Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the main purpose of the asexual phase in sexual reproduction?
What is the main purpose of the asexual phase in sexual reproduction?
- To produce gametes for fertilization
- To cause pathogenesis through cell division (correct)
- To transform merozoites into micro and macrogametes
- To create an oocyst through sporogony
What happens to the zygote after fertilization in the sexual reproduction phase?
What happens to the zygote after fertilization in the sexual reproduction phase?
- It transforms into either a tachyzoite or a bradyzoite
- It forms an oocyst surrounded by a protective wall (correct)
- It immediately bursts to release merozoites
- It undergoes rapid division to become shizonts
How many sporozoites are typically contained within a single sporulated oocyst?
How many sporozoites are typically contained within a single sporulated oocyst?
- 16
- 2
- 8 (correct)
- 4
Which of the following statements correctly distinguishes between tachyzoites and bradyzoites?
Which of the following statements correctly distinguishes between tachyzoites and bradyzoites?
What is the process of sporogony primarily responsible for?
What is the process of sporogony primarily responsible for?
In asexual reproduction, what is the term for the fragile baby form that ends up in the host?
In asexual reproduction, what is the term for the fragile baby form that ends up in the host?
The trophozoite is the ___ and ____ form
The trophozoite is the ___ and ____ form
Once the trophozoites are ready, they will copy and paste themselves. What are the terms used for “copy and paste”?
Once the trophozoites are ready, they will copy and paste themselves. What are the terms used for “copy and paste”?
What occurs during the excystment process?
What occurs during the excystment process?
How does the presence of a cyst stage influence the infectious potential of an organism?
How does the presence of a cyst stage influence the infectious potential of an organism?
What is the result of shizogony/merogony in the context of pathogens?
What is the result of shizogony/merogony in the context of pathogens?
If an organism exclusively exists in the trophozoite stage, what will be its infectious form?
If an organism exclusively exists in the trophozoite stage, what will be its infectious form?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Asexual Reproduction
- Protozoa reproduce asexually through schizogony/merogony.
- Schizogony is responsible for pathogenesis (disease development).
- During schizogony, cells divide asexually, usually three times.
- The cells die when the schizonts (asexual reproductive units) burst out.
- Schizonts transform into merozoites when they reach their final stage of asexual reproduction.
Sexual Reproduction
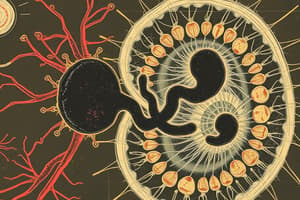
- Sexual reproduction involves gametogony and sporogony.
- Merozoites differentiate into gametes, forming an oocyst.
- Gametogony involves the formation of macrogametes (female) and microgametes (male).
- Microgametes fertilize macrogametes, producing a zygote.
- A wall forms around the zygote to create an oocyst.
- Oocysts undergo sporogony, which produces a sporulated oocyst filled with sporozoites.
- Sporozoites are the infective form of the protozoa.
- Each sporulated oocyst contains eight sporozoites, housed in either two or four sporocysts.
Intermediate Host Forms
- Some parasites have distinct forms within an intermediate host.
- Tachyzoites are rapidly dividing forms associated with vertical transmission (mother to offspring) and abortions.
- Bradyzoites are slowly dividing forms that cause muscle chills until consumed by a final host.
- Tachyzoites and bradyzoites represent different strategies for sporozoites: rapid replication or a dormant stage.
Trophozoite and Cyst Life Stages
- Trophozoites multiply through schizogony/merogony, leading to potential host cell destruction and pathogenesis.
- Some organisms can develop into a cyst stage for survival outside the host.
- Cysts are protective, infective, and exogenous.
- The cyst is the infectious stage if present.
- If the organism lacks a cyst stage, trophozoites become the default infectious stage.
- Cysts or trophozoites are transmitted to new hosts, initiating reinfection.
- Cysts undergo excystation, releasing the trophozoite.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.