Podcast
Questions and Answers
ما هي وظيفة غشاء البلازما؟
ما هي وظيفة غشاء البلازما؟
يحيط غشاء البلازما بكل خلية، ويسمح لها بالتفاعل مع بيئتها الخارجية وخلايا أخرى. يقوم بغشاء البلازما بالعديد من الوظائف مثل تنظيم مرور المواد داخل وخارج الخلية، والحفاظ على شكل الخلية، و نقل الإشارات بين الخلايا.
ما هي الطبقات الثلاث لغشاء البلازما؟
ما هي الطبقات الثلاث لغشاء البلازما؟
- طبقة خارجية كثيفة، طبقة داخلية كثيفة، طبقة وسطى رقيقة (correct)
- طبقة خارجية كثيفة، طبقة داخلية رقيقة، طبقة وسطى كثيفة
- طبقة خارجية رقيقة، طبقة داخلية كثيفة، طبقة وسطى كثيفة
هل غشاء البلازما مرن؟
هل غشاء البلازما مرن؟
True (A)
ما هو الغشاء المائي؟
ما هو الغشاء المائي؟
هل غشاء البلازما متماثل من حيث التركيب؟
هل غشاء البلازما متماثل من حيث التركيب؟
ما هي وظائف البروتينات في غشاء البلازما؟
ما هي وظائف البروتينات في غشاء البلازما؟
ما هي أنواع التنقل في غشاء البلازما؟
ما هي أنواع التنقل في غشاء البلازما؟
اشرح الفرق بين النقل السلبي والنقل النشط.
اشرح الفرق بين النقل السلبي والنقل النشط.
ما هي أنواع النقل السلبي؟
ما هي أنواع النقل السلبي؟
يستخدم النقل النشط طاقة من ATP.
يستخدم النقل النشط طاقة من ATP.
اشرح عمل pompe Na+/K+ ?
اشرح عمل pompe Na+/K+ ?
ما هي أنواع النقل النشط؟
ما هي أنواع النقل النشط؟
ما هي أنواع النقل الثانوي؟
ما هي أنواع النقل الثانوي؟
ما هي endocytose؟
ما هي endocytose؟
ما هي أنواع endocytose؟
ما هي أنواع endocytose؟
لا تحتوي البكتيريا على mitochondria .
لا تحتوي البكتيريا على mitochondria .
هل غشاء البلازما هو الغشاء الذي يحيط بجميع الخلايا؟
هل غشاء البلازما هو الغشاء الذي يحيط بجميع الخلايا؟
ما هو سمك غشاء البلازما تقريبًا؟
ما هو سمك غشاء البلازما تقريبًا؟
ما هي المكونات الأساسية لغشاء البلازما؟
ما هي المكونات الأساسية لغشاء البلازما؟
غشاء البلازما ______ وهو مصطلح يشير إلى وجود طبقتين دهنيتين تفصل بينهما طبقة رقيقة من البروتينات.
غشاء البلازما ______ وهو مصطلح يشير إلى وجود طبقتين دهنيتين تفصل بينهما طبقة رقيقة من البروتينات.
يُعد غشاء البلازما بنية متماثلة في جميع أنواع الخلايا.
يُعد غشاء البلازما بنية متماثلة في جميع أنواع الخلايا.
ما هو اسم الترابط الذي يربط غشاء البلازما بالهيكل الخلوي؟
ما هو اسم الترابط الذي يربط غشاء البلازما بالهيكل الخلوي؟
ما هو اسم الطبقة الخارجية الرقيقة التي تغطي غشاء البلازما؟
ما هو اسم الطبقة الخارجية الرقيقة التي تغطي غشاء البلازما؟
ما هي الأنواع الرئيسية للدهون التي تُشكل غشاء البلازما؟
ما هي الأنواع الرئيسية للدهون التي تُشكل غشاء البلازما؟
توجد البروتينات في غشاء البلازما بكميات متساوية على جانبي الغشاء.
