What are glia cells and what are their functions?
Understand the Problem
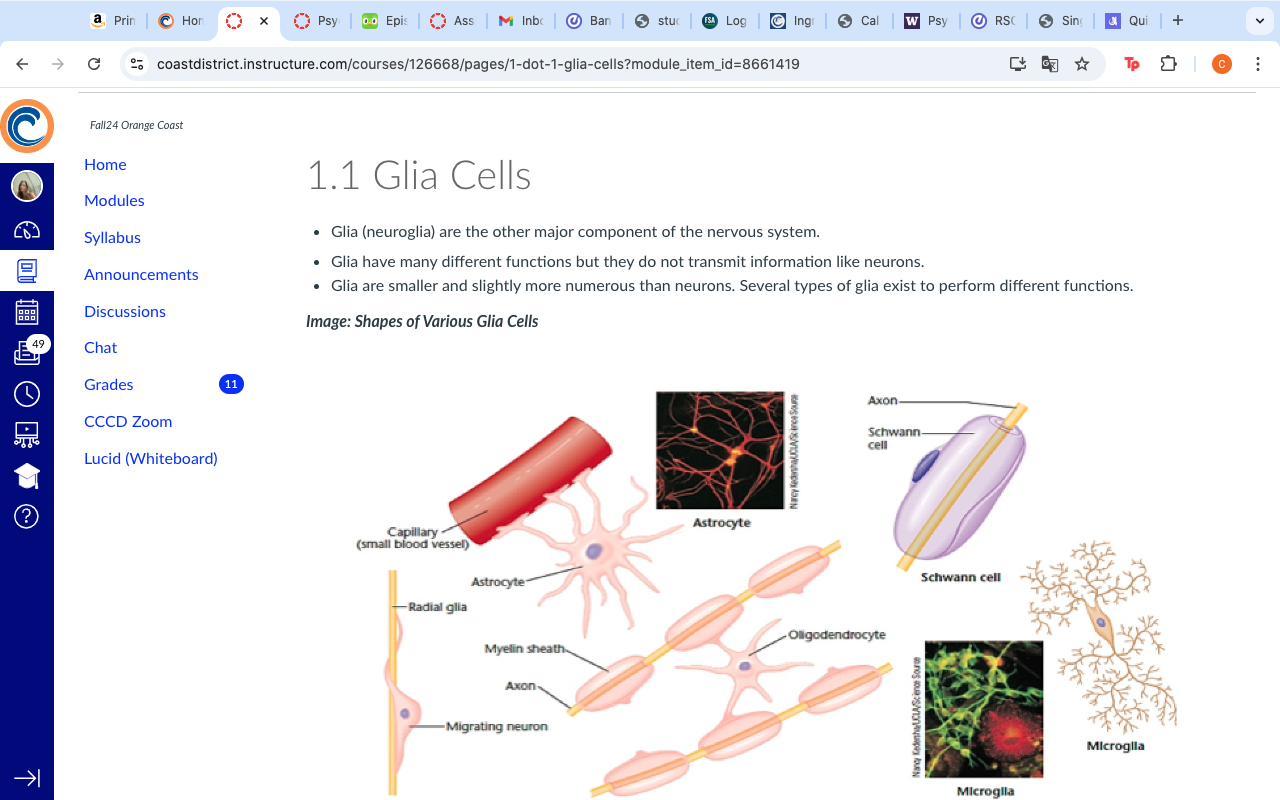
The question appears to be related to the information on glia cells, their functions, and their variations depicted in the image. It highlights the importance of glia in the nervous system and depicts various types of glial cells.
Answer
Glial cells support neurons, maintain homeostasis, and form myelin.
Glial cells are non-neuronal cells in the nervous system that support and protect neurons. They help maintain homeostasis, form myelin sheaths, support neurotransmission, clean up debris, and guide neuronal development. Key types include astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, Schwann cells, microglia, and ependymal cells.
Answer for screen readers
Glial cells are non-neuronal cells in the nervous system that support and protect neurons. They help maintain homeostasis, form myelin sheaths, support neurotransmission, clean up debris, and guide neuronal development. Key types include astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, Schwann cells, microglia, and ependymal cells.
More Information
Glial cells are critical for brain health and function by maintaining the environment that ensures proper neurotransmission. They outnumber neurons and are essential in nervous system development and repair.
Tips
A common mistake is thinking glial cells transmit nerve impulses; they support neuronal function instead.
Sources
- Glial cells: Types and function - MedicalNewsToday - medicalnewstoday.com
- Neuroglial Cells - Neuroscience - NCBI Bookshelf - ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- Glial Cells - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics - sciencedirect.com
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information