Podcast
Questions and Answers
What are the main functions of the ankle joint?
What are the main functions of the ankle joint?
- Allows only for upward and downward movement.
- Functions as a hinge joint allowing for triplane motion. (correct)
- Acts only as a stabilizing structure.
- Functions solely as a pivot point.
Which ligaments are classified as medial ligaments of the ankle?
Which ligaments are classified as medial ligaments of the ankle?
- Posterior tibiofibular ligament, Inferior transverse ligament.
- Lateral collateral ligament, AITFL.
- Anterior talofibular ligament, Calcaneofibular ligament.
- Superficial deltoid, Deep deltoid. (correct)
What does the Lauge-Hansen classification system primarily consider?
What does the Lauge-Hansen classification system primarily consider?
- The type of treatment required for ankle fractures.
- The radiographic features of the fibular fracture.
- The involvement of soft tissue injuries.
- The foot position and direction of talar motion. (correct)
In the context of ankle fractures, what does the Danis-Weber classification relate to?
In the context of ankle fractures, what does the Danis-Weber classification relate to?
Which of the following is NOT a ligamentous structure associated with the medial aspect of the ankle?
Which of the following is NOT a ligamentous structure associated with the medial aspect of the ankle?
Which of the following best describes the purpose of the syndesmotic ligaments in the ankle?
Which of the following best describes the purpose of the syndesmotic ligaments in the ankle?
Which term refers to the first word in the Lauge-Hansen classification, describing the foot position?
Which term refers to the first word in the Lauge-Hansen classification, describing the foot position?
What anatomical structure is primarily responsible for the hinge motion at the ankle joint?
What anatomical structure is primarily responsible for the hinge motion at the ankle joint?
What characterizes a Stage 1 injury in Supination-Adduction according to the Lauge-Hansen classification?
What characterizes a Stage 1 injury in Supination-Adduction according to the Lauge-Hansen classification?
In the Danis-Weber classification, a Type C fracture is defined as:
In the Danis-Weber classification, a Type C fracture is defined as:
Which stage in the Lauge-Hansen Supination External Rotation classification involves injury to the posterior inferior tibiotalar ligament?
Which stage in the Lauge-Hansen Supination External Rotation classification involves injury to the posterior inferior tibiotalar ligament?
The injury characterized by a transverse fracture of the medial malleolus or deltoid ligament injury corresponds to which classification?
The injury characterized by a transverse fracture of the medial malleolus or deltoid ligament injury corresponds to which classification?
What type of fracture is identified in Danis-Weber Type B classification?
What type of fracture is identified in Danis-Weber Type B classification?
Which of the following describes the injury at Stage 2 of Pronation-Abduction classification?
Which of the following describes the injury at Stage 2 of Pronation-Abduction classification?
Which named fracture is specifically an AITFL avulsion from the anterolateral tibia?
Which named fracture is specifically an AITFL avulsion from the anterolateral tibia?
A fracture of the lateral malleolus distal to the syndesmosis is classified as:
A fracture of the lateral malleolus distal to the syndesmosis is classified as:
In the Lauge-Hansen classification, which stage corresponds to a vertical medial malleolar fracture?
In the Lauge-Hansen classification, which stage corresponds to a vertical medial malleolar fracture?
Which statement is true regarding the overlaps between Lauge-Hansen and Danis-Weber classifications?
Which statement is true regarding the overlaps between Lauge-Hansen and Danis-Weber classifications?
Which ligament serves as the main stabilization structure for the medial aspect of the ankle joint?
Which ligament serves as the main stabilization structure for the medial aspect of the ankle joint?
What is the correct order of foot position and talar motion in the Lauge-Hansen classification for Supination-External Rotation?
What is the correct order of foot position and talar motion in the Lauge-Hansen classification for Supination-External Rotation?
According to the Danis-Weber classification, which type of fracture is associated with a fibular fracture that is above the level of the syndesmosis?
According to the Danis-Weber classification, which type of fracture is associated with a fibular fracture that is above the level of the syndesmosis?
Which of the following best defines the relationship of the Inferior transverse tibiofibular ligament within the ankle anatomy?
Which of the following best defines the relationship of the Inferior transverse tibiofibular ligament within the ankle anatomy?
In the context of syndesmotic ligament injuries, which ligament is primarily a contributor to horizontal stability across the ankle?
In the context of syndesmotic ligament injuries, which ligament is primarily a contributor to horizontal stability across the ankle?
What is a key characteristic of a Pronation-Abduction injury in the Lauge-Hansen classification?
What is a key characteristic of a Pronation-Abduction injury in the Lauge-Hansen classification?
Which phrase best describes the Lauge-Hansen classification’s method of categorizing ankle fractures?
Which phrase best describes the Lauge-Hansen classification’s method of categorizing ankle fractures?
Which of the following is NOT a component of the syndesmotic ligaments in the ankle?
Which of the following is NOT a component of the syndesmotic ligaments in the ankle?
What type of fibular fracture is classified as Type A in the Danis-Weber classification?
What type of fibular fracture is classified as Type A in the Danis-Weber classification?
Which stage of the Lauge-Hansen Supination External Rotation classification involves a spiral fracture of the fibula?
Which stage of the Lauge-Hansen Supination External Rotation classification involves a spiral fracture of the fibula?
In the context of Lauge-Hansen classification, what does Stage 1 of Pronation-Abduction describe?
In the context of Lauge-Hansen classification, what does Stage 1 of Pronation-Abduction describe?
What is the injury characterized by a posterior malleolar fracture in the Pronation-Abduction classification?
What is the injury characterized by a posterior malleolar fracture in the Pronation-Abduction classification?
Which named fracture corresponds to an AITFL avulsion from the anteromedial fibula?
Which named fracture corresponds to an AITFL avulsion from the anteromedial fibula?
What characterizes Danis-Weber Type C classification?
What characterizes Danis-Weber Type C classification?
Which stage in Lauge-Hansen classifications describes a transverse avulsion type fracture of the distal fibula?
Which stage in Lauge-Hansen classifications describes a transverse avulsion type fracture of the distal fibula?
Which statement accurately reflects an overlap between the Danis-Weber and Lauge-Hansen classifications?
Which statement accurately reflects an overlap between the Danis-Weber and Lauge-Hansen classifications?
What type of injury is identified in Stage 3 of Supination-Adduction?
What type of injury is identified in Stage 3 of Supination-Adduction?
Which clinical evaluation aspect assesses the possibility of active bleeding in an ankle fracture case?
Which clinical evaluation aspect assesses the possibility of active bleeding in an ankle fracture case?
What is the primary goal of open reduction internal fixation (ORIF) in the management of ankle fractures?
What is the primary goal of open reduction internal fixation (ORIF) in the management of ankle fractures?
Which factor is NOT considered when evaluating the stability of an ankle fracture?
Which factor is NOT considered when evaluating the stability of an ankle fracture?
In the context of fracture healing processes, which phase primarily focuses on the re-establishment of structural integrity?
In the context of fracture healing processes, which phase primarily focuses on the re-establishment of structural integrity?
What classification scheme primarily helps in understanding the pattern of fracture based on external forces?
What classification scheme primarily helps in understanding the pattern of fracture based on external forces?
What is the significance of evaluating tibio-fibular overlap in ankle injuries?
What is the significance of evaluating tibio-fibular overlap in ankle injuries?
What does a widening of the medial clear space greater than 4 mm suggest?
What does a widening of the medial clear space greater than 4 mm suggest?
Which measurement indicates lateral ankle instability in a talar tilt evaluation?
Which measurement indicates lateral ankle instability in a talar tilt evaluation?
In evaluating syndesmotic injuries, which sign would indicate fibular shortening?
In evaluating syndesmotic injuries, which sign would indicate fibular shortening?
What does a normal measurement on the Shenton line suggest in ankle evaluations?
What does a normal measurement on the Shenton line suggest in ankle evaluations?
What is a primary purpose of performing a thorough neurovascular evaluation in ankle fractures?
What is a primary purpose of performing a thorough neurovascular evaluation in ankle fractures?
Which of the following is a possible outcome of insufficient treatment for a syndesmotic injury?
Which of the following is a possible outcome of insufficient treatment for a syndesmotic injury?
In the context of radiographic evaluation, what does a decrease in tibiotalar contact as reported by Ramsey and Hamilton indicate?
In the context of radiographic evaluation, what does a decrease in tibiotalar contact as reported by Ramsey and Hamilton indicate?
What defines an unstable ankle fracture?
What defines an unstable ankle fracture?
Which of the following is a disadvantage of closed reduction?
Which of the following is a disadvantage of closed reduction?
In the Charnley Maneuver, which step is performed last?
In the Charnley Maneuver, which step is performed last?
What is a key advantage of open reduction internal fixation (ORIF)?
What is a key advantage of open reduction internal fixation (ORIF)?
What does primary bone healing require?
What does primary bone healing require?
Which fracture pattern would be classified as spiral?
Which fracture pattern would be classified as spiral?
What is the primary role of a neutralization plate in ORIF?
What is the primary role of a neutralization plate in ORIF?
When is an interfragmentary screw primarily employed?
When is an interfragmentary screw primarily employed?
Which technique involves applying tension to compress the fracture line?
Which technique involves applying tension to compress the fracture line?
Which situation necessitates the fixation of a posterior malleolar fracture?
Which situation necessitates the fixation of a posterior malleolar fracture?
Which complication is commonly associated with open reduction internal fixation?