توجد البروتينات في غشاء البلازما بكميات متساوية على جانبي الغشاء.
ما هي الوظيفة الرئيسية للبروتينات في غشاء البلازما؟
ما هي الوظيفة الرئيسية للبروتينات في غشاء البلازما؟
قارن بين أنواع البروتينات الموجودة في غشاء البلازما وظيفتها:
قارن بين أنواع البروتينات الموجودة في غشاء البلازما وظيفتها:
توجد الكربوهيدرات في غشاء البلازما على السطح الخارجي فقط.
توجد الكربوهيدرات في غشاء البلازما على السطح الخارجي فقط.
ما هو دور الجليكوكاليكس في غشاء البلازما؟
ما هو دور الجليكوكاليكس في غشاء البلازما؟
اقترح ______ و ______ في عام 1971 نموذجًا جديدًا لغشاء البلازما أطلق عليه اسم نموذج الفسيفساء السائلة.
اقترح ______ و ______ في عام 1971 نموذجًا جديدًا لغشاء البلازما أطلق عليه اسم نموذج الفسيفساء السائلة.
يُعد غشاء البلازما بنية ثابتة وغير مرنة.
يُعد غشاء البلازما بنية ثابتة وغير مرنة.
ما هي أهم وظائف غشاء البلازما؟
ما هي أهم وظائف غشاء البلازما؟
ما هي أنواع النقل عبر غشاء البلازما؟
ما هي أنواع النقل عبر غشاء البلازما؟
تستطيع بعض المواد عبور غشاء البلازما دون الحاجة إلى طاقة.
تستطيع بعض المواد عبور غشاء البلازما دون الحاجة إلى طاقة.
ما هي أنواع النقل السلبي عبر غشاء البلازما؟
ما هي أنواع النقل السلبي عبر غشاء البلازما؟
ينتقل الماء عبر غشاء البلازما عن طريق ______ ، من المنطقة ذات التركيز العالي إلى المنطقة ذات التركيز المنخفض.
ينتقل الماء عبر غشاء البلازما عن طريق ______ ، من المنطقة ذات التركيز العالي إلى المنطقة ذات التركيز المنخفض.
يُعد النقل النشط نوعًا من النقل الذي يتطلب طاقة.
يُعد النقل النشط نوعًا من النقل الذي يتطلب طاقة.
ما هي أنواع النقل النشط عبر غشاء البلازما؟
ما هي أنواع النقل النشط عبر غشاء البلازما؟
ما هي أهمية النقل الحويصلي؟
ما هي أهمية النقل الحويصلي؟
يُعد نقل المواد من داخل الخلية إلى الخارج مثالًا على عملية الإخراج الخلوي (الإفراز).
يُعد نقل المواد من داخل الخلية إلى الخارج مثالًا على عملية الإخراج الخلوي (الإفراز).
ما هي أهمية انتقال المعلومات بين الخلايا؟
ما هي أهمية انتقال المعلومات بين الخلايا؟
يتم انتقال المعلومات بين الخلايا بشكل أساسي عن طريق إشارات كيميائية.
يتم انتقال المعلومات بين الخلايا بشكل أساسي عن طريق إشارات كيميائية.
يُطلق على ______ الخلايا التي تُطلق إشارات كيميائية إلى خلايا أخرى.
يُطلق على ______ الخلايا التي تُطلق إشارات كيميائية إلى خلايا أخرى.
تُعد البروتينات المتخصصة على سطح الخلايا المستقبلة للإشارات هي المسؤول عن استقبال الإشارة.
تُعد البروتينات المتخصصة على سطح الخلايا المستقبلة للإشارات هي المسؤول عن استقبال الإشارة.
ما هو دور البكتيريا في عملية تحرير الطاقة؟
ما هو دور البكتيريا في عملية تحرير الطاقة؟
تستطيع البكتيريا تحرير الطاقة بواسطة الميتوكوندريا.
