Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the anatomical significance of the depression inferior to the transverse sinus?
What is the anatomical significance of the depression inferior to the transverse sinus?
- It is specifically for the cerebellum. (correct)
- It connects the cerebellum and the spinal cord.
- It serves as the attachment point for the brainstem.
- It houses the major blood vessels supplying the cerebrum.
Which bone articulates laterally with the structures of the skull and the vertebral column?
Which bone articulates laterally with the structures of the skull and the vertebral column?
- Parietal bone
- Temporal bone (correct)
- Sphenoid bone
- Frontal bone
What is the location of the occipital condyles in relation to the foramen magnum?
What is the location of the occipital condyles in relation to the foramen magnum?
- Anteriorly positioned to the foramen magnum
- Medially located at the foramen magnum
- Posterior to the foramen magnum
- Lateral to the foramen magnum (correct)
Which structure articulates specifically with the atlas?
Which structure articulates specifically with the atlas?
Which of the following is NOT true about the lateral portion of the skull?
Which of the following is NOT true about the lateral portion of the skull?
What anatomical feature is more pronounced in males?
What anatomical feature is more pronounced in males?
Which of the following lines is found on the occipital bone?
Which of the following lines is found on the occipital bone?
Which sinuses are involved in the formation of the confluence of the sinuses?
Which sinuses are involved in the formation of the confluence of the sinuses?
What is the purpose of the depression located superior to the transverse sinus?
What is the purpose of the depression located superior to the transverse sinus?
Which of these structures has grooves for three sinuses on its internal surface?
Which of these structures has grooves for three sinuses on its internal surface?
What bones does the squamous portion of the occipital bone articulate with?
What bones does the squamous portion of the occipital bone articulate with?
Which sutures are associated with the articulation of the squamous portion of the occipital bone?
Which sutures are associated with the articulation of the squamous portion of the occipital bone?
Where is the squamous portion of the occipital bone located?
Where is the squamous portion of the occipital bone located?
Which statement about the squamous portion of the occipital bone is correct?
Which statement about the squamous portion of the occipital bone is correct?
Which of the following features does NOT describe the squamous portion of the occipital bone?
Which of the following features does NOT describe the squamous portion of the occipital bone?
What is one of the primary roles of the temporal bones in the skull?
What is one of the primary roles of the temporal bones in the skull?
How many temporal bones are found in the human skull?
How many temporal bones are found in the human skull?
Which of the following structures is housed within the temporal bones?
Which of the following structures is housed within the temporal bones?
What is found within the temporal bones that aids in the regulation of hearing?
What is found within the temporal bones that aids in the regulation of hearing?
Which of the following features is NOT characteristic of the temporal bones?
Which of the following features is NOT characteristic of the temporal bones?
What anatomical structure extends superiorly from the cribriform plate?
What anatomical structure extends superiorly from the cribriform plate?
Which foramina are associated with the crista galli?
Which foramina are associated with the crista galli?
Which part of the ethmoid bone is considered the largest?
Which part of the ethmoid bone is considered the largest?
What is the relationship between the crista galli and the foramen cecum?
What is the relationship between the crista galli and the foramen cecum?
Which statement accurately describes the cribriform plate?
Which statement accurately describes the cribriform plate?
What is the ethmoid bulla?
What is the ethmoid bulla?
What structure is located between the uncinate process and the ethmoid bulla?
What structure is located between the uncinate process and the ethmoid bulla?
What shape is the uncinate process described as?
What shape is the uncinate process described as?
Which of the following best defines the hiatus semilunaris?
Which of the following best defines the hiatus semilunaris?
Which paranasal sinus is closest to the ethmoid bulla?
Which paranasal sinus is closest to the ethmoid bulla?
Flashcards
Squamous portion of the occipital bone
Squamous portion of the occipital bone
The largest part of the occipital bone, located behind and above the foramen magnum.
Occipitomastoid suture
Occipitomastoid suture
The connection point between the squamous portion of the occipital bone and the temporal and parietal bones.
Lambdoid suture
Lambdoid suture
The connection point between the squamous portion of the occipital bone and the parietal bones.
Foramen magnum
Foramen magnum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Location of the squamous portion
Location of the squamous portion
Signup and view all the flashcards
External Occipital Protuberance
External Occipital Protuberance
Signup and view all the flashcards
Superior and Inferior Nuchal Lines
Superior and Inferior Nuchal Lines
Signup and view all the flashcards
Grooves for Sinuses
Grooves for Sinuses
Signup and view all the flashcards
Confluence of Sinuses
Confluence of Sinuses
Signup and view all the flashcards
Depression for Occipital Lobes
Depression for Occipital Lobes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cerebellar depression
Cerebellar depression
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lateral occipital portion
Lateral occipital portion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lateral portion of occipital bone
Lateral portion of occipital bone
Signup and view all the flashcards
Occipital condyles
Occipital condyles
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the temporal bones?