Which complication is commonly associated with open reduction internal fixation?
What is necessary for successful fracture pattern treatment?
What is necessary for successful fracture pattern treatment?
What is considered a disadvantage of using interfragmentary screws?
What is considered a disadvantage of using interfragmentary screws?
For a trimalleolar ankle fracture, what is the typical first method of stabilization?
For a trimalleolar ankle fracture, what is the typical first method of stabilization?
What is the primary advantage of minimally invasive fracture fixation using an intramedullary nail for elderly patients?
What is the primary advantage of minimally invasive fracture fixation using an intramedullary nail for elderly patients?
What challenge is most associated with managing diabetic ankle fractures?
What challenge is most associated with managing diabetic ankle fractures?
In evaluating syndesmotic injuries, what imaging finding indicates fibular shortening?
In evaluating syndesmotic injuries, what imaging finding indicates fibular shortening?
Which management strategy is crucial for addressing fracture blisters in ankle fractures?
Which management strategy is crucial for addressing fracture blisters in ankle fractures?
What factor limits the use of open reduction internal fixation (ORIF) in younger patients with ankle fractures?
What factor limits the use of open reduction internal fixation (ORIF) in younger patients with ankle fractures?
What is the main advantage of suture button fixation over screw fixation in syndesmotic injuries?
What is the main advantage of suture button fixation over screw fixation in syndesmotic injuries?
Which of the following best describes the purpose of a delta frame in unstable ankle fractures?
Which of the following best describes the purpose of a delta frame in unstable ankle fractures?
What is a common complication faced by diabetic patients with ankle fractures?
What is a common complication faced by diabetic patients with ankle fractures?
Which technique is emphasized to avoid blister formation during surgery?
Which technique is emphasized to avoid blister formation during surgery?
What is a significant consideration when evaluating syndesmotic injuries on X-rays?
What is a significant consideration when evaluating syndesmotic injuries on X-rays?
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO)?
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO)?
How does hemorrhoid-filled blister treatment differ from clear fluid-filled blister treatment?
How does hemorrhoid-filled blister treatment differ from clear fluid-filled blister treatment?
What is a primary risk associated with performing surgery after the formation of fracture blisters?
What is a primary risk associated with performing surgery after the formation of fracture blisters?
What defines a stable ankle fracture during evaluation?
What defines a stable ankle fracture during evaluation?
Which method is commonly used to evaluate the success of syndesmotic fixation post-operatively?
Which method is commonly used to evaluate the success of syndesmotic fixation post-operatively?
In diabetic ankle fracture management, which method helps to enhance healing in the absence of traditional fixation?
In diabetic ankle fracture management, which method helps to enhance healing in the absence of traditional fixation?
Which of the following is a hallmark of syndesmotic fixation with screws?
Which of the following is a hallmark of syndesmotic fixation with screws?
What is a key disadvantage of using intramedullary nail fixation in active young patients?
What is a key disadvantage of using intramedullary nail fixation in active young patients?
What is a typical goal of non-operative treatment for pilon fractures?
What is a typical goal of non-operative treatment for pilon fractures?
Which operative technique is most commonly employed for managing pilon fractures?
Which operative technique is most commonly employed for managing pilon fractures?
In the management of pilon fractures, what role does soft tissue play?
In the management of pilon fractures, what role does soft tissue play?
Which imaging technique is preferred for initial assessment of pilon fractures?
Which imaging technique is preferred for initial assessment of pilon fractures?
What classification scheme is most commonly used to categorize pilon fractures?
What classification scheme is most commonly used to categorize pilon fractures?
What is the primary limitation of non-operative treatment for displaced intra-articular fractures of the tibial plafond?
What is the primary limitation of non-operative treatment for displaced intra-articular fractures of the tibial plafond?
Which operative treatment technique is specifically designed for stabilizing fractures with minimal soft tissue disruption?
Which operative treatment technique is specifically designed for stabilizing fractures with minimal soft tissue disruption?
What is the main goal of stable fixation in pilon fracture management?
What is the main goal of stable fixation in pilon fracture management?
Which imaging technique is primarily used to assess the extent of bone fragments in pilon fractures?
Which imaging technique is primarily used to assess the extent of bone fragments in pilon fractures?
Type III fractures in the Ruedi and Allgower classification are characterized by which feature?
Type III fractures in the Ruedi and Allgower classification are characterized by which feature?
Which treatment approach is indicated for managing significant metaphyseal defects in pilon fractures?
Which treatment approach is indicated for managing significant metaphyseal defects in pilon fractures?
Which classification describes the degree of comminution associated with a fracture?
Which classification describes the degree of comminution associated with a fracture?
What is the role of axial compression in the evaluation of fracture fragments?
What is the role of axial compression in the evaluation of fracture fragments?
What is the primary objective during the application of an external fixator for ankle fractures?
What is the primary objective during the application of an external fixator for ankle fractures?
Which component is crucial for the reduction of pilon fractures associated with fibula fractures?
Which component is crucial for the reduction of pilon fractures associated with fibula fractures?
During which stage of surgical management is meticulous planning most critical?
During which stage of surgical management is meticulous planning most critical?
What is the typical duration before weight-bearing is encouraged after surgery for ankle fractures?
What is the typical duration before weight-bearing is encouraged after surgery for ankle fractures?
What is the significance of approaching the posterior aspect of the medial malleolar fragment during reduction?
What is the significance of approaching the posterior aspect of the medial malleolar fragment during reduction?
Which of the following best describes the outcome of high-energy pilon fractures?
Which of the following best describes the outcome of high-energy pilon fractures?
What is the focus of the initial treatment phase for soft tissue management in fractures?
What is the focus of the initial treatment phase for soft tissue management in fractures?
In the context of pilon fracture classifications, which fragment is typically addressed first during reduction?
In the context of pilon fracture classifications, which fragment is typically addressed first during reduction?
What characterizes the postoperative management plan after ankle fracture surgery?
What characterizes the postoperative management plan after ankle fracture surgery?
What is the primary aim of restoring the articular surface during surgery for ankle fractures?
What is the primary aim of restoring the articular surface during surgery for ankle fractures?
What is a significant impact of soft tissue trauma in the management of pilon fractures?
What is a significant impact of soft tissue trauma in the management of pilon fractures?
Which operative treatment approach is most appropriate for pilon fractures involving substantial displacement?
Which operative treatment approach is most appropriate for pilon fractures involving substantial displacement?
Which non-operative treatment option is typically suitable for non-displaced pilon fractures?
Which non-operative treatment option is typically suitable for non-displaced pilon fractures?
Which imaging technique is crucial for the detailed assessment of a pilon fracture?
Which imaging technique is crucial for the detailed assessment of a pilon fracture?
Which classification best describes pilon fractures that involve the tibial plafond?
Which classification best describes pilon fractures that involve the tibial plafond?
What role does accurate fibular length play in treating tibial deformity?
What role does accurate fibular length play in treating tibial deformity?
Which surgical technique is primarily focused on the reduction of the articular surface in pilon fractures?
Which surgical technique is primarily focused on the reduction of the articular surface in pilon fractures?
What is the primary goal of applying an external fixator in the management of fractures?
What is the primary goal of applying an external fixator in the management of fractures?
What is the recommended approach for soft tissue handling during surgical management of fractures?
What is the recommended approach for soft tissue handling during surgical management of fractures?
In the context of post-operative care, which recommendation is generally advised for early rehabilitation?
In the context of post-operative care, which recommendation is generally advised for early rehabilitation?
Which of the following surgical approaches is NOT mentioned in managing pilon fractures?
Which of the following surgical approaches is NOT mentioned in managing pilon fractures?
What is indicated to achieve the desired alignment of the talus during fracture treatment?
What is indicated to achieve the desired alignment of the talus during fracture treatment?
What is a significant outcome after poorly managed high-energy pilon fractures?
What is a significant outcome after poorly managed high-energy pilon fractures?
Which factor is most critical to address in the reduction and fixation of fractures?
Which factor is most critical to address in the reduction and fixation of fractures?
What is the appropriate timing for intervention in the surgical management of fractures?
What is the appropriate timing for intervention in the surgical management of fractures?
What is the primary focus of non-operative treatment for displaced intra-articular fractures of the tibial plafond?
What is the primary focus of non-operative treatment for displaced intra-articular fractures of the tibial plafond?
Which of the following operative treatment methods is NOT typically used in the management of Pilon fractures?
Which of the following operative treatment methods is NOT typically used in the management of Pilon fractures?
What does the AO classification for fractures include?
What does the AO classification for fractures include?
Which type of imaging technique is primarily used for assessing fracture fragments in tibial plateau injuries?
Which type of imaging technique is primarily used for assessing fracture fragments in tibial plateau injuries?
In the Ruedi and Allgower classification of fractures, which type indicates severely comminuted fractures with impaction?
In the Ruedi and Allgower classification of fractures, which type indicates severely comminuted fractures with impaction?
What is a critical principle when performing fixation for a Pilon fracture?
What is a critical principle when performing fixation for a Pilon fracture?
What is a fundamental limitation of non-operative treatment in managing intra-articular fractures?
What is a fundamental limitation of non-operative treatment in managing intra-articular fractures?
Which imaging technique is most suitable for detecting signs of axial compression injuries?
Which imaging technique is most suitable for detecting signs of axial compression injuries?
What aspect of morphology is primarily assessed for deformity correction?
What aspect of morphology is primarily assessed for deformity correction?