تستطيع البكتيريا تحرير الطاقة بواسطة الميتوكوندريا.
تُطلق ______ على الطيات التي توجد في غشاء البلازما في البكتيريا.
تُطلق ______ على الطيات التي توجد في غشاء البلازما في البكتيريا.
Flashcards
سمك الغشاء البلازمي
سمك الغشاء البلازمي
75 أنجستروم
الغشاء البلازمي
الغشاء البلازمي
البنية التي تحيط بكل الخلايا
البنية الثلاثية الطبقات للغشاء البلازمي
البنية الثلاثية الطبقات للغشاء البلازمي
يظهر كطبقتين كثيفتين وفصل ضوئيين بينهما
الطبقتان الكثيفات
الطبقتان الكثيفات
Signup and view all the flashcards
الطبقة الضوئية
الطبقة الضوئية
Signup and view all the flashcards
الغشاء الواحدي
الغشاء الواحدي
Signup and view all the flashcards
الجيلوكساليكس
الجيلوكساليكس
Signup and view all the flashcards
التركيب الجزيئي للغشاء البلازمي
التركيب الجزيئي للغشاء البلازمي
Signup and view all the flashcards
النسبة المئوية للبروتينات في الغشاء
النسبة المئوية للبروتينات في الغشاء
Signup and view all the flashcards
النسبة المئوية للدهون في الغشاء
النسبة المئوية للدهون في الغشاء
Signup and view all the flashcards
النسبة المئوية للكربوهيدرات في الغشاء
النسبة المئوية للكربوهيدرات في الغشاء
Signup and view all the flashcards
الفسفوليبيدات
الفسفوليبيدات
Signup and view all the flashcards
الكولستيرول
الكولستيرول
Signup and view all the flashcards
الجليكوليبيدات
الجليكوليبيدات
Signup and view all the flashcards
البروتينات الطرفية
البروتينات الطرفية
Signup and view all the flashcards
البروتينات المتكاملة
البروتينات المتكاملة
Signup and view all the flashcards
النقل البسيط
النقل البسيط
Signup and view all the flashcards
النقل المُيسّر
النقل المُيسّر
Signup and view all the flashcards
النقل النشط
النقل النشط
Signup and view all the flashcards
الانتشار
الانتشار
Signup and view all the flashcards
الانتشار البسيط
الانتشار البسيط
Signup and view all the flashcards
الانتشار المُيسّر
الانتشار المُيسّر
Signup and view all the flashcards
الانتشار المتسق
الانتشار المتسق
Signup and view all the flashcards
الاندماج الخلوي
الاندماج الخلوي
Signup and view all the flashcards
البلعمة
البلعمة
Signup and view all the flashcards
الإفراز الخلوي (الإخراج)
الإفراز الخلوي (الإخراج)
Signup and view all the flashcards
ما هو الغشاء البلازمي؟
ما هو الغشاء البلازمي؟
Signup and view all the flashcards
ما هي وظيفة الغشاء البلازمي؟
ما هي وظيفة الغشاء البلازمي؟
Signup and view all the flashcards
ما هو سمك الغشاء البلازمي؟
ما هو سمك الغشاء البلازمي؟
Signup and view all the flashcards
ما هي البنية الثلاثية الطبقات للغشاء البلازمي؟
ما هي البنية الثلاثية الطبقات للغشاء البلازمي؟
Signup and view all the flashcards
ما هي أهمية الطبقة الخارجية الكثيفة في الغشاء البلازمي؟
ما هي أهمية الطبقة الخارجية الكثيفة في الغشاء البلازمي؟
Signup and view all the flashcards
ما هي أهمية الطبقة الداخلية الكثيفة في الغشاء البلازمي؟
ما هي أهمية الطبقة الداخلية الكثيفة في الغشاء البلازمي؟
Signup and view all the flashcards
ماذا تعني "التمييز الخلوي"؟
