Podcast
Questions and Answers
In epithelial tissue, the top side that faces toward the empty space of an organ is known as the ______ surface.
In epithelial tissue, the top side that faces toward the empty space of an organ is known as the ______ surface.
apical
The thin sheet of protein that anchors the basal surface of epithelial tissue to underlying tissues is called the ______ membrane.
The thin sheet of protein that anchors the basal surface of epithelial tissue to underlying tissues is called the ______ membrane.
basement
Epithelium characterized by a single layer of uniformly shaped cells is classified as ______ epithelium.
Epithelium characterized by a single layer of uniformly shaped cells is classified as ______ epithelium.
simple
Epithelium that appears layered but consists of only one layer of cells, where not all cells reach the surface, is known as ______ epithelium.
Epithelium that appears layered but consists of only one layer of cells, where not all cells reach the surface, is known as ______ epithelium.
Epithelial tissue found in areas subject to abrasion, such as skin and the lining of the mouth, is known as ______ squamous epithelium.
Epithelial tissue found in areas subject to abrasion, such as skin and the lining of the mouth, is known as ______ squamous epithelium.
The primary function of pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium, commonly found in the respiratory tract, is ______.
The primary function of pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium, commonly found in the respiratory tract, is ______.
In connective tissue, the cells responsible for producing fibers and maintaining the extracellular matrix are called ______.
In connective tissue, the cells responsible for producing fibers and maintaining the extracellular matrix are called ______.
The connective tissue fibers that provide strength and flexibility, and are composed of the protein collagen, are known as ______ fibers.
The connective tissue fibers that provide strength and flexibility, and are composed of the protein collagen, are known as ______ fibers.
The type of connective tissue characterized by interwoven bundles of collagenous fibers found in the dermis of the skin is known as ______ irregular connective tissue.
The type of connective tissue characterized by interwoven bundles of collagenous fibers found in the dermis of the skin is known as ______ irregular connective tissue.
Connective tissue that is densely packed with collagenous fibers arranged in an orderly manner, such as in tendons and ligaments, is classified as ______ connective tissue.
Connective tissue that is densely packed with collagenous fibers arranged in an orderly manner, such as in tendons and ligaments, is classified as ______ connective tissue.
The connective tissue specialized for storing lipids and providing insulation and cushioning is known as ______ tissue.
The connective tissue specialized for storing lipids and providing insulation and cushioning is known as ______ tissue.
The type of cartilage that appears smooth and semi-transparent, found in the bridge of the nose and at joints, is ______ cartilage.
The type of cartilage that appears smooth and semi-transparent, found in the bridge of the nose and at joints, is ______ cartilage.
The functional unit of compact bone, consisting of a central canal surrounded by concentric rings of lacunae, is called an ______.
The functional unit of compact bone, consisting of a central canal surrounded by concentric rings of lacunae, is called an ______.
The liquid matrix of blood, which contains erythrocytes, leukocytes, and platelets, is called ______.
The liquid matrix of blood, which contains erythrocytes, leukocytes, and platelets, is called ______.
The term used to describe a muscle cell's plasma membrane is ______.
The term used to describe a muscle cell's plasma membrane is ______.
Skeletal muscle is also called ______ muscle, because it is under conscious control.
Skeletal muscle is also called ______ muscle, because it is under conscious control.
Unique to cardiac muscle tissue are structures called ______ discs, which facilitate coordinated contractions between neighboring cells.
Unique to cardiac muscle tissue are structures called ______ discs, which facilitate coordinated contractions between neighboring cells.
The nervous tissue cells that transmit electrical signals throughout the body are called ______.
The nervous tissue cells that transmit electrical signals throughout the body are called ______.
The type of glial cells that insulate neuron processes in the peripheral nervous system and speed up signal conduction are called ______ cells.
The type of glial cells that insulate neuron processes in the peripheral nervous system and speed up signal conduction are called ______ cells.
The gaps between Schwann cells along a neuron process are called nodes of ______.
The gaps between Schwann cells along a neuron process are called nodes of ______.
Sponges are known as ______ feeders because they filter water through pores on their body to obtain food.
Sponges are known as ______ feeders because they filter water through pores on their body to obtain food.
The cells lining the spongocoel in sponges that engulf and digest food particles are called ______.
The cells lining the spongocoel in sponges that engulf and digest food particles are called ______.
The structure that releases poison and barbed threads to cause pain and incapacitate victims in cnidarians are called ______.
The structure that releases poison and barbed threads to cause pain and incapacitate victims in cnidarians are called ______.