Which technique is emphasized for effectively managing morphological deformities?
Which technique is emphasized for effectively managing morphological deformities?
What is the recommended post-operative protocol in the initial weeks following surgery?
What is the recommended post-operative protocol in the initial weeks following surgery?
What role do compression socks play in the management of post-operative recovery?
What role do compression socks play in the management of post-operative recovery?
In the context of surgical approaches, which joint is notably involved in articular incongruity requiring attention?
In the context of surgical approaches, which joint is notably involved in articular incongruity requiring attention?
What is the primary goal in achieving anatomical reduction of the calcaneus during surgery?
What is the primary goal in achieving anatomical reduction of the calcaneus during surgery?
What is crucial for correcting a varus deformity during the Joint Depression-Sinus tarsi approach?
What is crucial for correcting a varus deformity during the Joint Depression-Sinus tarsi approach?
In the context of percutaneous reduction with ring fixation, which of the following is given less consideration?
In the context of percutaneous reduction with ring fixation, which of the following is given less consideration?
What surgical approach uses skeletal traction followed by fracture reduction?
What surgical approach uses skeletal traction followed by fracture reduction?
What impact does a minimally invasive approach have on post-operative protocols?
What impact does a minimally invasive approach have on post-operative protocols?
Which of the following ROWE classifications describes a fracture involving the sustentaculum tali?
Which of the following ROWE classifications describes a fracture involving the sustentaculum tali?
Which type of morphology needs to be addressed to ensure optimal joint function following correction?
Which type of morphology needs to be addressed to ensure optimal joint function following correction?
Regarding post-operative protocols, what is a critical factor for ensuring successful outcomes after calcaneal surgery?
Regarding post-operative protocols, what is a critical factor for ensuring successful outcomes after calcaneal surgery?
Which incision length characterization relates to the sinus tarsi approach originally used?
Which incision length characterization relates to the sinus tarsi approach originally used?
Which statement accurately reflects the soft tissue considerations during the anterior process fracture treatment?
Which statement accurately reflects the soft tissue considerations during the anterior process fracture treatment?
In the Joint Depression-Sinus tarsi Approach, what is vital to ensure after the anatomical correction?
In the Joint Depression-Sinus tarsi Approach, what is vital to ensure after the anatomical correction?
What type of calcaneal fracture is most commonly associated with a fall from height and results in intra-articular damage?
What type of calcaneal fracture is most commonly associated with a fall from height and results in intra-articular damage?
What is a primary consideration regarding soft tissue during the Joint Depression-Sinus tarsi approach?
What is a primary consideration regarding soft tissue during the Joint Depression-Sinus tarsi approach?
In addressing shortening of the tuberosity fragment, which aspect is prioritized?
In addressing shortening of the tuberosity fragment, which aspect is prioritized?
In the context of deformity correction techniques, which procedure prioritizes sparing soft tissue integrity?
In the context of deformity correction techniques, which procedure prioritizes sparing soft tissue integrity?
What is a key goal of the sinus tarsi approach in terms of deformity correction?
What is a key goal of the sinus tarsi approach in terms of deformity correction?
What is the primary focus of the Joint Depression-Sinus tarsi approach in surgical treatment?
What is the primary focus of the Joint Depression-Sinus tarsi approach in surgical treatment?
In the context of percutaneous fixation, which of the following classifications is specifically referenced?
In the context of percutaneous fixation, which of the following classifications is specifically referenced?
What is the recommended non-weightbearing (NWB) duration in a splint for a patient post-Joint Depression-Sinus tarsi surgery?
What is the recommended non-weightbearing (NWB) duration in a splint for a patient post-Joint Depression-Sinus tarsi surgery?
What aspect of imaging is crucial for evaluating articular incongruity in surgeries related to the subtalar joint?
What aspect of imaging is crucial for evaluating articular incongruity in surgeries related to the subtalar joint?
What is one of the key postoperative treatments following a Joint Depression-Sinus tarsi approach?
What is one of the key postoperative treatments following a Joint Depression-Sinus tarsi approach?
What is the primary indication for using the Joint Depression-Sinus Tarsi Approach?
What is the primary indication for using the Joint Depression-Sinus Tarsi Approach?
Which outcome is NOT associated with the use of the Joint Depression-Sinus Tarsi Approach?
Which outcome is NOT associated with the use of the Joint Depression-Sinus Tarsi Approach?
What does the morphology correction in the Joint Depression-Sinus Tarsi Approach specifically target?
What does the morphology correction in the Joint Depression-Sinus Tarsi Approach specifically target?
Which of the following accurately describes the surgeon's role in the Joint Depression-Sinus Tarsi Approach?
Which of the following accurately describes the surgeon's role in the Joint Depression-Sinus Tarsi Approach?
What is the initial length of the incision used in the Joint Depression-Sinus Tarsi Approach?
What is the initial length of the incision used in the Joint Depression-Sinus Tarsi Approach?
In the context of the Joint Depression-Sinus Tarsi Approach, which aspect of healing is highlighted as being generally quicker?
In the context of the Joint Depression-Sinus Tarsi Approach, which aspect of healing is highlighted as being generally quicker?
Which of the following describes a key factor in patient selection for the Joint Depression-Sinus Tarsi Approach?
Which of the following describes a key factor in patient selection for the Joint Depression-Sinus Tarsi Approach?
What is a critical aspect of imaging in the management of fractures treated via the Joint Depression-Sinus Tarsi Approach?
What is a critical aspect of imaging in the management of fractures treated via the Joint Depression-Sinus Tarsi Approach?
What does a decrease in Böhler’s angle suggest about a calcaneal fracture?
What does a decrease in Böhler’s angle suggest about a calcaneal fracture?
Which of the following correctly describes the Critical angle of Gissane?
Which of the following correctly describes the Critical angle of Gissane?
In the Sanders classification, which Roman numeral indicates a fracture without displacement?
In the Sanders classification, which Roman numeral indicates a fracture without displacement?
What is the purpose of the Essex-Lopresti classification?
What is the purpose of the Essex-Lopresti classification?
What do Broden’s Views in imaging allow for?
What do Broden’s Views in imaging allow for?
Which feature is indicative of the medial wall reduction procedure during surgery?
Which feature is indicative of the medial wall reduction procedure during surgery?
What anatomical aspect is primarily evaluated using the Harris Beath axial view?
What anatomical aspect is primarily evaluated using the Harris Beath axial view?
What is the characteristic angle for Böhler’s angle in a healthy calcaneus?
What is the characteristic angle for Böhler’s angle in a healthy calcaneus?
Which type of fracture characterizes a fall from height with the foot dorsiflexed, leading to joint depression and comminution?
Which type of fracture characterizes a fall from height with the foot dorsiflexed, leading to joint depression and comminution?
What occurs in Sanders Type II fractures that distinguishes it from Type I fractures?
What occurs in Sanders Type II fractures that distinguishes it from Type I fractures?
In the Hawkins Classification, what is the prognosis associated with a Hawkins Type 3 fracture?
In the Hawkins Classification, what is the prognosis associated with a Hawkins Type 3 fracture?
What is indicated by the presence of a shear fracture that divides the calcaneus into two parts, according to the Essex-Lopresti classification?
What is indicated by the presence of a shear fracture that divides the calcaneus into two parts, according to the Essex-Lopresti classification?
Which classification system provides a predictive value for avascular necrosis in talar neck fractures?
Which classification system provides a predictive value for avascular necrosis in talar neck fractures?
Which statement describes a characteristic feature of Sanders IV fractures?
Which statement describes a characteristic feature of Sanders IV fractures?
What type of fracture occurs at the metaphyseal-diaphyseal junction, according to the Stewart Classification?
What type of fracture occurs at the metaphyseal-diaphyseal junction, according to the Stewart Classification?
Under the Sneppen classification, which type pertains to a crush injury in the talar bone?
Under the Sneppen classification, which type pertains to a crush injury in the talar bone?
What is the primary difference between Sanders Type I and Type II fractures?
What is the primary difference between Sanders Type I and Type II fractures?
What feature is common to Sanders IIIAB fractures?
What feature is common to Sanders IIIAB fractures?
In Watson-Jones classification, which type involves an avulsion fracture of the tuberosity?
In Watson-Jones classification, which type involves an avulsion fracture of the tuberosity?
A 'total incongruity of the TMT joint' is classified under which type in Hardcastle classification?
A 'total incongruity of the TMT joint' is classified under which type in Hardcastle classification?
What common characteristic is shared by Type I and Type II fractures in the Berndt & Harty classification?
What common characteristic is shared by Type I and Type II fractures in the Berndt & Harty classification?
What is the primary distinction of Sanders Type IIIC fractures?
What is the primary distinction of Sanders Type IIIC fractures?
What characterizes a Stage II Pilon fracture according to the Ruedi/Allgower classification?
What characterizes a Stage II Pilon fracture according to the Ruedi/Allgower classification?
In the Danis-Weber classification, Type A fractures are associated with which of the following?
In the Danis-Weber classification, Type A fractures are associated with which of the following?
Which statement accurately describes a Growth Plate Injury of type SH III?
Which statement accurately describes a Growth Plate Injury of type SH III?
In Pilon fractures classified as Stage I, what is the condition of the joint fragments?
In Pilon fractures classified as Stage I, what is the condition of the joint fragments?
For calcaneal fractures, which Rowe classification type represents an avulsion fracture of the tuberosity?
For calcaneal fractures, which Rowe classification type represents an avulsion fracture of the tuberosity?
