Podcast
Questions and Answers
Match the following improper fractions with their mixed number representations:
Match the following improper fractions with their mixed number representations:
7/4 = 1 3/4 9/4 = 2 1/4 11/5 = 2 1/5 5/5 = 1
Match the following mixed numbers with their improper fraction equivalents:
Match the following mixed numbers with their improper fraction equivalents:
3 1/2 = 7/2 2 2/3 = 8/3 1 3/4 = 7/4 4 1/5 = 21/5
Match the following steps for adding improper fractions:
Match the following steps for adding improper fractions:
Find a common denominator = True Add numerators = True Convert to mixed numbers = False Simplify the result = True
Match the following mixed number addition problems with their solutions:
Match the following mixed number addition problems with their solutions:
Match the following improper fractions with their characteristics:
Match the following improper fractions with their characteristics:
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Addition and Subtraction of Fractional Numbers
Improper Fractions
-
Definition: A fraction where the numerator is greater than or equal to the denominator (e.g., 7/4, 5/5).
-
Conversion to Mixed Numbers:
- Divide the numerator by the denominator.
- The quotient is the whole number part, and the remainder over the denominator is the fractional part.
- Example: 9/4 → 2 (whole) and 1/4 (fraction) → Mixed number: 2 1/4.
-
Addition/Subtraction with Improper Fractions:
- Ensure fractions have a common denominator.
- Add or subtract the numerators, keeping the denominator the same.
- Simplify if necessary.
- Example: 7/4 + 5/4 = (7 + 5)/4 = 12/4 = 3 (improper fraction simplified).
Mixed Numbers
-
Definition: A combination of a whole number and a fraction (e.g., 2 3/5).
-
Conversion to Improper Fractions:
- Multiply the whole number by the denominator and add the numerator.
- Place the result over the original denominator.
- Example: 2 3/5 → (2×5 + 3)/5 = 13/5.
-
Addition/Subtraction with Mixed Numbers:
- Convert mixed numbers to improper fractions.
- Find a common denominator for the fractions.
- Add or subtract the numerators and keep the denominator the same.
- Convert the result back to a mixed number if necessary.
- Example:
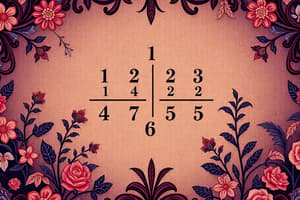
- 1 1/2 + 2 1/3
- Convert: 3/2 + 7/3.
- Common denominator: 6 → (3×3 + 7×2)/6 = (9 + 14)/6 = 23/6.
- Convert back: 23/6 = 3 5/6.
Key Points
- Always simplify fractions when possible.
- Keep track of proper and improper fractions during calculations.
- Converting between mixed numbers and improper fractions is crucial for addition and subtraction.
Improper Fractions
- Improper fractions have numerators equal to or greater than their denominators (e.g., 7/4, 5/5).
- To convert an improper fraction to a mixed number, divide the numerator by the denominator to obtain the whole number, while the remainder becomes the fractional part.
- Example of conversion: 9/4 results in 2 (whole) and 1/4 (fraction), yielding the mixed number 2 1/4.
- For addition or subtraction of improper fractions, ensure a common denominator is established first.
- Adjust the numerators and keep the denominator constant. Simplify the final result if needed.
- Example calculation: For 7/4 + 5/4, add numerators: (7 + 5)/4 = 12/4 = 3 after simplification.
Mixed Numbers
- Mixed numbers consist of a whole number combined with a fraction (e.g., 2 3/5).
- To convert a mixed number to an improper fraction, multiply the whole number by the denominator, add the numerator, and place this result over the original denominator.
- Example conversion: 2 3/5 converts to (2×5 + 3)/5 = 13/5.
- When adding or subtracting mixed numbers, first convert them to improper fractions.
- Find a common denominator, adjust the numerators, and maintain the common denominator through calculations.
- After obtaining the result, convert back to a mixed number when necessary.
- Example operation: Adding 1 1/2 and 2 1/3 converts to 3/2 + 7/3, with a common denominator of 6 leading to (3×3 + 7×2)/6 = (9 + 14)/6 = 23/6, which converts back to 3 5/6.
Key Points
- Always simplify fractions to their lowest form when possible for clarity.
- Differentiate between proper and improper fractions during calculations for accuracy.
- Conversions between mixed numbers and improper fractions play a crucial role in adding and subtracting fractional numbers.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.