The gastrovascular cavity in cnidarians has an ______ gut, meaning food and waste enter and exit through the same opening.
The gastrovascular cavity in cnidarians has an ______ gut, meaning food and waste enter and exit through the same opening.
A free-floating body plan in cnidarians with a downward-pointing mouth in a bell-shaped body is known as a ______.
A free-floating body plan in cnidarians with a downward-pointing mouth in a bell-shaped body is known as a ______.
Corals have a mutually symbiotic relationship with the algae ______, which perform photosynthesis and supply the coral with food.
Corals have a mutually symbiotic relationship with the algae ______, which perform photosynthesis and supply the coral with food.
Flatworms lack a coelom and instead have a solid mass of cells, not including the lumen of the ______ cavity.
Flatworms lack a coelom and instead have a solid mass of cells, not including the lumen of the ______ cavity.
Tapeworms (cestodes) absorb nutrients through their body wall because they do not have a ______ cavity.
Tapeworms (cestodes) absorb nutrients through their body wall because they do not have a ______ cavity.
Free-living flatworms (planarians) can regenerate because of ______ stem cells throughout their body.
Free-living flatworms (planarians) can regenerate because of ______ stem cells throughout their body.
Annelids exhibit ______, which is the repetition of similar body segments, as seen in segmented worms.
Annelids exhibit ______, which is the repetition of similar body segments, as seen in segmented worms.
Most mollusks have a shell composed of ______, a compound also found in eggshells.
Most mollusks have a shell composed of ______, a compound also found in eggshells.
Gastropods undergo a developmental process called ______, which results in their shells being coiled and their asymmetrical body plan.
Gastropods undergo a developmental process called ______, which results in their shells being coiled and their asymmetrical body plan.
Cephalopods use "jet propulsion" for movement by drawing water into their mantle cavity and squirting it out through a ______.
Cephalopods use "jet propulsion" for movement by drawing water into their mantle cavity and squirting it out through a ______.
Animals in the superphylum Ecdysozoa shed their ______ in a process called ecdysis.
Animals in the superphylum Ecdysozoa shed their ______ in a process called ecdysis.
Arthropods have an open circulatory system in which the circulatory fluid, called ______, is only partially enclosed in vessels.
Arthropods have an open circulatory system in which the circulatory fluid, called ______, is only partially enclosed in vessels.
Spiders have spinnerets that extrude silk threads, which they use to spin ______ and wrap their prey.
Spiders have spinnerets that extrude silk threads, which they use to spin ______ and wrap their prey.
Insects have a tracheal system, which is a network of tubes connected to the outside via openings called ______.
Insects have a tracheal system, which is a network of tubes connected to the outside via openings called ______.
The endoskeleton of echinoderms is made of ______, contributing to the prickly skin characteristic of most members of the phylum.
The endoskeleton of echinoderms is made of ______, contributing to the prickly skin characteristic of most members of the phylum.
Echinoderms regulate water entrance into their water vascular system through an opening called the ______.
Echinoderms regulate water entrance into their water vascular system through an opening called the ______.
Chordates are named for the ______, an internal flexible rod of connective tissue that supports the body.
Chordates are named for the ______, an internal flexible rod of connective tissue that supports the body.
[Blank] tissue is characterized by cells that contract or shorten, facilitating mobility of the body or movement of substances within it.
[Blank] tissue is characterized by cells that contract or shorten, facilitating mobility of the body or movement of substances within it.
The tissue responsible for transmitting information throughout the body in the form of electrical signals is known as ______ tissue.
The tissue responsible for transmitting information throughout the body in the form of electrical signals is known as ______ tissue.
[Blank] epithelium is characterized by a single layer of cells that vary in size and shape, giving the appearance of multiple layers, and is often ciliated.
[Blank] epithelium is characterized by a single layer of cells that vary in size and shape, giving the appearance of multiple layers, and is often ciliated.
The ______ membrane is a thin layer of protein that anchors the basal surface of epithelial tissue to underlying tissues.
The ______ membrane is a thin layer of protein that anchors the basal surface of epithelial tissue to underlying tissues.
The primary function of simple ______ epithelium, found in glands like the thyroid and pancreas, is secretion.
The primary function of simple ______ epithelium, found in glands like the thyroid and pancreas, is secretion.
The long, thick, stretchy pink (or orange) bits seen in loose connective tissue, known as ______ fibers, are composed of the protein collagen and provide strength and flexibility.
The long, thick, stretchy pink (or orange) bits seen in loose connective tissue, known as ______ fibers, are composed of the protein collagen and provide strength and flexibility.