Which statement describes a consequence of a Type C fracture in the Danis-Weber classification?
Which statement describes a consequence of a Type C fracture in the Danis-Weber classification?
What is the primary characteristic of a SH II growth plate injury?
What is the primary characteristic of a SH II growth plate injury?
Stage 3 of Supination-External Rotation injury classification involves what specific fracture?
Stage 3 of Supination-External Rotation injury classification involves what specific fracture?
Which type of calcaneal fracture is classified as Rowe IV?
Which type of calcaneal fracture is classified as Rowe IV?
What condition does a Stage V growth plate injury represent?
What condition does a Stage V growth plate injury represent?
Which Rowe classification type describes a fracture of the calcaneal tubercle?
Which Rowe classification type describes a fracture of the calcaneal tubercle?
The Ruedi/Allgower classification refers to which aspect of Pilon fractures?
The Ruedi/Allgower classification refers to which aspect of Pilon fractures?
Which type of fracture occurs in the distal fibula classified as Type A in Danis-Weber?
Which type of fracture occurs in the distal fibula classified as Type A in Danis-Weber?
What does a Stage 1 injury in Supination-Adduction classification entail?
What does a Stage 1 injury in Supination-Adduction classification entail?
What is the recommended treatment for Stage III lateral lesions?
What is the recommended treatment for Stage III lateral lesions?
Which surgical treatment option is specifically designed to facilitate ingrowth of fibrocartilage?
Which surgical treatment option is specifically designed to facilitate ingrowth of fibrocartilage?
What is NOT one of the criteria to evaluate avascular necrosis (AVN)?
What is NOT one of the criteria to evaluate avascular necrosis (AVN)?
Which imaging technique is essential for the assessment of osteochondral lesions?
Which imaging technique is essential for the assessment of osteochondral lesions?
What is a common post-operative complication following ankle arthroscopy?
What is a common post-operative complication following ankle arthroscopy?
What is the purpose of osteochondral autologous transplantation in the treatment of ankle lesions?
What is the purpose of osteochondral autologous transplantation in the treatment of ankle lesions?
Which surgical procedure involves both debridement and microfracture techniques?
Which surgical procedure involves both debridement and microfracture techniques?
What is a key factor influencing the choice between surgical and conservative treatment for ACL injuries?
What is a key factor influencing the choice between surgical and conservative treatment for ACL injuries?
Which method is an example of a conservative pre-collapse treatment for avascular necrosis of the talus?
Which method is an example of a conservative pre-collapse treatment for avascular necrosis of the talus?
What is the primary goal of core decompression in the treatment of avascular necrosis of the talus?
What is the primary goal of core decompression in the treatment of avascular necrosis of the talus?
Which of the following is a characteristic of fresh en bloc talar allograft in the treatment of AVN?
Which of the following is a characteristic of fresh en bloc talar allograft in the treatment of AVN?
What is a potential complication when using hyperbaric oxygen therapy for AVN treatment?
What is a potential complication when using hyperbaric oxygen therapy for AVN treatment?
Which imaging technique is most appropriate for evaluating the extent of avascular necrosis in the talus?
Which imaging technique is most appropriate for evaluating the extent of avascular necrosis in the talus?
What should be monitored as a possible post-operative complication after surgical treatment for AVN?
What should be monitored as a possible post-operative complication after surgical treatment for AVN?
Which aspect of treatment is critical for the management of post-operative complications in the context of AVN?
Which aspect of treatment is critical for the management of post-operative complications in the context of AVN?
What is a primary consideration when evaluating candidates for surgical intervention for AVN?
What is a primary consideration when evaluating candidates for surgical intervention for AVN?
Which surgical procedure is specifically indicated for post-collapse treatment of the talus in cases of Avascular Necrosis?
Which surgical procedure is specifically indicated for post-collapse treatment of the talus in cases of Avascular Necrosis?
What is a common clinical manifestation of a Talar Dome lesion after an ankle injury?
What is a common clinical manifestation of a Talar Dome lesion after an ankle injury?
In assessing post-operative complications from surgical treatment of talar injuries, which factor is least likely to influence recovery?
In assessing post-operative complications from surgical treatment of talar injuries, which factor is least likely to influence recovery?
Which imaging technique is most effective in the early detection of Talar Dome lesions post-injury?
Which imaging technique is most effective in the early detection of Talar Dome lesions post-injury?
Which statement correctly describes the criteria for evaluating Avascular Necrosis (AVN) of the talus?
Which statement correctly describes the criteria for evaluating Avascular Necrosis (AVN) of the talus?
Which of the following is NOT a recognized surgical option for treating Avascular Necrosis of the Talus?
Which of the following is NOT a recognized surgical option for treating Avascular Necrosis of the Talus?
What is the first step in managing a patient with Talar Dome lesions post-collapsed treatment?
What is the first step in managing a patient with Talar Dome lesions post-collapsed treatment?
Which post-operative condition is a significant concern in the management of Avascular Necrosis after surgical treatments?
Which post-operative condition is a significant concern in the management of Avascular Necrosis after surgical treatments?
What is the main arterial source responsible for supplying the talar body?
What is the main arterial source responsible for supplying the talar body?
Which of the following arteries is NOT involved in providing vascularity to the talus?
Which of the following arteries is NOT involved in providing vascularity to the talus?
What condition results from disruption of the vascular sling supplying the talar body?
What condition results from disruption of the vascular sling supplying the talar body?
Which artery contributes the least to the blood supply of the talus?
Which artery contributes the least to the blood supply of the talus?
What anatomical feature limits the blood supply to the talus?
What anatomical feature limits the blood supply to the talus?
Which artery is considered to provide the most vital blood supply to the medial part of the talus?
Which artery is considered to provide the most vital blood supply to the medial part of the talus?
What happens if the blood supply to the talus is disrupted?
What happens if the blood supply to the talus is disrupted?
Which artery's branches have a significant role in supplying vascularity to the talus?
Which artery's branches have a significant role in supplying vascularity to the talus?
What is the primary mechanism of injury associated with talar head fractures?
What is the primary mechanism of injury associated with talar head fractures?
What percentage of talar head fractures is likely to develop avascular necrosis (AVN)?
What percentage of talar head fractures is likely to develop avascular necrosis (AVN)?
In cases of displaced talar head fractures, which treatment is typically required?
In cases of displaced talar head fractures, which treatment is typically required?
How long is immobilization typically required for non-displaced talar head fractures?
How long is immobilization typically required for non-displaced talar head fractures?
What is a typical characteristic of a talar head fracture regarding its structure?
What is a typical characteristic of a talar head fracture regarding its structure?
What factor plays a crucial role in determining the treatment for talar head fractures?
What factor plays a crucial role in determining the treatment for talar head fractures?
What is a common outcome if a talar head fracture is left untreated?
What is a common outcome if a talar head fracture is left untreated?
Which joint is usually invaded in displaced talar head fractures?
Which joint is usually invaded in displaced talar head fractures?
Which type of fracture is classified as Group I according to Sneppen?
Which type of fracture is classified as Group I according to Sneppen?
What is the primary goal of immediate reduction for dislocated joints in talar body management?
What is the primary goal of immediate reduction for dislocated joints in talar body management?
Which type of fracture is classified under Group IV in Sneppen's classification system?
Which type of fracture is classified under Group IV in Sneppen's classification system?
What imaging techniques are primarily used to evaluate injuries of the talar body?
What imaging techniques are primarily used to evaluate injuries of the talar body?
In Sneppen's classification, which group consists of shearing fractures?
In Sneppen's classification, which group consists of shearing fractures?
What is a crucial aspect of post-operative care to decrease complications in talar body fractures?
What is a crucial aspect of post-operative care to decrease complications in talar body fractures?
What characterizes a Group III fracture according to Sneppen's classification?
What characterizes a Group III fracture according to Sneppen's classification?
What is an immediate step in the management of a dislocated talar body joint?
What is an immediate step in the management of a dislocated talar body joint?
What type of fracture accounts for 20% of talar fractures?
What type of fracture accounts for 20% of talar fractures?
What is the typical treatment duration for non-displaced or small comminuted fractures?
What is the typical treatment duration for non-displaced or small comminuted fractures?
What mechanism of injury is associated with fractures of the lateral process?
What mechanism of injury is associated with fractures of the lateral process?
Which phrase best describes the relationship between snowboarding and talar fractures?
Which phrase best describes the relationship between snowboarding and talar fractures?
In cases of large, displaced, intra-articular fragments, what surgical intervention is recommended?
In cases of large, displaced, intra-articular fragments, what surgical intervention is recommended?
What is a primary indicator for the treatment method chosen in talar fractures?
What is a primary indicator for the treatment method chosen in talar fractures?
What factor has led to an increased incidence of lateral process fractures?
What factor has led to an increased incidence of lateral process fractures?
What is the main focus when treating small comminuted fractures?
What is the main focus when treating small comminuted fractures?
What is the most common cause of talar neck fractures?
What is the most common cause of talar neck fractures?
How does the Hawkins classification correlate with talar neck fractures?
How does the Hawkins classification correlate with talar neck fractures?
What is the AVN rate associated with a Hawkins I talar neck fracture?
What is the AVN rate associated with a Hawkins I talar neck fracture?
Which treatment method is typically advised for a Hawkins I talar neck fracture?
Which treatment method is typically advised for a Hawkins I talar neck fracture?
What mechanism of injury is primarily responsible for leading to a talar neck fracture?
