Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of the skull?
What is the primary function of the skull?
- To assist in mastication
- To enable facial expression
- To protect the brain and house sensory organs (correct)
- To facilitate blood circulation
Which structures are contained within the neck region?
Which structures are contained within the neck region?
- Only the spinal cord
- Only muscles and nerves
- Bones of the skull and face
- Trachea, esophagus, and vascular systems (correct)
Which organ is NOT involved in the respiratory function of the head and neck?
Which organ is NOT involved in the respiratory function of the head and neck?
- Esophagus (correct)
- Pharynx
- Larynx
- Trachea
What can be a consequence of a head injury?
What can be a consequence of a head injury?
What are muscles of mastication primarily responsible for?
What are muscles of mastication primarily responsible for?
What role do major arteries in the head and neck serve?
What role do major arteries in the head and neck serve?
Which condition is considered a potential risk affecting the head and neck?
Which condition is considered a potential risk affecting the head and neck?
What type of problems can dental issues cause?
What type of problems can dental issues cause?
What is the primary purpose of imaging techniques like CT scans and MRIs in head and neck conditions?
What is the primary purpose of imaging techniques like CT scans and MRIs in head and neck conditions?
Which treatment method is frequently combined with others to treat cancer in head and neck cases?
Which treatment method is frequently combined with others to treat cancer in head and neck cases?
What is the role of biopsies in the context of head and neck conditions?
What is the role of biopsies in the context of head and neck conditions?
Which of the following is NOT typically part of the treatment approaches for head and neck conditions?
Which of the following is NOT typically part of the treatment approaches for head and neck conditions?
Why are neurological examinations important in managing head and neck conditions?
Why are neurological examinations important in managing head and neck conditions?
Flashcards
Vascular Head/Neck Issues
Vascular Head/Neck Issues
Conditions like aneurysms and vascular malformations in the head and neck need immediate attention.
Diagnostic Imaging
Diagnostic Imaging
CT scans and MRIs are used to evaluate head and neck issues.
Head/Neck Treatment Variety
Head/Neck Treatment Variety
Head and neck treatments depend on the condition and severity. It can vary broadly.
Cancer Treatment Options
Cancer Treatment Options
Signup and view all the flashcards
Interdisciplinary Care
Interdisciplinary Care
Signup and view all the flashcards
Head and Neck Anatomy
Head and Neck Anatomy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Skull Function
Skull Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Head and Neck Physiology
Head and Neck Physiology
Signup and view all the flashcards
Head and Neck Clinical Significance
Head and Neck Clinical Significance
Signup and view all the flashcards
Neurological Disorders
Neurological Disorders
Signup and view all the flashcards
Head Trauma
Head Trauma
Signup and view all the flashcards
ENT (Ear, Nose, and Throat) Disorders
ENT (Ear, Nose, and Throat) Disorders
Signup and view all the flashcards
Respiratory and Digestive Functions in Head and Neck
Respiratory and Digestive Functions in Head and Neck
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Anatomy
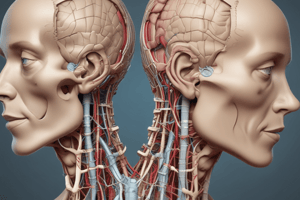
- The head and neck region encompasses a complex network of structures crucial for vital functions like breathing, swallowing, and communication.
- It includes the skull, face, and associated muscles, nerves, and blood vessels.
- The skull protects the brain and houses sensory organs.
- Bones of the cranium and facial skeleton form rigid yet flexible protection.
- Muscles of mastication (chewing) are crucial for oral function.
- The neck supports the head, allows for movement, and contains vital structures like the trachea, esophagus, and major blood vessels (carotid arteries and jugular veins).
Physiology
- The head and neck house the brain, crucial for higher-level functions such as thought, language, and memory.
- Sensory organs (eyes, ears, nose, and tongue) transmit information to the brain, enabling perception of the external world.
- The head and neck are vital for respiratory and digestive functions. Breathing depends on the larynx and trachea; swallowing involves the pharynx and esophagus.
- Blood circulation in the head is supplied by major arteries branching off the aorta, ensuring the brain and other tissues receive oxygen and nutrients.
- The head and neck contain complex networks of nerves, controlling muscle function and transmitting sensory information from various organs.
Clinical Significance
- Conditions affecting the head and neck can have significant consequences.
- Neurological disorders, such as stroke or brain tumors, can impact cognitive function and motor control.
- Head injuries can result in various levels of trauma, ranging from mild concussion to severe traumatic brain injury.
- Facial trauma can lead to disfigurement and dysfunction of the mouth and nose and damage to the sinuses.
- Cancer can develop in tissues like the larynx, pharynx, mouth, and neck, necessitating early detection and prompt treatment.
- Infections can affect the sinuses of the nasal cavity, causing sinusitis or other ENT issues potentially impacting the respiratory system, often requiring medical intervention.
- Dental problems impact mastication and speech and can need restorative or surgical treatment.
- Congenital disorders or abnormalities in the structures of the head and neck may need surgical or medical intervention, depending on the nature of the abnormality.
- ENT (Ear, Nose, and Throat) disorders cover a broad range of issues, including infections, allergies, and cancerous growth.
- Vascular issues in the head and neck, like aneurysms or vascular malformations, can lead to serious consequences if not managed immediately.
Diagnostic Techniques
- Imaging techniques, such as CT scans and MRIs, are essential for evaluating head and neck conditions.
- Endoscopy allows visualization of the inner structures of the throat and airways.
- Biopsies are often needed to confirm the presence of cancer or other abnormalities.
- Neurological examinations assess the function of the brain and nerves.
- Blood tests aid in assessing overall body health and can detect infections or other conditions that might be associated with head and neck issues.
Treatment Approaches
- Treatment of head and neck conditions varies significantly depending on the specific diagnosis and severity.
- Surgery may be needed for correcting structural abnormalities, removing tumors, or repairing injuries.
- Radiation therapy and chemotherapy are frequently used for cancer treatment and often used in combination therapies.
- Physiotherapy and speech therapy are integral parts of the rehabilitation process for patients undergoing trauma or recovery from certain conditions affecting the head and neck structures, including stroke recovery and treatment of speech impairment.
- Medications can be used to treat infections, control symptoms, and manage chronic conditions.
- Interdisciplinary care often benefits patients with complex head and neck issues, with specialists from various fields to coordinate treatment.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.