[Blank] connective tissue, found in the dermis of the skin, is characterized by interwoven bundles of collagenous fibers that twist and turn throughout the tissue.
[Blank] connective tissue, found in the dermis of the skin, is characterized by interwoven bundles of collagenous fibers that twist and turn throughout the tissue.
The cells of cartilage, known as ______, reside within lacunae and are responsible for building and maintaining the solid cellular matrix.
The cells of cartilage, known as ______, reside within lacunae and are responsible for building and maintaining the solid cellular matrix.
In bone tissue, ______ are tiny channels that extend from the central canal to deliver oxygen and nutrients to distant osteocytes.
In bone tissue, ______ are tiny channels that extend from the central canal to deliver oxygen and nutrients to distant osteocytes.
The liquid matrix of blood, called ______, contains erythrocytes, platelets, and leukocytes, each serving unique functions in oxygen transport, clotting, and immune defense.
The liquid matrix of blood, called ______, contains erythrocytes, platelets, and leukocytes, each serving unique functions in oxygen transport, clotting, and immune defense.
In muscle tissue, the plasma membrane of a muscle cell is referred to as the ______.
In muscle tissue, the plasma membrane of a muscle cell is referred to as the ______.
Unlike skeletal muscle, ______ muscle is found within organs and its movement is generally not under conscious control.
Unlike skeletal muscle, ______ muscle is found within organs and its movement is generally not under conscious control.
The tight connections between neighboring cardiac muscle cells, known as ______, allow the cells to coordinate the timing of their contractions.
The tight connections between neighboring cardiac muscle cells, known as ______, allow the cells to coordinate the timing of their contractions.
[Blank] cells are specialized glial cells that insulate and speed up the conduction of nerve signals by forming a myelin sheath around neuron processes.
[Blank] cells are specialized glial cells that insulate and speed up the conduction of nerve signals by forming a myelin sheath around neuron processes.
The bundle of neuron processes that cover long distances in the body, carrying nerve signals, are known as ______.
The bundle of neuron processes that cover long distances in the body, carrying nerve signals, are known as ______.
Sponges draw water into a central chamber called the ______ through pores on their body.
Sponges draw water into a central chamber called the ______ through pores on their body.
Cnidarians are named for their stinging cells, called ______, which release nematocysts containing poison and barbed threads.
Cnidarians are named for their stinging cells, called ______, which release nematocysts containing poison and barbed threads.
Corals have a mutualistic symbiotic relationship with ______, which perform photosynthesis and supply coral food in exchange for a home.
Corals have a mutualistic symbiotic relationship with ______, which perform photosynthesis and supply coral food in exchange for a home.
Tapeworms, belonging to the Class Cestoda, lack a ______ but absorb nutrients through their body wall.
Tapeworms, belonging to the Class Cestoda, lack a ______ but absorb nutrients through their body wall.
Rotifers are named for their crown of cilia around their mouth, known as a ______, that draws in water and food.
Rotifers are named for their crown of cilia around their mouth, known as a ______, that draws in water and food.
Gastropods undergo a developmental process called ______, which results in their asymmetrical body plan and coiled shells.
Gastropods undergo a developmental process called ______, which results in their asymmetrical body plan and coiled shells.
Cephalopods use ______ for mobility by drawing water into their mantle cavity and then expelling it through a siphon.
Cephalopods use ______ for mobility by drawing water into their mantle cavity and then expelling it through a siphon.
Arthropods have a rigid exoskeleton made of ______, a protein that provides protection and support.
Arthropods have a rigid exoskeleton made of ______, a protein that provides protection and support.
The circulatory fluid in arthropods with an open circulatory system is called ______
The circulatory fluid in arthropods with an open circulatory system is called ______
The ______ system in insects consists of a network of tubes connected to the outside via openings called spiracles, facilitating gas exchange.
The ______ system in insects consists of a network of tubes connected to the outside via openings called spiracles, facilitating gas exchange.