What mechanism of injury is primarily responsible for leading to a talar neck fracture?
What is the proper non-weight bearing status duration for treating a Hawkins I fracture?
What is the proper non-weight bearing status duration for treating a Hawkins I fracture?
Which factor does NOT influence the treatment of a talar neck fracture?
Which factor does NOT influence the treatment of a talar neck fracture?
What happens to the talar body as a result of continued force following the shear of the anterior tibia?
What happens to the talar body as a result of continued force following the shear of the anterior tibia?
What is a key factor that necessitates operative management of a fracture?
What is a key factor that necessitates operative management of a fracture?
Which of the following is NOT a recommended approach for non-operative management of non-displaced metatarsal fractures?
Which of the following is NOT a recommended approach for non-operative management of non-displaced metatarsal fractures?
What imaging technique is most commonly used to identify stress fractures in the bones?
What imaging technique is most commonly used to identify stress fractures in the bones?
What is the typical healing rate for non-displaced first metatarsal fractures managed non-operatively?
What is the typical healing rate for non-displaced first metatarsal fractures managed non-operatively?
What long-term functional outcome is expected after appropriate management of a non-displaced metatarsal fracture?
What long-term functional outcome is expected after appropriate management of a non-displaced metatarsal fracture?
What is the primary goal of non-operative management for a distal diaphyseal fracture?
What is the primary goal of non-operative management for a distal diaphyseal fracture?
Which imaging technique is often considered for complications like nonunion in metatarsal fractures?
Which imaging technique is often considered for complications like nonunion in metatarsal fractures?
Which operative technique is indicated for a nonunion associated with an avulsion fracture?
Which operative technique is indicated for a nonunion associated with an avulsion fracture?
What is the average time for healing of Jones fractures managed with open reduction internal fixation (ORIF)?
What is the average time for healing of Jones fractures managed with open reduction internal fixation (ORIF)?
What does a high nonunion rate of approximately 25% in metaphyseal-diaphyseal fractures indicate?
What does a high nonunion rate of approximately 25% in metaphyseal-diaphyseal fractures indicate?
In non-operative management of an avulsion fracture, what is the recommended duration for weight-bearing in a cast shoe?
In non-operative management of an avulsion fracture, what is the recommended duration for weight-bearing in a cast shoe?
What is highlighted regarding long-term functional outcomes for nonoperatively managed distal fifth metatarsal fractures?
What is highlighted regarding long-term functional outcomes for nonoperatively managed distal fifth metatarsal fractures?
What is the primary choice for successful fixation of a distal diaphyseal (Dancer’s) fracture when indicated?
What is the primary choice for successful fixation of a distal diaphyseal (Dancer’s) fracture when indicated?
What is a complication often associated with neglected avulsion fractures?
What is a complication often associated with neglected avulsion fractures?
What factor is crucial in determining the approach to manage a dancer's fracture?
What factor is crucial in determining the approach to manage a dancer's fracture?
What is the recommended approach for managing a Jones fracture in an athlete?
What is the recommended approach for managing a Jones fracture in an athlete?
Which factor predominantly influences the healing process of metatarsal fractures?
Which factor predominantly influences the healing process of metatarsal fractures?
What imaging technique is useful in differentiating between an open epiphysis and a fracture in skeletally immature patients?
What imaging technique is useful in differentiating between an open epiphysis and a fracture in skeletally immature patients?
What is the average time for athletes to return to play after surgical treatment of a Jones fracture?
What is the average time for athletes to return to play after surgical treatment of a Jones fracture?
What complications may arise from poor management of a recurrent cavovarus foot structure in the context of stress fractures?
What complications may arise from poor management of a recurrent cavovarus foot structure in the context of stress fractures?
Which statement best reflects the healing outcomes for the majority of metatarsal fractures?
Which statement best reflects the healing outcomes for the majority of metatarsal fractures?
Which operative approach has been observed in a study of NFL players with Jones fractures?
Which operative approach has been observed in a study of NFL players with Jones fractures?
In managing stress fractures, what is one critical consideration regarding patient education?
In managing stress fractures, what is one critical consideration regarding patient education?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
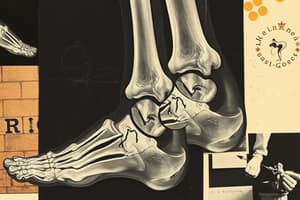
Ankle Anatomy
- Ankle joint consists of three osseous structures: Tibia, Fibula, and Talus.
- Functions as a hinge-type synovial joint allowing triplane motion.
Ligamentous Structures
- Medial Ligaments:
- Superficial Deltoid (including posterior tibiotalar, tibionavicular, and tibiocalcaneal ligaments)
- Deep Deltoid (anterior tibiotalar ligament)
- Lateral Ligaments:
- Anterior talofibular ligament
- Posterior talofibular ligament
- Calcaneofibular ligament
Syndesmotic Ligaments
- Four main components:
- Anterior inferior tibiofibular ligament (AITFL)
- Posterior inferior tibiofibular ligament (PITFL)
- Inferior transverse tibiofibular ligament
- Interosseous ligament
Ankle Fracture Classification Systems
-
Lauge-Hansen Classification:
- Based on foot position (supination/pronation) and talar motion direction (adduction/abduction/eversion).
- Four main groups: Supination-Adduction, Pronation-Abduction, Supination-External Rotation, Pronation-External Rotation.
-
Danis-Weber Classification:
- Based on the relationship of fibular fracture location to the syndesmosis.
- Three main types: Type A, Type B, Type C.
Lauge-Hansen Classification Details
-
Supination-Adduction:
- Stage 1: Transverse avulsion fracture of the distal fibula.
- Stage 2: Vertical medial malleolar fracture.
-
Pronation-Abduction:
- Stage 1: Transverse fracture of medial malleolus or deltoid ligament tear.
- Stage 2: Posterior malleolar fracture.
- Stage 3: Short, oblique fibular fracture.
-
Supination External Rotation:
- Stage 1: AITFL injury or avulsion.
- Stage 2: Spiral fibular fracture.
- Stage 3: Posterior inferior tibiotalar ligament injury.
- Stage 4: Transverse fracture of medial malleolus.
-
Pronation External Rotation:
- Stage 1: Transverse medial malleolar fracture or deltoid ligament injury.
- Stage 2: Anterior inferior tibiofibular ligament rupture.
- Stage 3: Oblique or spiral fibular fracture above syndesmosis.
- Stage 4: Posterior inferior tibiofibular ligament injury.
Danis-Weber Classification Types
- Type A: Fracture of lateral malleolus distal to the syndesmosis.
- Type B: Fracture of lateral malleolus at the level of the syndesmosis.
- Type C: Fracture of lateral malleolus above the syndesmosis.
Overlap Between Classifications
- Danis-Weber A corresponds to Lauge-Hansen SAD Stage 1.
- Danis-Weber B aligns with Lauge-Hansen SER Stage 2 or PAB Stage 3.
- Danis-Weber C relates to Lauge-Hansen PER Stage 3.
Named Ankle Fractures
- Tillaux-Chaput: AITFL avulsion fracture from anterolateral tibia.
- Wagstaff: AITFL avulsion fracture of anteromedial fibula.
- Volkmann: PITFL avulsion fracture from posterior lateral tibia.
- Bosworth: PITFL avulsion fracture from posterior medial fibula.
- Maisonneuve: Proximal fibular fracture near fibular neck.
Ankle Anatomy
- Ankle joint consists of three osseous structures: Tibia, Fibula, and Talus.
- Functions as a hinge-type synovial joint allowing triplane motion.
Ligamentous Structures
- Medial Ligaments:
- Superficial Deltoid (including posterior tibiotalar, tibionavicular, and tibiocalcaneal ligaments)
- Deep Deltoid (anterior tibiotalar ligament)
- Lateral Ligaments:
- Anterior talofibular ligament
- Posterior talofibular ligament
- Calcaneofibular ligament
Syndesmotic Ligaments
- Four main components:
- Anterior inferior tibiofibular ligament (AITFL)
- Posterior inferior tibiofibular ligament (PITFL)
- Inferior transverse tibiofibular ligament
- Interosseous ligament
Ankle Fracture Classification Systems
-
Lauge-Hansen Classification:
- Based on foot position (supination/pronation) and talar motion direction (adduction/abduction/eversion).
- Four main groups: Supination-Adduction, Pronation-Abduction, Supination-External Rotation, Pronation-External Rotation.
-
Danis-Weber Classification:
- Based on the relationship of fibular fracture location to the syndesmosis.
- Three main types: Type A, Type B, Type C.
Lauge-Hansen Classification Details
-
Supination-Adduction:
- Stage 1: Transverse avulsion fracture of the distal fibula.
- Stage 2: Vertical medial malleolar fracture.
-
Pronation-Abduction:
- Stage 1: Transverse fracture of medial malleolus or deltoid ligament tear.
- Stage 2: Posterior malleolar fracture.
- Stage 3: Short, oblique fibular fracture.
-
Supination External Rotation:
- Stage 1: AITFL injury or avulsion.
- Stage 2: Spiral fibular fracture.
- Stage 3: Posterior inferior tibiotalar ligament injury.
- Stage 4: Transverse fracture of medial malleolus.
-
Pronation External Rotation:
- Stage 1: Transverse medial malleolar fracture or deltoid ligament injury.
- Stage 2: Anterior inferior tibiofibular ligament rupture.