What are the temporal bones?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are mastoid air cells?
What are mastoid air cells?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What systems are contained within the temporal bones?
What systems are contained within the temporal bones?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How many temporal bones are there?
How many temporal bones are there?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the function of the temporal bones?
What is the function of the temporal bones?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Crista Galli
Crista Galli
Signup and view all the flashcards
Foramen Cecum
Foramen Cecum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ethmoid Labyrinth
Ethmoid Labyrinth
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ethmoidal Foramina
Ethmoidal Foramina
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cribriform Plate
Cribriform Plate
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ethmoid bulla
Ethmoid bulla
Signup and view all the flashcards
Uncinate process
Uncinate process
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hiatus semilunaris
Hiatus semilunaris
Signup and view all the flashcards
Where is the hiatus semilunaris located?
Where is the hiatus semilunaris located?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What structures define the hiatus semilunaris?
What structures define the hiatus semilunaris?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Human Anatomy: Axial Skeleton - Skull
- The skull comprises many separate bones joined by immobile sutures, except the mandible, which connects via a temporomandibular joint.
- Connective tissue between the bones is a sutural ligament.
- The skull has 22 bones: 8 form the cranium (enclosing the brain and meninges), and 14 form the face.
- The cranium's upper part is the vault, and the lower part is the base.
Cranial Bones
- Frontal bone (1)
- Parietal bones (2)
- Occipital bone (1)
- Temporal bones (2)
- Sphenoid bone (1)
- Ethmoid bone (1)
Facial Bones
- Zygomatic bones (2)
- Maxillae (2)
- Nasal bones (2)
- Lacrimal bones (2)
- Vomer (1)
- Palatine bones (2)
- Inferior nasal conchae (2)
- Mandible (1)
Frontal Bone
- Parts:
- Squamous portion (largest, forms forehead)
- Orbital portion (roof of orbit, anterior cranial fossa)
- Nasal portion (articulates with nasal bones and maxilla, forming nasal root)
Parietal Bone
- Characteristics:
- Forms most of the cranial vault
- Four corners develop after birth (fontanelles)
- Relatively square, forming roof and sides of cranial vault.
- Grooves on endocranial(brain inner) surface for middle meningeal artery branches
- Four angles: frontal, sphenoid, occipital, and mastoid
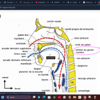
Occipital Bone
- Characteristics:
- Forms posterior part of cranial vault
- Articulates with the atlas
- One occipital bone
- Parts: Squamous portion, greatest portion, located posterior and superior to foramen magnum, external occipital protuberance, superior and inferior nuchal lines, grooves for sinuses, depressions for brain(superior) and cerebellum(inferior) structures, lateral portion, articulates with temporal bones, occipital condyles, hypoglossal canal, part of jugular foramen
Temporal Bone
- Characteristics:
- Forms part of base and lateral walls of skull; houses auditory and vestibular systems; contains mastoid air cells
- Two temporal bones
- Parts:
- Squamous part (largest, zygomatic process, glenoid fossa, mandibular fossa, temporomandibular joint)
- Petrous part (dense, houses auditory/vestibular systems, separates temporal/occipital lobes, internal acoustic meatus, carotid canal, tympanic fissure, jugular fossa)
- Mastoid part (air cells, posterior, superior/inferior borders with parietal/occipital)
- Tympanic part (external acoustic meatus, plate of bone)
- Styloid process (projection from temporal bone, stylomastoid foramen posterior)
Sphenoid Bone
- Characteristics:
- Forms part of middle cranial base and part of the middle cranial fossa.
- Single sphenoid bone
- Parts: Body, greater wings(four portions), lesser wings, pterygoid processes.
- Body (sella turcica, hypophyseal fossa, optic canal, superior/inferior parts)
- Greater wings(part of middle fossa, foramen spinosum, foramen rotundum, foramen ovale)
- Lesser wings(part of anterior cranial fossa)
- Pterygoid processes (lateral/medial plates)
Ethmoid Bone
- Characteristics:
- Forms part of middle portion of face, orbits, nasal cavity, nasal septum, anterior cranial fossa
- Single ethmoid bone
- Parts: Perpendicular plate, cribriform plate, ethmoid labyrinth, crista galli, superior/middle nasal conchae, ethmoid sinuses
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.