Match the type of epithelial tissue with its primary function:
Match the type of epithelial tissue with its primary function:
Match the connective tissue type with its main component:
Match the connective tissue type with its main component:
Match the muscle tissue type with its distinguishing feature:
Match the muscle tissue type with its distinguishing feature:
Match the nervous tissue component with its function:
Match the nervous tissue component with its function:
Match the sponge cell type with its function:
Match the sponge cell type with its function:
Match the Cnidarian class with its characteristic:
Match the Cnidarian class with its characteristic:
Match the class of Platyhelminthes with its key feature:
Match the class of Platyhelminthes with its key feature:
Match the feature to its animal:
Match the feature to its animal:
Match the mollusk class with its description:
Match the mollusk class with its description:
Match the arthropod subphylum with its defining characteristic:
Match the arthropod subphylum with its defining characteristic:
Match the tissue to its description:
Match the tissue to its description:
Match the part of a bone structure to its description:
Match the part of a bone structure to its description:
Match the feature to its location:
Match the feature to its location:
Match the animal with the definition:
Match the animal with the definition:
Match the subphylum with its description:
Match the subphylum with its description:
Match description to feature:
Match description to feature:
Match the description to the fiber:
Match the description to the fiber:
Match the term to the definition:
Match the term to the definition:
Match the feature to its function (Echinodermata):
Match the feature to its function (Echinodermata):
Match the term with its description:
Match the term with its description:
Match the mollusk class to its feeding strategy:
Match the mollusk class to its feeding strategy:
Match the cell with its product:
Match the cell with its product:
Match to best definition:
Match to best definition:
Match the arthropod to its defining features:
Match the arthropod to its defining features:
Match the layer or tissue with its correct description:
Match the layer or tissue with its correct description:
Match the connective tissue type with its function:
Match the connective tissue type with its function:
Match the animal with method of movement or unique traits:
Match the animal with method of movement or unique traits:
Match the muscle location/description with how they appear:
Match the muscle location/description with how they appear:
Match the nervous tissue term to the definition:
Match the nervous tissue term to the definition:
Match sponge term with description:
Match sponge term with description:
Match the feature with its function (Chordata):
Match the feature with its function (Chordata):
Match the structure with its location:
Match the structure with its location:
Match the animal to its definition:
Match the animal to its definition:
Match the type of connective tissue with its primary location in the body:
Match the type of connective tissue with its primary location in the body:
Match the type of muscle tissue with its distinguishing characteristic:
Match the type of muscle tissue with its distinguishing characteristic:
Match the cell type found in connective tissue with its respective function:
Match the cell type found in connective tissue with its respective function:
Match the structure within a neuron with its function:
Match the structure within a neuron with its function:
Match the component of blood with its primary function:
Match the component of blood with its primary function:
Match the class of Mollusca with its general characteristics:
Match the class of Mollusca with its general characteristics:
Match the key characteristic with the phylum:
Match the key characteristic with the phylum:
Match the phylum of Lophotrochozoa with its defining characteristic:
Match the phylum of Lophotrochozoa with its defining characteristic:
Match the main chordate feature with its function:
Match the main chordate feature with its function:
Match the Arthropoda subphylum with its defining trait:
Match the Arthropoda subphylum with its defining trait:
Match each structure of Echinodermata's water vascular system with its corresponding function:
Match each structure of Echinodermata's water vascular system with its corresponding function:
Match the class of Platyhelminthes with its main features :
Match the class of Platyhelminthes with its main features :
Match the structure with the appropriate tissue:
Match the structure with the appropriate tissue:
Match the function with the appropriate fiber:
Match the function with the appropriate fiber:
Match the type tissue with its location:
Match the type tissue with its location:
Match the following terms with the correct definition
Match the following terms with the correct definition
Match the following direction terms, with its appropriate meaning:
Match the following direction terms, with its appropriate meaning:
Match the cell type to its appropriate location:
Match the cell type to its appropriate location:
Match the type of epithelial tissue with its structural description:
Match the type of epithelial tissue with its structural description:
Match the function with the class of Platyhelminthes:
Match the function with the class of Platyhelminthes:
Match the following classes of Mullusca with their example:
Match the following classes of Mullusca with their example:
Match the appropriate definition with the term:
Match the appropriate definition with the term:
Match the subphylum of Chordata with the appropriate description:
Match the subphylum of Chordata with the appropriate description:
Flashcards
Epithelial Tissue
Epithelial Tissue
Inner and outer layers of organs; functions include protection, absorption, and secretion.
Squamous Epithelium
Squamous Epithelium
Flat, pancake-like epithelial cells.
Cuboidal Epithelium
Cuboidal Epithelium
Cube-shaped epithelial cells.
