Podcast
Questions and Answers
Cats are invertebrates because they lack a backbone.
Cats are invertebrates because they lack a backbone.
False (B)
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of multicellular organisms?
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of multicellular organisms?
- They are composed of multiple cells.
- They exhibit cellular differentiation.
- They can perform complex functions.
- They are always larger than unicellular organisms. (correct)
The process by which a cell becomes specialized to perform a specific function is called ______.
The process by which a cell becomes specialized to perform a specific function is called ______.
cellular differentiation
What is the main function of connective tissue in animals?
What is the main function of connective tissue in animals?
Match the following types of animal tissue with their primary function:
Match the following types of animal tissue with their primary function:
Which of the following is NOT a human organ system?
Which of the following is NOT a human organ system?
How does gas exchange occur in frogs when they are underwater?
How does gas exchange occur in frogs when they are underwater?
Plants transport water and minerals from their roots to their leaves through specialized tubes called the ______.
Plants transport water and minerals from their roots to their leaves through specialized tubes called the ______.
What are the three forces that push water upward in a plant?
What are the three forces that push water upward in a plant?
Unicellular organisms rely on phagocytosis for nutrients because they lack a digestive system.
Unicellular organisms rely on phagocytosis for nutrients because they lack a digestive system.
What is the primary function of the circulatory system in animals?
What is the primary function of the circulatory system in animals?
The ______ system is responsible for sending signals throughout the body, allowing animals to respond to their environment.
The ______ system is responsible for sending signals throughout the body, allowing animals to respond to their environment.
Match the following organ systems to their functions:
Match the following organ systems to their functions:
Which of the following groups of organisms can perform photosynthesis?
Which of the following groups of organisms can perform photosynthesis?
Explain the role of cilia in paramecia.
Explain the role of cilia in paramecia.
Trees lose their leaves in winter to conserve energy and prevent water loss.
Trees lose their leaves in winter to conserve energy and prevent water loss.
Flashcards
Vertebrate
Vertebrate
An animal with a backbone; includes mammals, birds, reptiles, etc.
Unicellular Organism
Unicellular Organism
An organism made up of a single cell.
Multicellular Organism
Multicellular Organism
An organism made up of many cells.
Cellular Differentiation
Cellular Differentiation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Differentiated Cell
Differentiated Cell
Signup and view all the flashcards
Xylem
Xylem
Signup and view all the flashcards
Animal Tissues
Animal Tissues
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gas Exchange
Gas Exchange
Signup and view all the flashcards
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cilia
Cilia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Phagocytosis
Phagocytosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Circulatory System
Circulatory System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nervous System
Nervous System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Musculoskeletal System
Musculoskeletal System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Response to Environment
Response to Environment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dropping Leaves
Dropping Leaves
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Animal Organization and Function
- Vertebrates vs. Invertebrates: Cats are vertebrates, possessing a backbone. Invertebrates lack a backbone.
Cell Organization
- Unicellular Organisms: Organisms composed of a single cell.
- Multicellular Organisms: Organisms composed of more than one cell.
- Cellular Differentiation: The process where cells become specialized to perform specific functions.
- Specialized Cells: Cells with unique functions, such as blood cells carrying oxygen.
Levels of Organization (Increasing Complexity)
- Cells
- Tissues
- Organs
- Organ Systems
- Organisms
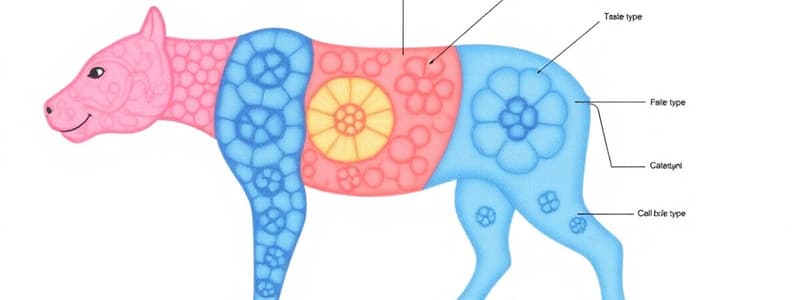
Animal Tissues
- Connective Tissue: Supports and connects other tissues (e.g., bone, blood).
- Epithelial Tissue: Forms coverings (e.g., skin, lining of internal passages).
- Muscle Tissue: Enables movement.
- Nervous Tissue: Transmits signals to the brain.
Differentiated Cells
- A differentiated cell is a specialized cell with a specific function. An example is a blood cell, carrying oxygen.
Human Organ Systems
- Circulatory
- Digestive
- Musculoskeletal
- Respiratory
- Nervous
Gas Exchange (Humans vs. Frogs)
- Humans: Air enters through nose/mouth, travels to lungs (alveoli), oxygen diffuses into blood, carbon dioxide diffuses out.
- Frogs (underwater): Can absorb oxygen through skin and mouth.
Plant Transport
- Plants transport water and minerals from roots to leaves via the xylem. Factors include root pressure, capillary action, and transpiration pull from stomata.
Photosynthesis Organisms
- Algae, trees, flowers, and other plants can perform photosynthesis.
Paramecium Cilia
- Paramecia use cilia for movement and feeding, to move through water and ingest food.
Unicellular Phagocytosis
- Unicellular organisms use phagocytosis to engulf food particles, forming a food vacuole for nutrient digestion.
Organ System Functions (Table)
- Circulatory: Transports oxygen, uses heart and blood vessels.
- Respiratory: Supplies oxygen for breathing, uses nose and trachea.
- Digestive: Digests food, uses mouth and stomach.
- Musculoskeletal: Supports the body, uses bones.
- Nervous: Sends signals to the brain, uses brain.
Environmental Response (Vertebrates)
- Vertebrates respond to their environment using the nervous and musculoskeletal systems. The nervous system detects danger; the musculoskeletal system allows movement away from it.
Major Organism Groups
- Fungi
- Bacteria
- Animals
- Plants
- Protists
Environmental Response Example (Human)
- Touching a hot stove—nervous system signals pain, leading to a withdrawal response.
Environmental Response Example (Trees)
- Trees lose leaves in cold/dry conditions to conserve water and energy.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.