Which of the following is most linked to Rickets and/or Osteomalacia?
What alterations in serum concentrations are typically observed in osteomalacia?
What alterations in serum concentrations are typically observed in osteomalacia?
What are pseudofractures (Looser zones)?
What are pseudofractures (Looser zones)?
In the context of osteomalacia, what does the term 'Impaired metabolism' refer to regarding bone?
In the context of osteomalacia, what does the term 'Impaired metabolism' refer to regarding bone?
What condition can result in bowed legs or deformed bones?
What condition can result in bowed legs or deformed bones?
What characterizes primary hyperparathyroidism?
What characterizes primary hyperparathyroidism?
What is a distinctive bone change observed in hyperparathyroidism?
What is a distinctive bone change observed in hyperparathyroidism?
What is a common cause of primary hyperparathyroidism?
What is a common cause of primary hyperparathyroidism?
What is the expected outcome of increased osteoclast activity secondary to production of PTH?
What is the expected outcome of increased osteoclast activity secondary to production of PTH?
What are the three phases of Paget's disease of bone?
What are the three phases of Paget's disease of bone?
Diagnostic results of Paget's Disease include
Diagnostic results of Paget's Disease include
Histologically, what pattern is seen in the acute phase of Paget's disease of bone?
Histologically, what pattern is seen in the acute phase of Paget's disease of bone?
How does osteolytic activity relate to sclerosteosis?
How does osteolytic activity relate to sclerosteosis?
Regarding bone remodeling, what signifies the initiation of the process?
Regarding bone remodeling, what signifies the initiation of the process?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Autoimmune Arthritis
- Inflammatory and autoimmune processes can affect joints as part of systemic involvement.
- Autoimmune arthritides include rheumatoid arthritis (RA), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), psoriatic arthritis, Behçet disease, and ankylosing spondylitis.
- Systemic autoimmune arthritides and 'connective tissue disorders' are often used interchangeably.
- Please also refer to immunology lectures.
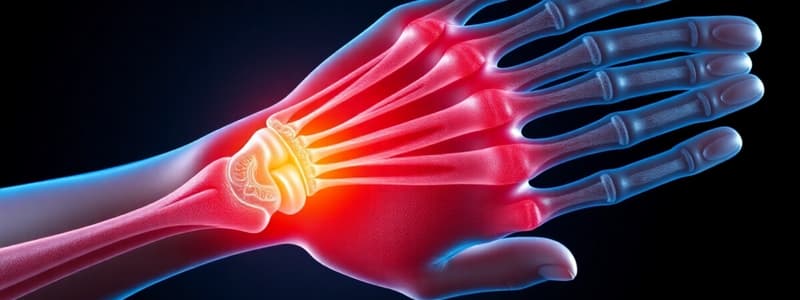
Rheumatoid Arthritis
- RA is a common, chronic, multisystem, progressive autoimmune disorder.
- RA primarily involves the joints, but most patients have at least one other site of involvement.
- Seldom can RA present with no joint involvement
- Other sites of involvement include skin, lung, heart, pericardium, subcutis, vessels, salivary and lacrimal glands, with common presentations including rheumatoid nodules and vasculitis.
- The incidence where Females > Males is 3:1
- Approximately 0.5-1% of the population is affected, with variations in prevalence depending on ethnicity and a slight familial tendency.
- If you have a family member with SLE or scleroderma, the likelihood of developing RA goes up substantially
- Onset commonly occurs in the 30s and 40s across all age groups, with the disease following a progressive and relapsing-remitting course.
- Some may first be diagnosed in their 70s that have had it since 30s/40s
- Rheumatoid arthritis is most commonly seen as a pediatric arthritis
- 75% of patients are HLA-DR4 positive.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis is unrelated to rheumatic fever or rheumatic heart disease which is caused by post-streptococcal infection.
Immunology of Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Raised serum Ig is typical, often exhibiting a characteristic antibody against Ig, known as Rheumatoid Factor (RF).
- Not everyone who has RF is positive will have RA, and vice versa
- Seronegative arthritis is RF negative, at least initially, with RF levels tending to correlate with severity.
- RF levels may sero convert over time
- Evidence indicates that disease progression is driven more by cellular immune mechanisms than humoral ones.
- Cellular & humoral immune responses are both adaptive immunity
Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis
- RA is initiated by CD4+ helper T cells.
- Exact triggers are mostly unknown, with interplay between susceptibility genes (HLA) and environmental factors.
- A lot of patients have a history of infection
- Failure of immune tolerance, and more common in smokers/ex smokers
- Pathological changes are mediated by cytokines released by CD4+ T cells in a immune cascade.
- HLA-DR4 is the susceptibility gene
- IFN-γ from Th1 cells activates macrophages and resident synovial cells.
- IL-17 from Th17 cells recruits neutrophils and monocytes.
- RANKL expressed on activated T cells stimulates bone resorption.
- TNF and IL-1 from macrophages stimulate resident synovial cells to secrete proteases that destroy hyaline cartilage.
- TNF has become extremely important in treatment.
Stages of Rheumatoid Arthritis
- The four stages of RA include triggering, maturation, targeting, and fulminant.
- Stage 1, Triggering stage involves anti-citrullinated peptide antibody (ACPA) production.
- Elevated ACPA production is caused by a combination of genetics and environment.
- Causal genetic factors include genes associated with MHC, particularly HLA-DR4 ("Shared epitope" hypothesis) and predicting response to treatment: HLA-DRB1, TRAF1, and others.
- Environmental factors could be noxious agents such as smoke and silica and infectious agents, Epstein-Barr Virus, and dietary factors influencing the gut.
- Stage 2, Maturation stage is initiated at the site of secondary lymphoid tissue or bone marrow.
- Citrullination of proteins active T-cells and B-cells results in more ACPA production.