Columnar Epithelium
Columnar Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Simple Epithelium
Simple Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stratified Epithelium
Stratified Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pseudostratified Epithelium
Pseudostratified Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Apical Surface
Apical Surface
Signup and view all the flashcards
Basal Surface
Basal Surface
Signup and view all the flashcards
Basement Membrane
Basement Membrane
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cilia
Cilia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Microvilli
Microvilli
Signup and view all the flashcards
Connective Tissue
Connective Tissue
Signup and view all the flashcards
Extracellular Matrix
Extracellular Matrix
Signup and view all the flashcards
Collagenous Fibers
Collagenous Fibers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Elastic Fibers
Elastic Fibers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Reticular Fibers
Reticular Fibers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fibroblasts
Fibroblasts
Signup and view all the flashcards
Macrophages
Macrophages
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mast Cells
Mast Cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chondrocytes
Chondrocytes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Osteocytes
Osteocytes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Loose Connective Tissue
Loose Connective Tissue
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dense Irregular Connective Tissue
Dense Irregular Connective Tissue
Signup and view all the flashcards
Regular Connective Tissue
Regular Connective Tissue
Signup and view all the flashcards
Elastic Connective Tissue
Elastic Connective Tissue
Signup and view all the flashcards
Reticular Connective Tissue
Reticular Connective Tissue
Signup and view all the flashcards
Adipose Tissue
Adipose Tissue
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hyaline Cartilage
Hyaline Cartilage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lacunae
Lacunae
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chondrocytes
Chondrocytes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Elastic Cartilage
Elastic Cartilage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Osteon
Osteon
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lamellae
Lamellae
Signup and view all the flashcards
Canaliculi
Canaliculi
Signup and view all the flashcards
Plasma
Plasma
Signup and view all the flashcards
Erythrocytes
Erythrocytes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Platelets
Platelets
Signup and view all the flashcards
Leukocytes
Leukocytes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Muscle Tissue
Muscle Tissue
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sarcolemma
Sarcolemma
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sarcoplasm
Sarcoplasm
Signup and view all the flashcards
Striated Muscle
Striated Muscle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Smooth Muscle
Smooth Muscle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cardiac Muscle
Cardiac Muscle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Neurons
Neurons
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glial Cells
Glial Cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Perikaryon
Perikaryon
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dendrites
Dendrites
Signup and view all the flashcards
Axons
Axons
Signup and view all the flashcards
Simple Squamous Epithelium
Simple Squamous Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Simple Columnar Epithelium
Simple Columnar Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Simple Columnar Ciliated Epithelium
Simple Columnar Ciliated Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pseudostratified Ciliated Columnar Epithelium
Pseudostratified Ciliated Columnar Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Loose Connective Tissue Location
Loose Connective Tissue Location
Signup and view all the flashcards
Reticular Connective Tissue Function
Reticular Connective Tissue Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Muscle Tissue Function
Muscle Tissue Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Striated Muscle Function
Striated Muscle Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nerves (l.s.)
Nerves (l.s.)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Grey Matter
Grey Matter
Signup and view all the flashcards
White Matter
White Matter
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ecdysis
Ecdysis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Arthropod Appendages
Arthropod Appendages
Signup and view all the flashcards
Water vascular system
Water vascular system
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tube feet
Tube feet
Signup and view all the flashcards
Madreporite
Madreporite
Signup and view all the flashcards
Notochord
Notochord
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pharyngeal gill slits
Pharyngeal gill slits
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
- Animal tissues are divided into four main types: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous.
- Epithelial tissue is found as inner and outer layers of organs, providing protection, absorption, and secretion.
- Connective tissue has a sparse scattering of cells in an extracellular matrix, connecting and supporting body structures.
- Muscle tissue is composed of cells that contract for mobility.
- Nervous tissue transmits information via electrical signals, consisting of neurons and glial cells.
Epithelial Tissue
- Classified by cell shape (squamous, cuboidal, columnar) and arrangement (simple, stratified, pseudostratified).
- All epithelial tissue has polarity, with an apical (top) and basal (bottom) side.
- The apical side faces toward the lumen (the empty space of an organ).
- The basement membrane attaches the basal surface to other tissues.
- Cilia are hair-like projections that move substances past cells.
- Microvilli are tiny extensions increasing surface area for absorption or adhesion.
Simple Squamous Epithelium
- Mainly provides protection and is found in lung, heart, and abdominal cavities.
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
- Specializes in secretion and is found in glands like the thyroid, salivary glands, and pancreas.
Simple Columnar Epithelium
- Nuclei are closer to the basal surface and are capable of secretion and absorption.
Simple Columnar Ciliated Epithelium
- Found in the respiratory tract (for removing foreign particles), uterus, and oviducts (for moving eggs), with a protective function.
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
- Found in skin, cheek, gums, cornea, and vagina, in areas prone to abrasion.
Pseudostratified Ciliated Columnar Epithelium
- Appears layered but is a single layer; all cells contact the basement membrane.
- Found in the respiratory tract for protection.
- Goblet cells secrete mucus.
- Goblet cells + ciliated columnar cells = pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium.
Connective Tissue
- Connects and supports body structures.
