Podcast
Questions and Answers
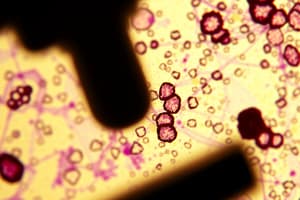
What is the total number of cells shown in the image of the cress root?
What is the total number of cells shown in the image of the cress root?
- 10
- 5 (correct)
- 25
- 2
What is the likely reason the cells in the cress root appear green in color?
What is the likely reason the cells in the cress root appear green in color?
- The cells have a high concentration of mitochondria to produce energy
- The cells contain chlorophyll and are able to perform photosynthesis (correct)
- The cells are filled with a colored pigment to attract pollinators
- The cells are undergoing rapid cell division and growth
Which sub-cellular structure is responsible for the production of energy in the cells shown in the cress root image?
Which sub-cellular structure is responsible for the production of energy in the cells shown in the cress root image?
- Mitochondria (correct)
- Nucleus
- Endoplasmic reticulum
- Chloroplast
What is the primary function of the cell wall in plant cells like those shown in the cress root image?
What is the primary function of the cell wall in plant cells like those shown in the cress root image?
What type of microscope was likely used to create the image of the cress root shown?
What type of microscope was likely used to create the image of the cress root shown?
If the magnification of the cress root image is x200, what is the actual size of the region shown in the image?
If the magnification of the cress root image is x200, what is the actual size of the region shown in the image?
What is the main function of the cell wall in a plant cell?
What is the main function of the cell wall in a plant cell?
What is the primary function of the cell wall in plant cells?
What is the primary function of the cell wall in plant cells?
Which of the following structures is responsible for converting light energy into chemical energy during photosynthesis in plant cells?
Which of the following structures is responsible for converting light energy into chemical energy during photosynthesis in plant cells?
Why might a red blood cell appear different under a light microscope compared to a plant cell?
Why might a red blood cell appear different under a light microscope compared to a plant cell?
If a plant cell has a diameter of 50 micrometers (μm) and a bacterial cell is 40 times smaller, what is the diameter of the bacterial cell in micrometers?
If a plant cell has a diameter of 50 micrometers (μm) and a bacterial cell is 40 times smaller, what is the diameter of the bacterial cell in micrometers?
Which part of a light microscope is responsible for focusing the light on the specimen?
Which part of a light microscope is responsible for focusing the light on the specimen?
Which two structures are found in plant cells but not in animal cells?
Which two structures are found in plant cells but not in animal cells?
What is the role of mitochondria in animal cells?
What is the role of mitochondria in animal cells?
What is the primary function of the vacuole in plant cells?
What is the primary function of the vacuole in plant cells?
What could be a reason for not being able to observe cells through a microscope?
What could be a reason for not being able to observe cells through a microscope?
How do red blood cells differ in structure from plant cells?
How do red blood cells differ in structure from plant cells?
Which of the following techniques is used to observe and study the structure of cells?
Which of the following techniques is used to observe and study the structure of cells?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Cell Structure and Microscopy
- Cells can be kept in a culture solution for 25 hours and the number of live cells can be monitored over time.
- The number of live cells increases during the first 20 hours, then decreases after 20 hours.
- One reason for the decrease in live cells after 20 hours could be a lack of nutrients or accumulation of waste products.
Microscope Use
- A student prepared animal cells to view using a microscope and used a microscope with a light source.
- The student used a light microscope to view the cells.
- Part A of the microscope is the eyepiece lens.
- Part B of the microscope is the condenser lens, which focuses light onto the specimen.
- If the student could not see any cells when looking through part A, it may be because the microscope was not focused correctly.
Cell Measurement
- The width of a cell can be measured using a ruler and a microscope.
- The real width of a cell can be calculated using the equation: real size mm = measured width mm / magnification.
- The width of a cheek cell can be calculated in micrometres (µm) by converting the measured width from mm to µm.
Cell Comparison
- Red blood cells are specialized animal cells that have a unique structure compared to plant cells.
- A red blood cell is 8 µm in diameter, while a bacterial cell is 40 times smaller, with a diameter of 0.2 µm.
Cell Parts and Functions
- Animal and plant cells have several parts, each with a different function.
- Cell parts include the nucleus, cytoplasm, cell membrane, and mitochondria, among others.
- The nucleus contains genetic material, the cytoplasm is the jelly-like substance inside the cell membrane, and mitochondria produce energy for the cell.
- Plant cells have additional parts, including a cell wall and chloroplasts, which are not found in animal cells.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.