- Stage 3, The Targeting Stage involves synovitis and joint swelling, and ACPA leads to elevation in cytokines e.g. TNF-alpha, IL-17A etc.
- Stage 3 also involves infiltration of monocytes, macrophages, mast cells, DC cells, T and B cells which are the predominant cell types.
- Stage 4, the Fulminant stage, involves pannus, and synovial hyperplasia encroaches on articular cartilage.
- This involves an inappropriate attempts at healing & repair coupled with inflammation
- There is bone and cartilage destruction, and impacts joint capsules and ligaments.
- Fibrous fusion results in ankylosis.
Clinical Presentation of Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Clinical presentation includes fatigue, malaise, musculoskeletal pain (worse in the morning), and localized joint symptoms persisting and progressing over weeks to months, and unpredictable course.
- Wax and wanes, good days & bad days
- Generally symmetrical and small joints >> large joints (usually distal→proximal progression and frequency).
- Hands & feet
- In hands and feet, MCP and PIP joints of all digits are affected, which leads to radial deviation of the wrist, ulnar deviation of the fingers, and flexion-hyperextension of fingers (swan-neck and boutonnière deformities).
- Systemic symptoms and lesions vary, and can include pulmonary fibrosis from lung lesions and skin and subcutaneous nodules, and purpura, or range of other symptoms.
- Sequelae include joint fusion, deformity of joints, disability, and side effects of immunosuppression.
Pathological Findings of Rheumatoid Arthritis in Joints
- The result is a protein and lymphocyte rich inflammatory infiltrate.
- Like in tonsils
- This includes severe lymphocytosis in joints, lymphoid tissue with germinal centers and secondary follicles, and plasma cells producing autoantibodies including anti-citrullinated peptide antibodies/ACPAs, IgM and IgA against IgG Fc regions.
- Oedematous, thickened, and hyperplastic synovium and fibrin rich exudate (pannus).
- A pannus will form a layer on a surface.
- Angiogenesis results in increased vascularity
- Osteoclastic activity in subchondral bone lead to bone microcysts and collapse.
- A fibrous ankylosis, which ossifies into bone, forms between the joint spaces
- healing process similiar to a fracture
Pathological Findings - Extra-articular
- Rheumatoid nodules are necrotic cores rimmed by palisaded macrophages (special type of granuloma), hand, arm, foot, elbow.
- Necrobotic granuloma
- Vasculitis is typically leukocytoclastic pattern, small and large arteries, purpura of skin and nails, ulcers of skin, can also affect internal organs such as the pleura, pericardium, and lung, leading to chronic pulmonary fibrosis, and eyes (uveitis and keratoconjunctivitis).
- Non-healing
- Tendonitis and myositis also occurs and contributes to deformities
- Non-specific
Comparative Features of Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Osteoarthritis is caused by mechanical injury to articular cartilage, while Rheumatoid Arthritis is autoimmunity.
- Inflammation exacerbates cartilage damage in Osteoarthritis, while cartilage destruction is caused by T-cells and antibodies to joint antigens in Rheumatoid Arthritis.
- Joint involvement is primarily weight bearing joints in Osteoarthritis while Rheumatoid Arthritis small joints of fingers and progresses to multiple joints.
- Pathologically, Osteoarthritis has cartilage degeneration and fragmentation, bone spurs, subchondral cysts; minimal inflammation whereas Rheumatoid Arthritis has inflammatory pannus invading and destroying cartilage; severe chronic inflammation; joint fusion (ankylosis).
- Rheumatoid Arthritis has various antibodies present, including ACPA and rheumatoid factor.
- Osteoarthritis has no serum antibodies while Rheumatoid Arthritis involvement extends to other organs (lungs, heart, others).
Crystal Arthropathies: Urate (Gout)
- Hyperuricemia leads to precipitation of urate crystals in joints, activation of inflammatory cascade, tissue damage, and formation of articular and subcutaneous tophi.
- Gout usually appears after 20-30 years of hyperuricemia.
- About 10% of individuals with hyperuricemia develop gout.
- Risk factors to Gout include age of the person and duration of the hyperuricemia, sex (males > females), genetic predisposition including X-linked HGPRT abnormalities and some inherited forms, alcohol consumption, diet including high urates (offal, red meat, soft drinks, seafood, beer, corn syrup), and the use of thiazides.
Crystal Arthropathies: CPPD (Calcium Pyrophosphate Deposition Disease)
- CPPD is caused by calcium pyrophosphate deposition.
- This used to be known a Pseudo gout
- Usually people over 50 are affected, mostly asymptomatic and may be associated with same process that causes DJD.
- degenerative joint disease (osteoarthritis)
- If symptoms present it is very similar to Gout , however treatment is different as there is no specific management (symptom relief only).
Reactive (postinfectious) arthritis
- Immunologically mediated, not due to direct joint infection.
- This is a common Differential Diagnosis for young people with joint pain
- Reactive arthritis has a Triad of arthritis, nongonococcal urethritis or cervicitis and conjunctivitis.
- Includes mono or oligoarticular arthritis that occurs days to weeks after genitourinary (Chlamydia) or gastrointestinal infection (Shigella, Salmonella, Yersinia, Campylobacter and others).
- Usually lasts for up to 6 months, symptoms may recur and if chronic can result in joint fusion and tendon changes.
Septic Arthritis / Osteomyelitis
- Refer to microbiology notes and workshop specimens.
Further resources
- American College of Rheumatology: Classification, response and remission criteria for a wide range of rheumatological disease: https://www.rheumatology.org/Practice-Quality/Clinical-Support/Criteria
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: in and out of the joint (eMedicine slideshow and quiz) https://reference.medscape.com/slideshow/rheumatoid-arthritis-6006748#1
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.