- Consists of an extracellular matrix (solid, liquid, or gelatinous) and fibers.
- Collagenous fibers composed of collagen provide strength and flexibility.
- Elastic fibers composed of elastin provide elasticity.
- Reticular fibers are branched and hold tissues and organs together.
- Fibroblasts produce all fibers in connective tissue.
- Macrophages engulf and digest foreign particles.
- Mast cells release histamine as part of the inflammation process.
- Chondrocytes are cartilage cells.
- Osteocytes are bone cells.
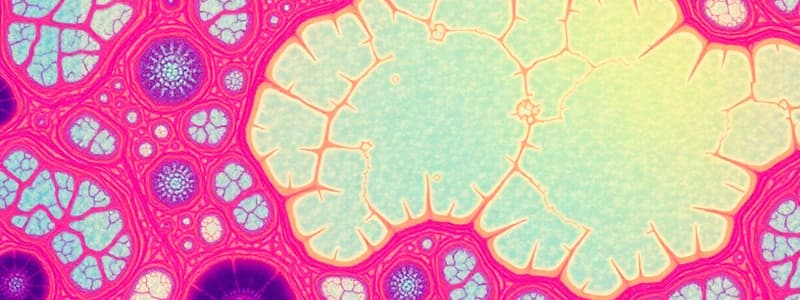
Loose Connective Tissue
- Found around organs and attached to epithelium.
- Contains loosely scattered fibers with fibroblasts, collagenous, and elastic fibers with mast cells in an extracellular matrix.
- Collagenous fibers are long, thick, stretchy, pink (or orange).
- Fibroblasts appear as dark purple circles (usually the nucleus).
- Mast cells appear as grainy bits.
Dense Irregular Connective Tissue
- Found in the dermis of the skin and submucosa of the digestive tract.
- Composed mostly of tightly packed collagenous fibers and fibroblasts in interwoven bundles.
- Collagenous fibers are interwoven bundles that twist and turn throughout tissue instead of in parallel lines.
Regular Connective Tissue
- Collagenous fibers are densely packed together in an orderly manner, also has fibroblasts.
Elastic Connective Tissue
- Composed of densely packed collagenous and elastic fibers; fibroblasts are compacted and hard to see, the tissue is stretchy.
Reticular Connective Tissue
- Branching tissue holding organs together.
- Reticular fibers appear branched.
Adipose Tissue
- Stores lipid for energy reserves, insulation, and cushioning.
- Contains a large lipid vacuole that takes up most of the space.
- Fibroblasts are found between adipose cells in the hypodermis.
Hyaline Cartilage
- Solid matrix that supports the body.
- The term "hyaline" means "glass" in Greek.
- It is smooth and semitransparent, and found in the nose and joints.
- Lacunae are spaces where cells are located.
- Chondrocytes are cartilage cells that build and maintain the matrix.
Elastic Cartilage
- Similar to hyaline cartilage but with elastic fibers, making it more stretchy and flexible, found in the epiglottis.
Bone
- Provides support.
- Osteon is the functional unit consisting of a central canal surrounded by concentric rings of lacunae.
- Living osteons contain blood vessels and nerves that support osteocytes.
- Lamellae are layers of solid matrix between lacunae.
- Canaliculi are tiny channels delivering nutrients to osteocytes.
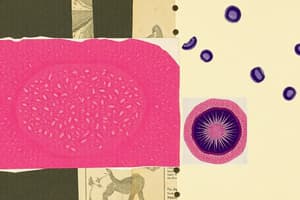
Blood
- Liquid matrix (plasma) containing: erythrocytes to carry oxygen, platelets for clotting, and leukocytes.
- Platelets are the smallest, little purple dots.
- Leukocytes are big with purple blobs, which are the nucleus.
Muscle Tissue
- Contractile tissue with cells that can shorten to cause movement.
- Composed of muscle fibers (cells) made of myofibrils and myofilaments.
- Sarcolemma is the plasma membrane and sarcoplasm is the cytoplasm of the muscle cell.
Striated (Skeletal) Muscle
- Has striped appearance, is attached to bones, and is associated with voluntary movements.
- A bands are the thicker myofilaments and darker bands, I bands are the thinner myofilaments and lighter bands. Both not visible in cross-section samples
- Will look roughly circular in cross sections.
Smooth Muscle
- Found within organs and its movement is not under conscious control.
- Less regularly arranged than skeletal muscle, so there are no striations.
- Cells usually have a single nucleus and tend to be smaller than striated
Cardiac Muscle
- Fibers interweave, cells have one or more nuclei, and exhibit striations.