ماذا تعني "التمييز الخلوي"؟
Signup and view all the flashcards
ما هو الغشاء الواحدي؟
ما هو الغشاء الواحدي؟
Signup and view all the flashcards
ما هي مكونات الغشاء البلازمي؟
ما هي مكونات الغشاء البلازمي؟
Signup and view all the flashcards
ما هي وظيفة الدهون في الغشاء البلازمي؟
ما هي وظيفة الدهون في الغشاء البلازمي؟
Signup and view all the flashcards
ما هي وظيفة البروتينات في الغشاء البلازمي؟
ما هي وظيفة البروتينات في الغشاء البلازمي؟
Signup and view all the flashcards
ما هي وظيفة السكريات في الغشاء البلازمي؟
ما هي وظيفة السكريات في الغشاء البلازمي؟
Signup and view all the flashcards
ما هو الانتشار؟
ما هو الانتشار؟
Signup and view all the flashcards
ما هو الانتشار المُيسّر؟
ما هو الانتشار المُيسّر؟
Signup and view all the flashcards
ما هو النقل النشط؟
ما هو النقل النشط؟
Signup and view all the flashcards
ما هي وظيفة البروتينات النّاقلة في الغشاء البلازمي؟
ما هي وظيفة البروتينات النّاقلة في الغشاء البلازمي؟
Signup and view all the flashcards
ما هو النقل الخلوي؟
ما هو النقل الخلوي؟
Signup and view all the flashcards
ما هي البلعمة؟
ما هي البلعمة؟
Signup and view all the flashcards
ما هي الإفراز الخلوي؟
ما هي الإفراز الخلوي؟
Signup and view all the flashcards
ما هو التركيب الجزيئي للغشاء البلازمي؟
ما هو التركيب الجزيئي للغشاء البلازمي؟
Signup and view all the flashcards
ما هي أنواع البروتينات في الغشاء البلازمي؟
ما هي أنواع البروتينات في الغشاء البلازمي؟
Signup and view all the flashcards
ما هو دور السكريات في الغشاء البلازمي؟
ما هو دور السكريات في الغشاء البلازمي؟
Signup and view all the flashcards
ما هي أهمية النقل النشط للخلية؟
ما هي أهمية النقل النشط للخلية؟
Signup and view all the flashcards
ما هي أهمية الإفراز الخلوي للخلية؟
ما هي أهمية الإفراز الخلوي للخلية؟
Signup and view all the flashcards
ما هو الانتشار المُيسّر بواسطة بروتينات الأنابيب؟
ما هو الانتشار المُيسّر بواسطة بروتينات الأنابيب؟
Signup and view all the flashcards
ما هو الانتشار المُيسّر بواسطة بروتينات النقل؟
ما هو الانتشار المُيسّر بواسطة بروتينات النقل؟
Signup and view all the flashcards
ما هي أهمية التمييز الخلوي في التطور الجنيني؟
ما هي أهمية التمييز الخلوي في التطور الجنيني؟
Signup and view all the flashcards
ما هي أهمية التواصل بين الخلايا في الأنظمة الحيوية؟
ما هي أهمية التواصل بين الخلايا في الأنظمة الحيوية؟
Signup and view all the flashcards
ما هي الوظائف الرئيسية للغشاء البلازمي؟
ما هي الوظائف الرئيسية للغشاء البلازمي؟
Signup and view all the flashcards
ما هو الجلود السكرية؟
ما هو الجلود السكرية؟
Signup and view all the flashcards
ما هي أهمية السكريات في الجلود السكرية؟
ما هي أهمية السكريات في الجلود السكرية؟
Signup and view all the flashcards
ما هي أهمية البروتينات في النقل الخلوي؟
ما هي أهمية البروتينات في النقل الخلوي؟
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
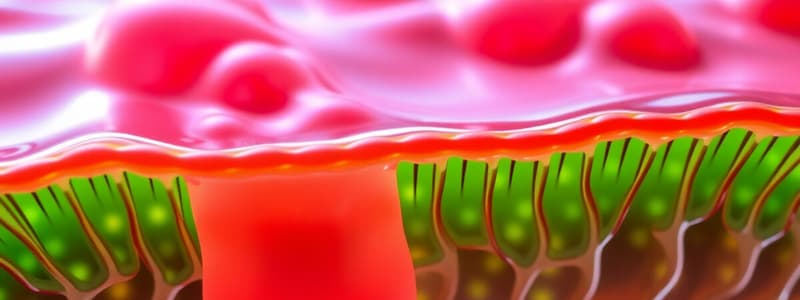
Structure of the Plasma Membrane
- The plasma membrane surrounds all cells.
