Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the process by which stream load breaks material down, often associated with physical weathering?
What is the process by which stream load breaks material down, often associated with physical weathering?
- Transportation
- Cavitation
- Erosion
- Scouring (correct)
Which of the following methods of transportation describes materials that are bounced along the stream bed?
Which of the following methods of transportation describes materials that are bounced along the stream bed?
- Traction
- Solvation
- Saltation (correct)
- Suspension
What factor does NOT affect a stream’s capacity to transport materials?
What factor does NOT affect a stream’s capacity to transport materials?
- Turbulence
- Chemical weathering (correct)
- Discharge
- Velocity
In the context of fluvial processes, what term describes the total possible load a stream can transport?
In the context of fluvial processes, what term describes the total possible load a stream can transport?
Which particle size category includes particles with a diameter greater than 256 mm?
Which particle size category includes particles with a diameter greater than 256 mm?
Which of the following best characterizes a youthful stream?
Which of the following best characterizes a youthful stream?
Which of the following describes the process of sediment deposition when stream velocity decreases?
Which of the following describes the process of sediment deposition when stream velocity decreases?
In terms of stream processes, what does competence refer to?
In terms of stream processes, what does competence refer to?
What measure indicates the ability of a stream to move particles of a particular size?
What measure indicates the ability of a stream to move particles of a particular size?
What is a distinct feature of braided streams?
What is a distinct feature of braided streams?
Which dimension refers to the length of a stream?
Which dimension refers to the length of a stream?
What sediment classification has a diameter less than 0.063 mm?
What sediment classification has a diameter less than 0.063 mm?
How does the interaction with aquifers affect stream depth?
How does the interaction with aquifers affect stream depth?
Which method of transportation describes sediment that is held in the water by the stream's velocity?
Which method of transportation describes sediment that is held in the water by the stream's velocity?
What is defined as the 95th percentile of the largest particle size in a sediment sample?
What is defined as the 95th percentile of the largest particle size in a sediment sample?
What characterizes an alluvial channel?
What characterizes an alluvial channel?
In what order does a stream profile show changes from the headwaters to the mouth?
In what order does a stream profile show changes from the headwaters to the mouth?
What is a primary feature of an anabranched stream?
What is a primary feature of an anabranched stream?
Which type of stream morphology is likely to be found near glaciers?
Which type of stream morphology is likely to be found near glaciers?
The process of deposition is primarily associated with which stream process?
The process of deposition is primarily associated with which stream process?
What characterizes the upper reaches (headwaters) of a stream?
What characterizes the upper reaches (headwaters) of a stream?
Which of the following features is associated with the lower reaches of a stream?
Which of the following features is associated with the lower reaches of a stream?
What is the role of the base level in stream dynamics?
What is the role of the base level in stream dynamics?
Which statement correctly describes fluvial terraces?
Which statement correctly describes fluvial terraces?
What defines an alluvial fan?
What defines an alluvial fan?
Which of the following is NOT a feature of lower reaches of streams?
Which of the following is NOT a feature of lower reaches of streams?
How does fluvial transport relate to erosion?
How does fluvial transport relate to erosion?
Which feature is formed as a result of lateral erosion in river systems?
Which feature is formed as a result of lateral erosion in river systems?
What is the primary cause of the formation of meanders in a river?
What is the primary cause of the formation of meanders in a river?
What happens to sediment transport and deposition at the river's delta?
What happens to sediment transport and deposition at the river's delta?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
4-Dimensional Aspect of Streams
- Streams are 4-dimensional entities with longitudinal, lateral, vertical, and temporal components.
- Length of the stream is longitudinal dimension.
- Width of the floodplain is the lateral dimension.
- Depth and interaction with aquifers (hyporheic zone) constitute the vertical dimension.
- Downwelling and upwelling are important processes in the hyporheic zone.
- The temporal dimension encompasses daily, seasonal, and annual variations, reflecting dynamic changes in stream characteristics over time.