- Intercalated discs are tight connections between cells that coordinate contractions.
Nervous Tissue
- Functions to send electrical signals throughout the body.
- Found in the central and peripheral nervous system.
- Composed of neurons (carry signals) and glial cells (support neurons).
- Perikaryon (cell body) contains nucleus and organelles.
- Neuron processes (dendrites and axons) carry signals.
Neurons and Glial Cells
- Neurons are large, while glial cells are small.
Nerves
-
Bundles of neuron processes covered by Schwann cells, which insulate and speed up the signal.
-
Myelin is a lipid that insulates the nerve signal.
-
The myelin sheath is multiple Schwann cells wrapped around the neuron process.
-
Nodes of Ranvier are gaps between Schwann cells.
Spinal Cord
- Divided into grey matter (perikaryon and glial cells) and white matter (neuron processes with myelin).
- Oligodendrocytes insulate in the spinal cord.
- The central canal is a hollow area in the middle.
Animalia
- Animals are in domain Eukarya, kingdom Animalia.
- Includes 7-8 million extant (alive) species, with about 1 million formally described.
- Animals are distinguished from other eukaryotes by their inability to perform photosynthesis.
Linnean Classification
- Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species.
- Clades are monophyletic and do not have an agreed-upon rank.
Phylum Porifera
- Sponges, composed of ~5,500 species, are asymmetrical.
- They lack true tissues, but some cells have special functions.
- Sponges are sessile filter feeders with sac-like bodies.
- Sponges pull water through pores on their body, entering a central chamber called the spongocoel.
- Choanocytes line the spongocoel and engulf and digest food particles.
- Amoebocytes transport nutrients and produce spicules.
- Water exits through the osculum.
- Spongin fibers are composed of protein spongin.
- Spicules are composed of either calcium carbonate or silica.
- Connected to the environment by the basal disc.
Class Calcarea Order Leucosolenida Family Grandtiidae Genus Grantia
- The genus Grantia has a folded body wall to increase surface area for food capture and waste disposal.
- The body plan is a tall tube.
Phylum Ctenophora
- Comb jellies, with ~100 extant marine animals.
- Move using eight rows of cilia (comb rows).
- Comb rows are rows of fused cilia that beat synchronously to propel animal.
- Radially symmetrical.
- They are generally considered to have two simple tissues
- Use colloblasts on tentacles to capture prey; don't sting.
Phylum Cnidaria
- Stinging nettles, with ~10,000 mostly marine animals.
- Are split into subphylum Medusozoa and subphylum Anthozoa.
- Are radially symmetrical.
- Have two simple tissues: epidermis (external) and gastrodermis (internal).
- Cnidocytes release nematocysts containing poison and barbed threads.
- Digestion is extracellular in the gastrovascular cavity with an incomplete gut.
- Body plans: polyp (sessile) and medusa (free-floating).
Subphylum Medusozoa
- Cnidarians with a medusa stage, including jellies, box jellies, and hydrozoans.
Subphylum Anthozoa
- Corals and sea anemones, lack a medusa stage, remain polyps.
- Sea anemones are soft, fairly large, polyps
- Corals are colonies of anthozoan polyps that construct a calcium carbonate skeleton and has a symbiotic relationship with algae zooxanthellae.
Class Hydrozoa Order Leptothecata Family Campanulariidae Genus Obelia
- Genus Obelia has both polyp and medusa stages.
- Polyps live in colonies and can be specialized for feeding or asexual reproduction.
- Reproductive polyps reproduce tiny medusae via budding that produce more polyps via sexual reproduction completing the cycle.
Superphylum Lophotrochozoa
- Have bilateral symmetry and true tissues.
- Some have a lophophore for suspension feeding.
- Some have trochophore larva.
- Defined by shared DNA.
Phylum Platyhelminthes
- Flatworms, with ~20,000 species, have bilateral symmetry and flattened bodies.
- Most have an incomplete gut with a gastrovascular cavity.
- Lack a coelom and circulatory system.
- Flat bodies allow for easy exchange by diffusion.
Phylum Platyhelminthes Class Cestoda
- Tapeworms, absorbing nutrients through the body wall.
- Has scolex (hooks and suckers) to attach to the intestinal wall.
- Proglottids are repeated segments, filling posterior segments with eggs.
Phylum Platyhelminthes Class Trematoda
- Flukes are obligate parasites with complex lifecycles.
Phylum Platyhelminthes Class Turbellaria
- Planarians are free-living freshwater flatworms.
- Can regenerate due to pluripotent stem cells.
- Have eyespots, auricles (touch and chemical sensation), pharynx, and a branched gastrovascular cavity.
