Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary focus of behaviorism?
What is the primary focus of behaviorism?
- Environmental events (correct)
- Biological factors
- Cultural influences
- Internal mental processes
Who proposed methodological behaviorism and in what year?
Who proposed methodological behaviorism and in what year?
- John B. Watson, 1959
- Albert Bandura, 1960
- B.F. Skinner, 1924 (correct)
- Ivan Pavlov, 1900
What is radical behaviorism?
What is radical behaviorism?
- A technique that Skinner assessed the reinforcement histories of the discriminative stimuli that emit behavior
- A theory that behavior can be decomposed into atomistic parts or molecules
- A form of psychotherapy that focuses on changing behavior patterns through conditioning techniques
- A philosophy that accepts feelings and introspection as behaviors subject to scientific investigation (correct)
What is applied behavior analysis?
What is applied behavior analysis?
What is the difference between behavior therapy and cognitive-behavior therapy?
What is the difference between behavior therapy and cognitive-behavior therapy?
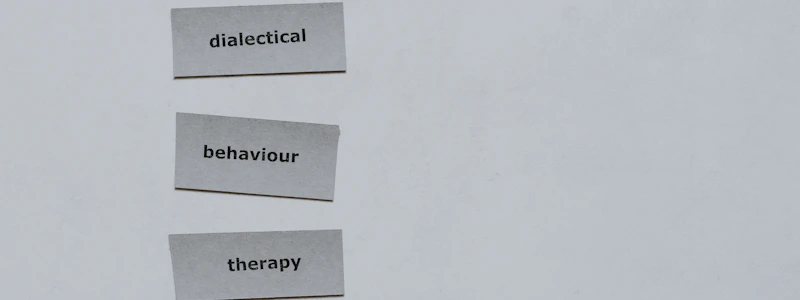
What is dialectical behavior therapy (DBT)?
What is dialectical behavior therapy (DBT)?
What is community reinforcement approach and family training?
What is community reinforcement approach and family training?
Who are some notable behaviorists?
Who are some notable behaviorists?
What is the focus of exposure therapies?
What is the focus of exposure therapies?
Flashcards
What is Behaviorism?
What is Behaviorism?
Understanding behavior through environmental events, reflexes, reinforcement, punishment, and motivational states.
Methodological Behaviorism
Methodological Behaviorism
Understanding behavior by measuring only observable behaviors and events.
Radical Behaviorism
Radical Behaviorism
Accepts internal states (feelings, thoughts) as behaviors subject to scientific investigation.
Discriminative Stimuli
Discriminative Stimuli
Signup and view all the flashcards
Behavior Informatics
Behavior Informatics
Signup and view all the flashcards
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA)
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Behavioral Therapy
Behavioral Therapy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Exposure Therapy
Exposure Therapy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Operant Conditioning
Operant Conditioning
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Behaviorism: A Systematic Approach to Understanding Behavior
-
Behaviorism is a systematic approach to understanding the behavior of humans and other animals.
-
It focuses primarily on environmental events and assumes that behavior is either a reflex or a consequence of an individual's history, reinforcement, punishment contingencies, and motivational state.
-
Behaviorism emerged in the early 1900s as a reaction to traditional forms of psychology and depth psychology.
-
John B. Watson devised methodological behaviorism in 1924, which sought to understand behavior by only measuring observable behaviors and events.
-
B.F. Skinner proposed radical behaviorism in 1959, which accepts feelings, states of mind, and introspection as behaviors subject to scientific investigation.
-
Operant conditioning, a technique that Skinner assessed the reinforcement histories of the discriminative stimuli that emit behavior, became the basis for his philosophy called radical behaviorism.
-
Applied behavior analysis, the application of radical behaviorism, is used in a variety of contexts, including applied animal behavior and treatment of mental disorders, such as autism and substance abuse.
-
Behaviorism and cognitive schools of psychological thought do not agree theoretically, but they have complemented each other in the cognitive-behavior therapies.
