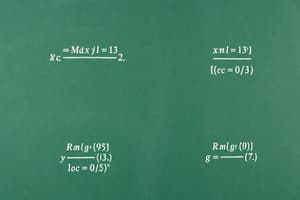Podcast
Questions and Answers
ما هي احتمالية أن تكون البطاقة الثالثة ملكًا إذا كان هناك ملكين قد تم سحبهما بالفعل؟
ما هي احتمالية أن تكون البطاقة الثالثة ملكًا إذا كان هناك ملكين قد تم سحبهما بالفعل؟
- 0.25
- 0.5
- 0.4
- 0.29 (correct)
كم عدد البطاقات المتبقية في المجموعة بعد سحب بطاقتين؟
كم عدد البطاقات المتبقية في المجموعة بعد سحب بطاقتين؟
- 52
- 50
- 51 (correct)
- 48
ما هي الاحتمالية الشرطية لسحب بطاقة Ace بعد سحب ملكين؟
ما هي الاحتمالية الشرطية لسحب بطاقة Ace بعد سحب ملكين؟
- 1/13
- 4/51 (correct)
- 1/52
- 3/50
إذا كانت P(K|K) تمثل الاحتمالية الشرطية، فما الذي تمثله K في هذه العلاقة؟
إذا كانت P(K|K) تمثل الاحتمالية الشرطية، فما الذي تمثله K في هذه العلاقة؟
ما هو العدد الإجمالي للبطاقات في المجموعة قبل السحب؟
ما هو العدد الإجمالي للبطاقات في المجموعة قبل السحب؟
ما هو الإجراء المتخذ إذا أظهر القرص الوجه؟
ما هو الإجراء المتخذ إذا أظهر القرص الوجه؟
ما هو الحدث المشروط الذي نريد حساب احتماليته في هذه الحالة؟
ما هو الحدث المشروط الذي نريد حساب احتماليته في هذه الحالة؟
متى يتم إلقاء النرد في هذه التجربة؟
متى يتم إلقاء النرد في هذه التجربة؟
ما هي النتيجة الأساسية التي يعتمد عليها حساب الاحتمالات هنا؟
ما هي النتيجة الأساسية التي يعتمد عليها حساب الاحتمالات هنا؟
ما الاحتمالات المطلوبة إذا كان هناك ذيل واحد على الأقل؟
ما الاحتمالات المطلوبة إذا كان هناك ذيل واحد على الأقل؟
Flashcards
عدد الملوك في 51 ورقة
عدد الملوك في 51 ورقة
هناك ثلاثة ملوك في مجموعة من 51 ورقة
احتمالية سحب ملك آخر (P(K|K))
احتمالية سحب ملك آخر (P(K|K))
هي احتمال سحب ملك ثالث بشرط أن يكون ملكان قد سبق سحبهم
احتمالية سحب واصلة (P(A|KK))
احتمالية سحب واصلة (P(A|KK))
هي احتمال سحب ورقة واصلة بشرط سحب ملكين مسبقاً
احتمالية ظهور عدد أكبر من 4 في النرد
احتمالية ظهور عدد أكبر من 4 في النرد
Signup and view all the flashcards
رمي العملة
رمي العملة
Signup and view all the flashcards
رمي النرد
رمي النرد
Signup and view all the flashcards
احتمال
احتمال
Signup and view all the flashcards
شروط
شروط
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Probability and Statistics (1st Year)
- Course Title: Probability and Statistics
- Course Code: BS116
- Academic Year: 2024/2025
- Course Type: Obligatory
- Coordinator: Dr. Hanaa Abdelhady
- Course Delivery: 3 hours lectures and 14 hours of practical sessions
- Credit: 2 credit hours
- Upon Completion: Students will be able to comprehend the axioms of probability, understand details of discrete and continuous random variables, and acquire knowledge on random sampling and its distributions, point estimation methods, testing hypotheses, and Chi-square tests, correlation, and regression.
Course Aims
- Understanding Probability Axioms
- Detailed explanation of discrete and continuous Random Variables and Correlation and Regression
- Understanding random sampling and its distributions
- Knowing estimation methods
- Recognizing hypothesis testing and Chi-square tests
Course Contents
- Introduction to PROBABILITY
- Conditional Probability and Bayes' Theorem
- Discrete Random Variables
- Continuous Random Variables
- Introduction to Random sampling
- Application of the central limit theorem
- Methods of point estimation
- Confidence interval for a population mean
- Introduction to Hypotheses testing
- Testing hypothesis: the difference between two population means
- Chi-square tests
- The least squares method
- The correlation analysis
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.