- Stage 3: Oblique or spiral fibular fracture above syndesmosis.
- Stage 4: Posterior inferior tibiofibular ligament injury.
Danis-Weber Classification Types
- Type A: Fracture of lateral malleolus distal to the syndesmosis.
- Type B: Fracture of lateral malleolus at the level of the syndesmosis.
- Type C: Fracture of lateral malleolus above the syndesmosis.
Overlap Between Classifications
- Danis-Weber A corresponds to Lauge-Hansen SAD Stage 1.
- Danis-Weber B aligns with Lauge-Hansen SER Stage 2 or PAB Stage 3.
- Danis-Weber C relates to Lauge-Hansen PER Stage 3.
Named Ankle Fractures
- Tillaux-Chaput: AITFL avulsion fracture from anterolateral tibia.
- Wagstaff: AITFL avulsion fracture of anteromedial fibula.
- Volkmann: PITFL avulsion fracture from posterior lateral tibia.
- Bosworth: PITFL avulsion fracture from posterior medial fibula.
- Maisonneuve: Proximal fibular fracture near fibular neck.
Objectives
- Understand mechanisms of ankle fracture injury and classification schemes.
- Learn management principles for open reduction internal fixation (ORIF) of ankle fractures.
- Identify concepts and details associated with fixation devices for ankle fractures.
- Evaluate internal fixation devices based on established criteria.
Clinical Evaluation
- Assess patient's overall appearance: looks of distress and pain levels.
- Examine gross appearance of the limb: check for deformity, open wounds, and swelling.
- Assess vascular status: check dorsalis pedis and posterior tibial arteries, skin temperature, capillary refill, and active bleeding.
Neurological Status
- Evaluate sensation and compare to patient’s baseline.
- Assess active movement capabilities and perform a musculoskeletal exam to determine stability.
Radiographic Evaluation
- Initial evaluation requires three standard views: Anteroposterior (AP), Mortise, and Lateral.
- Medial clear space: widening greater than 4 mm indicates deltoid ligament injury and lateral talar translation.
- Tibio-fibular overlap should be less than 10 mm and indicates syndesmotic integrity.
Talar Tilt Assessment
- Mortise view used to measure distance between tibial articular surface and talar surface.
- Normal distance is approximately 2 mm or less; greater indicates lateral ankle instability.
Fibular Shortening Assessment
- Evaluated using Shenton line and Dime sign to observe joint line integrity and curvature of the fibula.
Ankle Fracture Evaluation
- Assess for additional injuries and determine if fracture is stable or unstable.
- Determine whether the injury is open or closed, and consider urgency of treatment.
Closed Reduction vs Open Reduction with Internal Fixation
- Closed Reduction Advantages: lower infection risk, less anesthesia complication, potentially shorter recovery time.
- Closed Reduction Disadvantages: imperfect anatomical reduction, possibility of loss of correction, complications from casting.
Closed Reduction Techniques
- Charnley Maneuver: involves exaggerating the deformity, distracting the limb, reducing the deformity, and immobilizing with a splint/cast.
- Quigly Maneuver: requires lifting the foot by the hallux and externally rotating the leg, ensuring medial malleolus integrity.
Open Reduction Internal Fixation
- Advantages include anatomical reduction, earlier weight-bearing, and increased stability.
- Disadvantages can involve soft tissue incision, hardware complications, distress of correction, and infection risks.
Vassal Principle
- Major fracture correction (typically fibula) aids in correcting lesser fractures due to shared soft tissue structures.
Bone Healing Types
- Primary Bone Healing: requires rigid fixation and leads to no callus formation.
- Secondary Bone Healing: involves significant callus formation and stabilization through endochondral healing.
Fracture Pattern Types
- Focus on treating the specific fracture pattern, which can be transverse, vertical, spiral (short/long), or oblique.
Open Reduction Internal Fixation Hardware
- Use various clamp options for anatomical reduction and temporary fixation before final fixation.
- Interfragmentary screws are important for spiral fibular fractures, utilizing lag techniques for insertion.
Plating Techniques
- Neutralization Plates: protect lag screws and can be either locking or non-locking.
- Buttress Plates: used for intraarticular fractures, particularly around metaphyseal fractures.
- Anti-glide Plates: placed posteriorly to prevent proximal movement of fracture fragments.
Management of Specific Fractures
- Medial malleolar fractures often require two cancellous screws or wires.
- Tension Band Wire Technique applies compression for medial malleolar fractures but is not first line.
- Posterior Malleolar fractures require fixation if it involves more than 25% of joint surface.
Post-Operative Care
- Immobilization with posterior splint or short leg cast; non-weight bearing for 6-8 weeks.
- Possible progression to weight bearing in a CAM boot; may include physical therapy.
- Routine post-operative pain management and DVT prophylaxis for 2-3 weeks.
Objectives of Ankle Fractures
- Understand injury mechanisms and classification for ankle fractures.
- Learn management principles for open reduction internal fixation (ORIF) of ankle fractures.
- Familiarize with concepts and details of ankle fracture fixation devices.
- Identify criteria for evaluating ankle fracture internal fixation devices.
Fracture Blisters
- Develop within 24-48 hours post-injury; more common in high-energy trauma.
- Two types: clear fluid-filled and hemorrhagic-filled, which can coexist.
- Not indicators of injury severity; hemorrhagic blisters signify more serious soft tissue injury.
- Treatment for clear fluid blisters typically sees healing in about 12 days, while hemorrhagic takes about 16 days.
- Surgery can be attempted before blister formation; incisions can help avoid or address blisters.
Syndesmotic Injuries
- Syndesmosis assessed on AP X-ray; instability requires fixation of the syndesmosis ligament.
- The “Cotton hook test” evaluates syndesmosis post-fracture fixation.
- Important to anatomically reduce syndesmosis due to its role in joint stability.
Syndesmotic Fixation Devices
- Screw Fixation:
- Fully threaded cortical screws should not compress the syndesmosis.
- Inserted in a posterior to anterior orientation at a 30-degree angle; placed 1.5-2 cm proximal to the ankle joint.
- Suture Button Fixation:
- Involves a synthetic suture with metallic buttons, allowing dynamic motion similar to natural ligaments.
Diabetic Ankle Fractures
- Present challenges due to comorbid conditions and peripheral neuropathy affecting weight-bearing ability.
- High risk of wound healing complications and Charcot neuroarthropathy.
- New fixation techniques include:
- Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) to preserve periosteum.
- Super construct hardware designs for stronger fixation.
- Intramedullary nailing as a minimally invasive option.
External Fixation with Delta Frames
- Utilized for unstable or open ankle fractures for soft tissue stabilization.
- Delta frames help maintain reduction and prevent equinus deformity.
- Left in place until swelling resolves, then replaced with traditional internal fixation.
Intramedullary Nail Fixation
- Indicated for elderly patients, acute trauma in active individuals, and poly-trauma patients.
- Contraindicated in young, active patients with high physical demands, not primary fixative choice for most.
- Benefits include reduced wound complications, decreased symptomatic reactions, faster recovery, and earlier weight-bearing.
Case Study: 53-Year-Old Male
- Presents with a closed tri-malleolar ankle fracture complicated by non-verbal status.
- Physical exam indicates instability with mild edema and no significant deformity.
- Initial conservative treatment includes casting and non-weight bearing (NWB).
- Treatment plan evolves to open reduction with internal fixation; later considered hardware removal and TTC fusion with intramedullary nail.
IM Nail Fixation Summary
- Intramedullary nail fixation offers a minimally invasive stabilization method following traumatic injury.
- Optimal for elderly with lower physical demands; selected for revision or reconstruction in younger patients on a case-by-case basis.
Overview of Pilon Fractures
- Pilon fractures refer to intra-articular fractures of the tibial plafond, often described as tibial plafond fractures.
- The term "pilon" originated from the French word for pestle, symbolizing the talus's impact on the tibial plafond.
Classification of Pilon Fractures
- Ruedi and Allgower classify pilon fractures into three types:
- Type I: Non-displaced fractures
- Type II: Displaced fractures with loss of articular congruency
- Type III: Displaced and severely comminuted fractures with impaction
- AO Classification adds more detail:
- Extra-articular: 43A
- Partial intra-articular: 43B
- Completely intra-articular: 43C
- Fractures further categorized by degree of comminution: 1, 2, 3.
Mechanisms of Injury and Anatomy
- Pilon fractures typically result from axial loading or high-energy trauma, leading to complex fracture patterns.
- Key anatomical features include soft tissues, which play a crucial role in fracture stability and healing.
Imaging
- Diagnostic imaging includes X-rays and CT scans to evaluate fracture patterns and severity.
Non-Operative Treatment
- Nonoperative management is limited to truly nondisplaced fractures or patients unable to undergo surgery.
Operative Treatment Options
- Surgery options include:
- External fixation
- Open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF)
- Minimally invasive plate fixation
- Medullary nailing
- Arthrodesis
- Combination of techniques.
Principles of Fracture Fixation
- Essential to restore anatomical alignment of the fibula and tibial articular surface.
- Requires stable fixation, often using buttress plating and possible bone grafting for defects.
Surgical Techniques
- Soft tissue management is crucial for successful outcomes.
- Anterior-medial and posterior-lateral approaches are common surgical maneuvers.
- Reduction sequences focus on re-establishing fractured fragments in anatomical position.
Post-Operative Care
- Splinting is required in a neutral position until suture removal (2-3 weeks post-surgery).