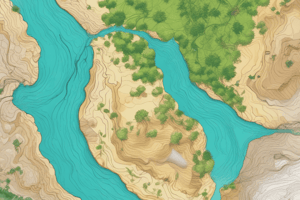
Stream Morphology - Profile
- The stream profile represents a longitudinal view, focusing on the stream's slope and gradient.
- It extends from the headwaters to the mouth (base level) and depicts the stream's decreasing gradient as it progresses downstream.
Stream Morphology - Pattern
- Stream patterns capture the birds-eye view of a stream.
- Meandering patterns, characterized by sinuous bends, are common in floodplain depositional zones.
- Straight patterns are often unnatural, typically resulting from anthropogenic modifications.
- Braided patterns, with multiple intertwined channels, are prevalent in glacial environments and near the mouth, where high sediment loads and rapid flow prevail.
- Anabranched patterns resemble larger braids, but with vegetated islands, indicating a more stable, less active channel pattern
Stream Morphology - Channelized
- A channelized stream or straight channel is often a human-made intervention, altering the natural flow of rivers, impacting ecological processes, and reducing biodiversity.
Stream Morphology - Latitudinal Profile
- The latitudinal profile represents a cross-section of the stream.
- It encompasses various features such as the main channel, side channels, and the distribution of substrate material.
- Vegetation type and distribution along the channel are also critical components.
Stream Morphology - Channel Types
- Alluvial Channels are formed by the river's transport of sediment and are dynamic, constantly changing.
- Non-alluvial Channels are bounded by bedrock or concrete, often deeply cut into bedrock deposits.
Stream Morphology - Kokanee Glacier
- The Kokanee Glacier, a prominent glacier in the Canadian Rockies, exhibits a distinct stream profile showcasing the transition from steep gradients in the upper reaches to gentler gradients below.
Stream Profile - Upper Reaches (Headwaters)
- Headwaters exhibit steep gradients, characterized by vertical erosion, V-shaped valleys, rapids, waterfalls, gorges, and lag boulders.
Stream Profile - Lower Reaches
- Lower reaches are characterized by gentle gradients, lateral erosion, U-shaped valleys, terraces, floodplains, meanders, oxbows, point bars, cut banks, and alluvial deposits.
Stream Profile - Base Level
- Base level signifies the limit of a stream's erosive power.
- Below base level, no further vertical erosion can occur.
- Examples of base levels include alluvial fans and deltas.
Alluvial Fans and Deltas
- Alluvial fans are cone-shaped deposits formed at the foot of mountains, where a stream slows down.
- Deltas are triangular-shaped deposits formed at the mouth of a river where it enters a larger body of water like a lake or ocean.
Fluvial Transport
- Fluvial transport encompasses the work of a river, primarily erosion and transportation, most active during periods of high flow. It encompasses three key processes: erosion, transportation, and deposition.
Fluvial Processes - Erosion
- Erosion, also known as degradation, is the removal of weathered materials from the stream channel.
- Erosion is driven by physical processes like scouring, cavitation, or chemical weathering (dissolution).
Fluvial Processes - Transportation
- Transportation involves the movement and dilution of wastes and redistribution of materials.
- Bedload, suspension, and solution are the main modes of transportation.
Fluvial Processes - Deposition (Aggradation)
- Deposition, or aggradation, occurs when a stream slows down and deposits sediments, creating features like floodplains, alluvial fans, fertile soil, levees.
Fluvial Determinants
- Three key variables govern a stream's capacity for fluvial processes: velocity, discharge, and turbulence/laminar flow.
Stream Capacity
- Capacity refers to the total amount of sediment a stream can transport.
Stream Competence
- Competence describes a stream's ability to move particles of a specific size.
- It is often measured using D-95 (95th percentile largest) and D-50 (50th percentile) values.
Particle Size
- Different particle sizes have different transportation characteristics.
- Large particles (boulders, cobbles) are typically found in headwaters, while smaller particles (sand, silt) prevail in lower reaches.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.