Phylum Syndermata
- Rotifers (~1,800 species) and acanthocephalans (~1,100 species).
Rotifers
- Named for the crown of cilia around their mouth.
- Have an alimentary canal and pseudocoelom.
- Many reproduce asexually via parthenogenesis.
Phylum Brachiopoda
- Lamp shells, resemble clams.
- Shells are dorsal and ventral with a lophophore (ciliated tentacles) and a true coelom.
- A pedicel attaches the animal to the substrate.
Phylum Annelida
- Segmented worms, with ~17,000 species, exhibit metamerism.
- Have septa, setae and a complete gut.
- Are found in virtually every habitat.
Phylum Mollusca
- Mollusks, with ~100,000 species, have bilateral symmetry, true tissues, complete gut, coelom, and a shell composed of calcium carbonate.
- Have a foot (for movement), mantle (creates the shell), and radula (feeding structure).
Phylum Mollusca Class Polyplacophora
- Chitons, with multiple valves on their dorsal surface.
- Found in intertidal zones, using their radula to scrape algae.
Phylum Mollusca Class Bivalvia
- Clams, oysters, mussels, scallops with two valves (shells).
- Tend to be filter feeders.
Phylum Mollusca Class Gastropoda
- Snails and slugs, undergo torsion, resulting in coiled shells, and have two pairs of tentacles.
Phylum Mollusca Class Cephalopoda
- Squids, octopods, cuttlefish, and nautiloids, have dorsoventral elongation.
- Have excellent vision and jet propulsion.
- Mostly have 8 arms, while squids and cuttlefish also have 2 tentacles.
Annelida and Mollusca
- Found in a variety of freshwater, saltwater, and terrestrial environments.
- Are bilaterally symmetrical with true tissues, complete gut and a ceolom to store organs.
- Can be distinguished by setae.
Superphylum Ecdysozoa
- Animals have a cuticle that is periodically shed (ecdysis).
Phylum Nematoda
- Roundworms are unsegmented, live in aquatic and moist terrestrial environments.
- They have a tough cuticle, alimentary canal, pseudocoelom, and longitudinal muscles, but no circulatory system.
Phylum Tardigrada
- Water bears that can survive extreme conditions by entering a state of dormancy.
Phylum Arthropoda
- Arthropods, with over 1M species, have appendages that are jointed, segmented bodies, chitinous exoskeleton, alimentary canal, and hemocoel.
Subphylum Chelicerata
- Spiders, ticks, mites, scorpions, horseshoe crabs, and sea spiders.
- Six pairs of appendages: chelicerae (feeding), pedipalps (sensory), and four walking legs.
- Lack antennae.
- Body divided into cephalothorax and abdomen.
- Spiders have spinnerets for silk.
Subphylum Myriapoda
- Centipedes and millipedes.
- Have one pair of antennae, three pairs of mouthparts, and many legs.
- Millipedes are herbivores with two pairs of legs per segment, and centipedes are carnivores with one pair.
Subphylum Pancrustacea
- Include crustaceans (crabs, lobsters, shrimps) and insects.
Subphylum Pancrustacea Class Insecta
- Have more named species than all other forms of life combined.
- Have one pair of antennae, tracheal system, three body segments (head, thorax, abdomen), and three pairs of legs.
- Many insects have wings.
Superphylum Deuterostomia
- Unite by a developmental pattern where the anus forms before the mouth.
- Includes Echinodermata and Chordata.
Phylum Echinodermata
- Sea stars, brittle stars, sea urchins, sea cucumbers, and crinoids.
- They are bilaterally symmetrical.
- Have a water vascular system with tube feet, madreporite, endoskeleton with spines, and gills.
- Pathway of water: madreporite → stone canal → ring canal → radial canal → ampulla → podium.
- They have an oral and aboral surface.
Phylum Chordata
- Mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, fish.
- Name comes from having a notochord.
- United by: notochord, pharyngeal gill slits, muscular post-anal tail, dorsal hollow nerve cord.
Subphylum Cephalochordata
- Lancelets, suspension feeders using cirri around the mouth.
Subphylum Urochordata
- Tunicates, larvae are free-swimming.
- Adults are sessile filter feeders with pharyngeal slits.
Subphylum Vertebrata
- Have bony structures supporting the dorsal midline.
- Usually endoskeleton composed of bone
- Slide preparation terminology:
- Whole mount: the entire structure is placed on the slide.
- Cross section: sample is taken perpendicular to the main axis of the organism or structure.
- Longitudinal section: slice is taken parallel to the main axis.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.