- Its structure is complex, enabling interaction with the surrounding environment and other cells.
- The membrane is 75 Å thick.
- Electron microscopy shows a trilaminar structure (three layers): two dense layers separated by a light layer.
- The dense layers (inner and outer) are 20-25 Å thick.
- The light layer is 30-40 Å thick.
- This trilaminar structure is found in all animal and plant cells, as well as in intracellular membranes (mitochondria, chloroplasts, endoplasmic reticulum).
- The outer dense layer is covered by a thin glycoprotein film (glycocalyx) with fibers perpendicular to the membrane.
- The inner dense layer has a microfilament network connected to the cytoskeleton.
Chemical Composition of the Plasma Membrane
- The membrane is composed of 52% protein, 40% lipids (mostly phospholipids), and 8% carbohydrates.
- The percentages may vary depending on the cell type or organelle.
Lipids
- Lipids are amphiphilic molecules with hydrophilic heads and hydrophobic tails.
- Types include:
- Phospholipids (55% of membrane lipids): arranged in a bilayer. Their distribution is asymmetrical within the bilayer.
- Cholesterol (25% of membrane lipids): found in both layers, mainly in the outer layer.
- Glycolipids (18% of membrane lipids): located on the outer surface; their amount and type vary based on the cell and tissue.
Proteins
- Proteins facilitate the exchange of molecules between the internal and external environments.
- Types include:
- Peripheral proteins: located on both sides of the membrane, mainly hydrophilic zones.
- Integral proteins: span the lipid bilayer, including hydrophobic regions as well as hydrophilic portions that interact with the internal and external environments.
Membrane Architecture
- Singer and Nicholson's fluid mosaic model describes the plasma membrane as a fluid mosaic of proteins and lipids embedded in a lipid bilayer.
- Embedded proteins, carbohydrates, and glycoproteins are displayed on the outer membrane surface.
Membrane Function
- The membrane controls the passage of water and dissolved substances across the cell.
- Types of transport include:
- Simple diffusion: molecules move through the lipid bilayer.
- Facilitated diffusion: molecules move through transport proteins.
- Active transport: molecules move against the concentration gradient requiring ATP.
Active transport
- Primary Active Transport:uses energy directly from ATP hydrolysis. An example is the sodium-potassium pump.
- Secondary Active Transport: uses the concentration gradient established by primary active transport to move another molecule.
Vesicular Transport
- Exocytosis: substances inside the cell are released to the extracellular environment.
- Endocytosis: substances from the extracellular environment are internalized.
There are three main types of endocytosis:
- Receptor-mediated endocytosis: used to absorb specific molecules.
- Phagocytosis: used to engulf large particles such as bacteria.
- Pinocytosis: used to absorb dissolved substances or small particles.
Cell Signaling
- Cells receive signals (chemical messages) from the environment.
- Receptors on the cell surface are essential in receiving signals & initiating responses.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Related Documents
Description
يغطي غشاء البلازما جميع الخلايا ويتميز بتركيب معقد يمكّنه من التفاعل مع البيئة المحيطة. يحتوي على بنية ثلاثية الطبقات، ويتكون من بروتينات ودهون وكربوهيدرات بنسبة معينة. تُعد هذه الخصائص مهمة لفهم وظائف الخلية.