- Gradual physical therapy begins, aiming for active range of motion.
- Weight-bearing is typically restricted for about 12 weeks, with progressive transitions into a removable boot.
Patient Outcomes
- High-energy pilon fractures often yield poor functional outcomes.
- Midterm results show similar effectiveness between ORIF and external fixation methods.
Overview of Pilon Fractures
- Pilon fractures refer to intra-articular fractures of the tibial plafond, often described as tibial plafond fractures.
- The term "pilon" originated from the French word for pestle, symbolizing the talus's impact on the tibial plafond.
Classification of Pilon Fractures
- Ruedi and Allgower classify pilon fractures into three types:
- Type I: Non-displaced fractures
- Type II: Displaced fractures with loss of articular congruency
- Type III: Displaced and severely comminuted fractures with impaction
- AO Classification adds more detail:
- Extra-articular: 43A
- Partial intra-articular: 43B
- Completely intra-articular: 43C
- Fractures further categorized by degree of comminution: 1, 2, 3.
Mechanisms of Injury and Anatomy
- Pilon fractures typically result from axial loading or high-energy trauma, leading to complex fracture patterns.
- Key anatomical features include soft tissues, which play a crucial role in fracture stability and healing.
Imaging
- Diagnostic imaging includes X-rays and CT scans to evaluate fracture patterns and severity.
Non-Operative Treatment
- Nonoperative management is limited to truly nondisplaced fractures or patients unable to undergo surgery.
Operative Treatment Options
- Surgery options include:
- External fixation
- Open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF)
- Minimally invasive plate fixation
- Medullary nailing
- Arthrodesis
- Combination of techniques.
Principles of Fracture Fixation
- Essential to restore anatomical alignment of the fibula and tibial articular surface.
- Requires stable fixation, often using buttress plating and possible bone grafting for defects.
Surgical Techniques
- Soft tissue management is crucial for successful outcomes.
- Anterior-medial and posterior-lateral approaches are common surgical maneuvers.
- Reduction sequences focus on re-establishing fractured fragments in anatomical position.
Post-Operative Care
- Splinting is required in a neutral position until suture removal (2-3 weeks post-surgery).
- Gradual physical therapy begins, aiming for active range of motion.
- Weight-bearing is typically restricted for about 12 weeks, with progressive transitions into a removable boot.
Patient Outcomes
- High-energy pilon fractures often yield poor functional outcomes.
- Midterm results show similar effectiveness between ORIF and external fixation methods.
Minimally Invasive Approaches
- Preference for minimally invasive techniques among patients to enhance recovery.
- Benefits include reduced stiffness, shorter hospital stays, and faster healing times.
- Minimally invasive methods also promote less soft tissue damage.
Joint Depression-Sinus Tarsi Approach
- Particularly indicated for Sanders Type 2 fractures.
- Minimal involvement required with anterior process or calcaneocuboid.
- Optimal outcomes depend on the skill of the surgeon and monitoring of deformities.
- Historical incision length began at 1 cm but has since increased.
Corrective Focus
- Emphasis on addressing various deformities:
- Morphological aspects: Width and Varus alignment.
- Shortening conditions: Restoring height and length.
- Articular incongruity concerning subtalar and calcaneocuboid joints.
Tuberosity Fragment Management
- Addressing shortening involves restoring height and length.
- Correcting varus malalignment to achieve valgus orientation.
- Managing widening by medially shifting the structure.
External Fixation & Percutaneous Reduction
- Percutaneous reduction beneficial when soft tissue and bone fragmentation concerns are absent.
- Joint distraction protects the subtalar joint surfaces from bearing stresses, preserving the reduced posterior facet.
Surgical Goals
- Prioritize soft tissue respect and anatomic reduction of the calcaneus.
- Aim for full weight-bearing capability immediately post-surgery.
- Focus on restoring patient functionality.
Surgical Technique Overview
- Initial skeletal traction applied to achieve proper alignment.
- Followed by fracture reduction and application of the external frame.
Advantages of the Technique
- Short operating time of less than 45 minutes.
- Maintains soft tissue integrity leading to reproducible results.
- Weight-bearing capability is enhanced through effective fixation strategies.
Rowe Classification of Calcaneal Fractures
- Classification ranges from extra-articular fractures (Type I) to more complex intra-articular fractures (Type IV).
- Each type has specific traumatic mechanisms and treatment considerations based on displacement.
Post-Operative Considerations
- Non-weight bearing (NWB) advised for 2-3 weeks in a splint, followed by an NWB boot for about 8 weeks.
- Transitioning to a weight-bearing boot around week 4, integrated with therapy and the use of compression socks.
Percutaneous Fixation Strategy
- Tongue-type fixation indicated for Sanders Type 2C fractures.
- Timing of surgery is crucial for optimal healing and functional recovery.
Imaging – Lateral Findings
- Double Density Sign: Indicative of certain fractures.
- Loss of Height in Posterior Facet: Suggests significant injury to the calcaneal structure.
- Shortening of the Calcaneus: A radiologic finding indicating possible fracture or injury.
- Böhler’s Angle:
- Measured between the highest point of the anterior process and posterior facet, with a tangent to the tuberosity's superior edge.
- Normal range: 20° to 40°.
- A decrease in this angle indicates displacement of the posterior facet.
- Neutral Triangle: Important in assessing calcaneal alignment.
- Critical Angle of Gissane:
- Formed by two strong cortical columns beneath the lateral talus.
- Normal range: 95° to 105°.
- Increased angle is associated with fractures.
Special Imaging Techniques
- Harris Beath Axial View:
- Identifies disruption and displacement of the articular surface and the lateral wall.
- Evaluates heel width translation and tuberosity angulation.
- Broden’s Views:
- Allows visualization of the entire posterior facet using angled X-rays.
- Now commonly replaced by CT scans for pre-op evaluations.
CT Imaging – Sanders Classification
- Utilizes coronal CT imaging to classify posterior facet joint depression fractures.
- Types I to IV indicate the number of fragments:
- Type I: No displacement.
- Type IV: Highly comminuted with four or more fragments.
- Locations described by letters A, B, and C:
- Type A: Lateral fracture line.
- Type B: Central fracture line.
- Type C: Medial fracture line near the sustenaculum tali.
Joint Depression – Sinus Tarsi Approach
- Indications: Sanders Type 2 fractures with minimal anterior process/calcaneocuboid involvement.
- Incision: Originally 1cm, now longer for better access.
- Goals:
- Correct deformities in morphology (width, varus/valgus alignment).
- Restore height and length.
- Address articular incongruity in subtalar and calcaneocuboid joints.
Post-Operative Care
- Non-Weight Bearing (NWB): Initial 2-3 weeks in a splint followed by NWB boot for around 8 weeks.
- Weightbearing Boot: Used for 4 weeks post-surgery.
- Rehabilitation: Therapy and compression socks recommended.
Percutaneous Fixation
- Tongue Type (Sanders 2C): A specific fixation technique for fractures.
- Timing of Surgery: Critical to address fractures effectively.
- Goals: Like other procedures, focus on correcting all deformities related to morphology and articular congruity.
Fracture Classifications
- Essex-Lopresti tongue type fracture features a primary intra-articular shear fracture that separates the sustentaculum tali from the lateral body, accompanied by a secondary fracture through the tuberosity resembling an avulsion.
- Rowe V fracture occurs from a fall with the foot dorsiflexed, leading to an intra-articular fracture with joint depression and comminution, similar to Essex-Lopresti joint depression fractures.
Essex-Lopresti Joint Depression Type Fracture
- Characterized by a shear fracture that splits the calcaneus into two fragments: the sustentaculum and the tuberosity.
- Lateral portion of the posterior facet gets isolated and impacted into the body, often resulting in a blow-out fracture of the lateral wall.
- The foot's position during injury influences the specific blow-out fracture type.
- Significant decrease in both height and width of the calcaneus can occur.
Sanders Classification
- Constructs a CT classification based on coronal and axial imaging, examining the widest posterior facet section.
- Divides the calcaneus into four columns using three fracture lines labeled A, B, and C from lateral to medial.
- Features four main types of fractures with various subclassifications focused on the complexity of injury.
Sanders Types
- Type I: All nondisplaced intra-articular fractures, irrespective of fracture lines.
- Type II: Two-part fractures of the posterior facet subdivided into IIA (lateral), IIB (central), and IIC (medial).
- Type III: Three-part fractures featuring a centrally depressed fragment, subclassified into IIIAB, IIIAC, and IIIBC based on the positioning of fracture lines.
- Type IV: Comminuted four-part fractures with joint depression and a high fragmentation count.
Talar Fractures
Sneppen Classification
- Classifies based on anatomical location:
- I: Transchondral dome fractures
- II: Shear fractures
- III: Posterior tubercle fractures
- IV: Lateral process fractures
- V: Crush injuries
Hawkins Classification
- Excellent correlation with prognosis, indicating AVN (avascular necrosis) risk associated with talar neck fractures:
- Type 1: Non-displaced, AVN risk 0-13%
- Type 2: Displaced with subtalar subluxation, AVN risk 20-50%
- Type 3: Dislocated subtalar and ankle joints, AVN risk 83-100%
- Type 4: Complex fractures including talonavicular subluxation, rare variant.