-
Behaviourism is a psychological movement that can be contrasted with philosophy of mind.
-
Behaviorism takes a functional view of behavior, and it is sometimes argued that Ludwig Wittgenstein defended a logical behaviorist position.
-
Gilbert Ryle defended a distinct strain of philosophical behaviorism, and Daniel Dennett acknowledges himself to be a type of behaviorist.
-
Behaviorism focuses on one particular view of learning: a change in external behavior achieved through using reinforcement and repetition to shape the behavior of learners.Behaviorism: Theory, Criticisms, and Contemporary Applications
-
Behavior can be decomposed into atomistic parts or molecules, but it is best understood as the ultimate product of an organism's history.
-
A complete understanding of behavior requires understanding of selection history at three levels: biology, behavior, and culture.
-
Theoretical behaviorism recognizes that an organism has a state and sensitivity to stimuli and the ability to emit responses that can be selected by operant reinforcement.
-
Cultural analysis has always been at the philosophical core of radical behaviorism, and behavior analysis is frequently used in game development.
-
Behavior informatics and behavior computing explore behavior intelligence and behavior insights from the informatics and computing perspectives.
-
Behaviorism was largely eclipsed as a result of the cognitive revolution, which criticized it for not examining mental processes.
-
Behavior therapy identifies and helps change people's unhealthy behaviors or destructive behaviors through learning theory and conditioning.
-
Applied behavior analysis (ABA) applies the principles of behavior analysis to change behavior and has emerged into a thriving field with many applications (e.g., developmental disabilities, animal behavior, clinical psychology).
-
Early behavioral interventions based on ABA are empirically validated for teaching children with autism, and ABA is the standard of care for adults with substance-use disorders.
-
Cognitive-behavior therapy often overlaps considerably with the clinical behavior analysis subfield of ABA, but differs in that it initially incorporates cognitive restructuring and emotional regulation to alter a person's cognition and emotions.
-
Dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) includes cognitive restructuring, emotional regulation, distress tolerance, counterconditioning, and contingency management, and is widely researched for reducing the risk of suicide in psychiatric patients with borderline personality disorder.
-
Exposure therapies, ranging from eye movement desensitization and reprocessing therapy to exposure and response prevention, are well-established in the research literature for treating phobic, post-traumatic stress, and other anxiety disorders.Behavioral Therapy Summary
-
Behavioral therapy is a form of psychotherapy that focuses on changing behavior patterns through conditioning techniques.
-
The approach is based on the idea that behaviors are learned and can be unlearned or modified.
-
Behavioral therapy can be used to treat a wide range of mental health conditions, including anxiety, depression, and substance abuse.
-
The therapy is often short-term and structured, with a focus on specific goals and measurable outcomes.
-
Techniques used in behavioral therapy include exposure therapy, cognitive restructuring, and operant conditioning.
-
Exposure therapy involves gradually exposing a person to the object or situation that triggers their anxiety or fear, while cognitive restructuring helps people identify and challenge negative thoughts and beliefs.
-
Operant conditioning involves rewarding positive behaviors and ignoring or punishing negative behaviors to encourage positive change.
-
Behavioral therapy has been found to be as effective as medication for some conditions, and more effective than traditional talk therapy for others.
-
Other therapies that incorporate behavioral learning principles include community reinforcement approach and family training, and habit reversal training.
-
Some notable behaviorists include B.F. Skinner, Ivan Pavlov, and Albert Bandura.
-
Behavioral therapy is often used in conjunction with other forms of treatment, such as medication and talk therapy.
-
APA 7th edition format: Last name, First initial. (Year). Title of article. Title of Journal, volume number(issue number), page range.
-
Further reading on behavioral therapy can be found in books such as "Cognitive Behavioural Therapy: A Teach Yourself Guide" by Christine Wilding and "Behavioral Activation: Distinctive Features" by Jonathan Kanter and Andrew Busch.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.