Navicular Fractures
Watson-Jones Classification
- Classification includes:
- I: Avulsion of the tuberosity
- II: Dorsal chip fracture
- III: Body fracture
- IV: Stress fracture
Tarsal-Metatarsal Fractures
Quenu and Kuss Classification
Hardcastle Classification
- Type A: Total incongruity of TMT joint
- Type B1: Partial incongruity affecting the first ray
- Type B2: Partial incongruity affecting one or more lateral metatarsals
- Type C1 and C2: Divergent patterns with partial or total displacement.
Fifth Metatarsal Fractures
Stewart Classification
- Type 1: Fractures at the metaphyseal-diaphyseal junction.
Ankle Fractures
Lauge-Hansen Classification
- Describes injuries based on foot positioning and talus movement:
- Supination-adduction, Pronation-abduction, Supination-external rotation, Pronation-external rotation.
- Specific stages outline ligament ruptures and various fractures associated with each type of motion.
Pilon Fractures
Ruedi/Allgower Classification
- Stage I: No comminution or joint displacement.
- Stage II: Some displacement without comminution.
- Stage III: Comminution and/or impact of the joint surface.
Growth Plate Injuries
Salter-Harris Classification
- SH I: Through hypertrophic zone, requires high suspicion for diagnosis; excellent prognosis after closed reduction.
- SH II: Partially through physis and into metaphysis, known as Thurston-Holland sign; good prognosis.
- SH III: Extends through physis into the joint, requiring ORIF.
- SH IV: Involves the metaphysis, physis, and epiphysis; ORIF needed.
- SH V: Compression injuries, challenging to diagnose but possible to treat if growth potential remains.
- Additional classifications SH VI to IX exist for various injury complexities and impact on growth.
Calcaneal Fractures
- Classified into extra-articular and intra-articular fractures.
- Rowe classification specifies different fracture types, including:
- I (tubercle fracture), II (beak and avulsion fractures), III (oblique fractures), IV (body fractures with STJ involvement), and V (joint depression with comminution).
Osteochondroses Treatment Approaches
- Stage I & II lesions and Stage III medial lesions typically managed with conservative treatment using weight-bearing solutions (WB SLC).
- Stage III lateral lesions and Stage IV lesions generally require surgical intervention.
Surgical Treatment Options for Talar Dome
-
Ankle Arthroscopy
- Debridement of osteochondral defects (OCD) to promote fibrocartilage growth.
- Micro-fracture technique (marrow stimulation) employed.
- Chondrocyte implantation considered for recovery.
-
Ankle Arthrotomy
- Similar to arthroscopy, this allows for direct access to debride OCD.
- Microfracture technique may be used here as well.
- Osteochondral Autologous Transplantation provides options like:
- Mosaicplasty to patch lesions with healthy cartilage.
- En bloc talar shoulder transplantation for extensive damage.
Avascular Necrosis (AVN) of the Talus
-
Pre-collapse Conservative Treatments
- Patellar Tendon Bearing (PTB) Braces aim to offload pressure but may face compliance issues.
- Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT) has anecdotal support and high costs.
-
Pre-collapse Surgical Treatments
- Core decompression targets intact cartilage; reduces internal pressure and enhances revascularization.
- Fresh en bloc talar allograft replaces both necrotic cartilage and bone for comprehensive healing.
-
Post-collapse Surgical Treatments
- Tibiotalocalcaneal (TTC) and Tibiocalcaneal (Blair) fusions are options for severe cases.
- Total Ankle Replacement (TAR) is traditionally contraindicated with AVN but may have evolving standards.
Fractures and Lesions of the Talar Dome
- Talar dome lesions constitute 1% of talar fractures, originating from localized injuries to articular cartilage and subchondral bone.
- Commonly linked with previous ankle fractures or inversion sprains.
- Symptoms may include persistent pain, swelling, joint locking, instability, and restricted range of motion, often presenting after an initial period of improvement post-injury.
Anatomy of the Talar Fractures
- Blood supply to the talus is limited due to minimal soft tissue attachments and extensive cartilaginous surfaces.
- The three main distal leg arteries contribute to the vascularity of the talus:
- Posterior tibial artery provides key blood supply via deltoid branches and the artery of the tarsal canal (supplying 2/3 of talar body).
- Anterior tibial artery, through dorsalis pedis, supplies the talar head and neck.
- Peroneal artery, via the artery of the tarsal sinus, also contributes.
Talar Head Fractures
- Comprise less than 10% of all talar fractures.
- Often result from violent dorsiflexion of a fully plantarflexed foot, creating medial and lateral fragments.
- Treatment varies depending on:
- Displacement
- Joint involvement
- Comminution
- Non-displaced fractures typically require immobilization for 6-8 weeks.
- Displaced fractures necessitate open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) and usually involve the talonavicular (T-N) joint.
- Approximately 10% of talar head fractures lead to avascular necrosis (AVN).
Fractures of the Lateral Process
- Account for around 20% of talar fractures.
- Known as “snowboarder’s fracture” due to increased incidence in snowboarding.
- Caused by compression during inversion and dorsiflexion.
- Treatment is determined by the extent of displacement and joint involvement.
- Non-displaced and small comminuted fractures are managed with non-weight bearing (NWB) short leg cast (SLC) for 4-6 weeks.
- Large, displaced intra-articular fragments may require ORIF.
Fractures of the Talar Body
- Categorized into three types: compression, shearing, and crush fractures.
- Sneppen classification divides fractures based on location into groups:
- Group I: Compression fracture (osteochondral dome fracture).
- Group II: Shearing fractures (coronal, sagittal, transverse).
- Group III: Posterior process fracture.
- Group IV: Lateral process fracture.
- Group V: Crush injury.
- Goals for managing fractures include:
- Evaluating injury extent via radiographs and CT scans.
- Immediate closed reduction of dislocated joints.
- Anatomic reduction and stable fixation of fractures.
- Facilitating union and reducing risk of AVN with proper post-operative care.
Talar Neck Fractures
- Recognized as the second most common talar fracture.
- Caused by forced axial loading of the tibia through the talus, often during motor vehicle accidents or falls.
- Displacement and joint involvement dictate treatment strategies.
- Classified by Hawkins, correlating with prognosis and predicting AVN occurrence.
Hawkins Classification
- Grouped into categories that assess the risk of AVN and treatment needs:
- Hawkins I: Nondisplaced talar neck fracture; AVN rate of 0-13%, best prognosis, typically treated conservatively.
- Treatment for Hawkins I often involves NWB SLC for 6-8 weeks.
Bone Scan
- Tech-99 is a radiopharmaceutical commonly used for bone scanning.
- Useful for detecting stress fractures.
- Its application has limitations.
Management Overview
- Two primary management strategies: Non-Operative and Operative.
Management: Non-Operative
- Nondisplaced or minimally displaced metatarsal fractures are generally treated non-operatively.
- Goals include maintaining the metatarsal heads' parabola, sagittal plane position, and congruent metatophalangeal joints.
Non-Operative Management Protocols
- Non-displaced first metatarsal fractures require 4-6 weeks of non-weight bearing (NWB) in a cast or boot, followed by 6-8 weeks of protected weight-bearing as tolerated (WBAT).
- For a single non-displaced central metatarsal fracture, 6-8 weeks of WBAT in a surgical shoe or boot is standard; transition to regular footwear occurs once bone callus is visible and tenderness resolves.
- Multiple non-displaced central metatarsal fractures: 4-6 weeks NWB in cast or boot, followed by 6-8 weeks WBAT in boot.
Closed Reduction Techniques
- Closed reduction may be performed if necessary, employing local/hematoma block, sedation, and finger traps.
Management: Operative
- Indications for surgery include fractures with over 3-4 mm displacement or angulation greater than 10 degrees, as these can complicate healing.
Fracture Classifications
- Common classification systems include Lawrence & Botte, Stewart, and Torg.
Distal Diaphyseal Fractures
- Known as "Dancer’s fractures," these occur due to forced dorsiflexion of a plantarflexed and inverted forefoot.
Avulsion Fractures
- Commonly associated with peroneus brevis or plantar fascia injuries.
- Nondisplaced and mildly displaced avulsion fractures can be managed non-operatively with weight-bearing as tolerated in a stiff-soled shoe or boot for 4-8 weeks.
Imaging Techniques
- Standard imaging is similar to other metatarsal fractures, with CT and MRI considered for cases of delayed healing, non-union, or suspected stress fractures.
Management: Non-Operative for Specific Fractures
- Majority of distal diaphyseal fractures are treated non-operatively; studies show excellent long-term functional outcomes.
- For Jones fractures, nonunion rates can be as high as 25%. Healing averages 10 weeks with open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF), compared to 24 weeks for non-operative management.
Management: Operative for Avulsion and Distal Diaphyseal Fractures
- Surgical methods include bicortical screw, intramedullary screw, tension band, and plate fixation for avulsion fractures.
- For distal diaphyseal fractures, small plate and screw construct is commonly employed.
Jones Fracture Surgical Considerations
- Operative treatment results in faster healing rates and lower re-fracture rates, with intramedullary fixation preferred.
- Lateral decubitus position is used during surgery; correct guidewire placement is crucial.
Special Considerations
- Metatarsus adductus and cavovarus foot structure can influence fracture risk and management strategies.
- Athletes are often recommended for operative treatment to ensure quick return to play, shown to be effective in NFL players.
- Skeletally immature patients require special attention to avoid misdiagnosing open epiphysis as fractures.
Summary
- Treatment for metatarsal fractures primarily depends on displacement and angulation.
- Special circumstances, like Jones fractures, warrant close patient education.
- Most metatarsal fractures heal without complications.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.